|
Triazoles
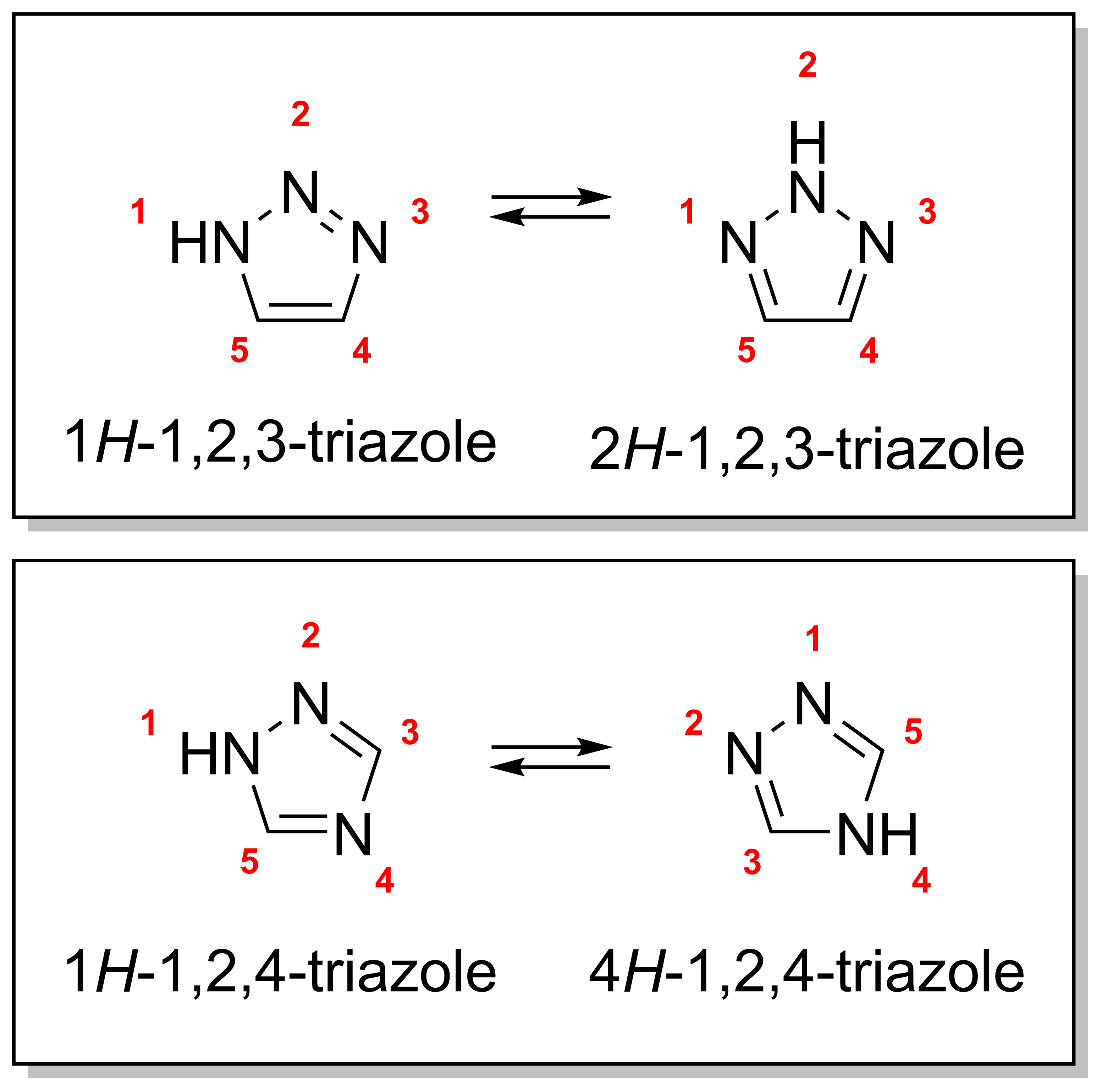
A triazole is a heterocyclic compound featuring a five-membered ring of two carbon atoms and three nitrogen atoms with molecular formula C2H3N3. Triazoles exhibit substantial Isomer, isomerism, depending on the positioning of the nitrogen atoms within the ring. Many triazoles are versatile, biologically active compounds commonly used as fungicides and plant retardants. However, triazoles are also useful in bioorthogonal chemistry, because the large number of nitrogen atoms causes triazoles to react similar to Azide, azides. Lastly, the many free lone pairs in triazoles make them useful as coordination compounds, although not typically as Piano stool complex, haptic ligands. Isomerism There are four triazole isomers, which are conventionally divided into two pairs of Tautomer, tautomers. In the 1,2,3-Triazole, 1,2,3-triazoles, the three nitrogen atoms are adjacent; in the 1,2,4-Triazole, 1,2,4-triazoles, an interstitial carbon separates out one nitrogen atom. Each category ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Click Chemistry
Click chemistry is an approach to chemical synthesis that emphasizes efficiency, simplicity, selectivity, and modularity in chemical processes used to join molecular building blocks. It includes both the development and use of "click reactions", a set of simple, Biocompatibility, biocompatible chemical reactions that meet specific criteria like high yield, fast reaction rates, and minimal byproducts. It was first fully described by K. Barry Sharpless, Hartmuth C. Kolb, and M. G. Finn of Scripps Research Institute, The Scripps Research Institute in 2001. The paper argued that synthetic chemistry could emulate the way nature constructs complex molecules, using efficient reactions to join together simple, non-toxic building blocks. The term "click chemistry" was coined in 1998 by Sharpless' wife, Jan Dueser, who found the simplicity of this approach to chemical synthesis akin to clicking together Lego blocks. In fact, the simplicity of click chemistry represented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pellizzari Reaction
The Pellizzari reaction was discovered in 1911 by Guido Pellizzari, and is the organic reaction of an amide and a hydrazide to form a 1,2,4-triazole. The product is similar to that of the Einhorn-Brunner reaction, but the mechanism itself is not regioselective. : Mechanism The mechanism begins by the nitrogen in the hydrazide attacking the carbonyl carbon on the amide to form compound 3. The negatively charged oxygen then abstracts two hydrogens from neighboring nitrogens in order for a molecule of water to be released to form compound 5. The nitrogen then performs an intramolecular attack on the carbonyl group to form the five-membered ring of compound 6. After another proton migration from the nitrogens to the oxygen, another water molecule is released to form the 1,2,4-triazole 8. : Uses The synthesis of the 1,2,4-triazole has a wide range of biological functions. 1,2,4-triazoles have antibacterial, antifungal, antidepressant Antidepressants are a class of medications us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antifungal Drug
An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as cryptococcal meningitis, and others. Such drugs are usually obtained by a doctor's prescription, but a few are available over the counter (OTC). The evolution of antifungal resistance is a growing threat to health globally. Routes of administration Ocular Indicated when the fungal infection is located in the eye. There is currently only one ocular antifungal available: natamycin. However, various other antifungal agents could be compounded in this formulation. Intrathecal Used occasionally when there's an infection of the central nervous system and other systemic options cannot reach the concentration required in that region for therapeutic benefit. Example(s): amphotericin B. Vaginal This may be used to treat some fungal inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huisgen 1,3-dipolar Cycloaddition
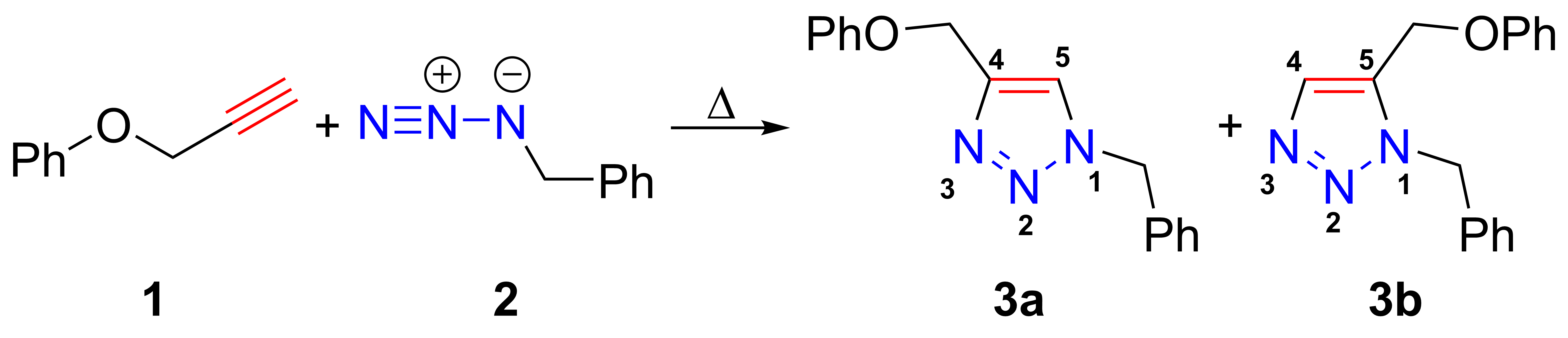
The azide-alkyne Huisgen cycloaddition is a 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between an azide and a terminal or internal alkyne to give a 1,2,3-triazole. Rolf Huisgen was the first to understand the scope of this organic reaction. American chemist Karl Barry Sharpless has referred to copper-catalyzed version of this cycloaddition as "the cream of the crop" of click chemistry and "the premier example of a click reaction". In the reaction above azide 2 reacts neatly with alkyne 1 to afford the product triazole as a mixture of 1,4-adduct (3a) and 1,5-adduct (3b) at 98 °C in 18 hours. The standard 1,3-cycloaddition between an azide 1,3-dipole and an alkene as dipolarophile has largely been ignored due to lack of reactivity as a result of electron-poor olefins and elimination side reactions. Some success has been found with non-metal-catalyzed cycloadditions, such as the reactions using dipolarophiles that are electron-poor olefins or alkynes. Although azides are not the most re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,2,3-Triazole
1,2,3-Triazole is one of a pair of isomeric chemical compounds with molecular formula CHN, called triazoles, which have a five-membered ring of two carbon atoms and three nitrogen atoms. 1,2,3-Triazole is a basic aromatic heterocycle. Synthesis The unsubstituted ring can be produced by an oxidative coupling of glyoxal, hydrazine and sodium nitrite. A wide range of methods exist for forming substituted 1,2,3-triazoles. These include the Banert cascade or the azide alkyne Huisgen cycloaddition in which an azide and an alkyne undergo a 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reaction. Under thermal conditions, regioselectivity is substrate dependent. Selectivity can be increased with metal catalysts, which have the added benefit of reacting without excessive or extensive heating. Copper catalyzed cycloadditions favor 1,4-disubstituted triazoles, Ruthenium catalyzed cycloaddition favor 1,5-disubstituted triazoles. This chemistry was expanded by Zhu et al. in 2018 wherein they report a two-step ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterocyclic Compound
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic organic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of organic heterocycles. Examples of heterocyclic compounds include all of the nucleic acids, the majority of drugs, most biomass (cellulose and related materials), and many natural and synthetic dyes. More than half of known compounds are heterocycles. 59% of US FDA-approved drugs contain nitrogen heterocycles. Classification The study of organic heterocyclic chemistry focuses especially on organic unsaturated derivatives, and the preponderance of work and applications involves unstrained organic 5- and 6-membered rings. Included are pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and furan. Another large class of organic heterocycles refers to those fused to benzene rings. For example, the fused benzene derivatives of py ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrazines
Hydrazines (R2N−NR2) are a class of chemical compounds with two nitrogen atoms linked via a covalent bond and which carry from one up to four alkyl or aryl substituents. Hydrazines can be considered as derivatives of the inorganic hydrazine (H2N−NH2), in which one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by hydrocarbon groups. Production * 1,1-dimethylhydrazine, 1,1-Dimethylhydrazine is produced by the reduction of N-Nitrosodimethylamine, ''N''-nitrosodimethylamine.Siegfried Hauptmann: ''Organische Chemie'', 2. durchgesehene Auflage, VEB Deutscher Verlag für Grundstoffindustrie, Leipzig, 1985, S. 522–523, . * The reduction of benzenediazonium chloride with tin(II) chloride and hydrochloric acid provides phenylhydrazine. * 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine is produced by the reaction of 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene with hydrazine. * Tetraphenylhydrazine is formed by the oxidation of diphenylamine with potassium permanganate in acetone. Classification Hydrazines can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrazide
Hydrazides in organic chemistry are a class of organic compounds with the formula where R is acyl (), sulfonyl (), phosphoryl (), phosphonyl () and similar groups (chalcogen analogs are included, for example sulfur analogs called thiohydrazides), (subscription required) and R' are any groups (typically hydrogen or organyl). Unlike hydrazine and alkylhydrazines, hydrazides are nonbasic owing to the inductive influence of the acyl, sulfonyl, or phosphoryl substituent. Sulfonyl hydrazides A common sulfonyl hydrazide is ''p''-toluenesulfonyl hydrazide, a white air-stable solid. They are also widely used as organic reagents. Toluenesulfonyl hydrazide is used to generate toluenesulfonyl hydrazones. When derived from ketones, these hydrazones participate in the Shapiro reaction and the Eschenmoser–Tanabe fragmentation. 2,4,6-Triisopropylbenzenesulfonylhydrazide is a useful source of diimide. Acyl hydrazides Acylhydrazines are derivatives of carboxylic acids, although the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imide
In organic chemistry, an imide is a functional group consisting of two acyl groups bound to nitrogen. The compounds are structurally related to acid anhydrides, although imides are more resistant to hydrolysis. In terms of commercial applications, imides are best known as components of high-strength polymers, called Polyimide, polyimides. Inorganic imides are also known as solid state or gaseous compounds, and the imido group (=NH) can also act as a ligand. Examples Simple example is diacetamide with the formula , formally the diacetylated derivative of ammonia. Commonly encountered imides, however, are cyclic, being derived from dicarboxylic acids. A common example is succinimide derived from succinic acid and ammonia. The names of these cyclic imides reflect the parent acid. Many imides are derived from primary amines as opposed to ammonia. These are indicated by ''N''-substituent in the prefix. For example, N-ethylsuccinimide is derived from succinic acid and ethylamine. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Chemistry
Green chemistry, similar to sustainable chemistry or circular chemistry, is an area of chemistry and chemical engineering focused on the design of products and processes that minimize or eliminate the use and generation of hazardous substances. While environmental chemistry focuses on the effects of pollutant, polluting chemicals on nature, green chemistry focuses on the environmentalism, environmental impact of chemistry, including lowering consumption of nonrenewable resources and technological approaches for preventing pollution. The overarching goals of green chemistry—namely, more resource-efficient and inherently safer design of molecules, materials, products, and processes—can be pursued in a wide range of contexts. History Green chemistry emerged from a variety of existing ideas and research efforts (such as atom economy and catalysis) in the period leading up to the 1990s, in the context of increasing attention to problems of chemical pollution and resource depletio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |