|
Thirteen Years' War (1454–1466)
The Thirteen Years' War (german: Dreizehnjähriger Krieg; pl, wojna trzynastoletnia), also called the War of the Cities, was a conflict fought in 1454–1466 between the Prussian Confederation, allied with the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, and the State of the Teutonic Order. The war began as an uprising by Prussian cities and local nobility to win independence from the Teutonic Knights. In 1454 Casimir IV married Elisabeth of Habsburg and the Prussian Confederation asked Poland's King Casimir IV Jagiellon for help and offered to accept the king as protector instead of the Teutonic Order. When the King assented, war broke out between supporters of the Prussian Confederation, backed by Poland, and backers of government by the Teutonic Knights. The Thirteen Years' War ended in the victory of the Prussian Confederation and Poland and in the Second Peace of Thorn (1466). This was soon followed by the War of the Priests (1467–1479), a drawn-out dispute over the independence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish–Teutonic War
Polish–Teutonic War may refer to: *Teutonic takeover of Danzig (Gdańsk) (1308–1309) *Polish–Teutonic War (1326–1332) over Pomerelia, concluded by the Treaty of Kalisz (1343) *the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War or ''Great War'' (1409–1411), ending the Lithuanian Crusade with the Peace of Thorn (1411) *the Hunger War (1414) over the border in Samogitia *the Gollub War (1422) over the border in Samogitia, ending with the Treaty of Melno *Polish–Teutonic War (1431–1435), part of the Lithuanian Civil War *Thirteen Years' War (1454–1466) or War of the Cities, a Polish-backed revolt of western Prussian cities against Teutonic rule *War of the Priests (Poland) (1467–1479), contesting the election of the Bishop of Warmia *Polish–Teutonic War (1519–1521), known as ''Reiterkrieg'' in German, over the Knights' status as a Polish vassal See also * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Polish-Teutonic War Polish–Teutonic wars, * Wars involving Poland Wars involving the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrzej Tęczyński (died 1461)
Andrzej Tęczyński, (b. 1480 – 2 January 1536) Count (title of the Holy Roman Empire, 1527), was a voivode of Lublin, voivode of Sandomierz, voivode of Kraków, Castellan of Kraków. He came from one of the most powerful clans in Lesser Poland, the Tęczyński family. Career *1503 - Royal Courtier *1510 - Secretary of the Crown *1510 - Chamberlain of Sandomierz *1511 - Castellan of Biecki *1512 - Referendary of the Crown *1515-1519 - Voivode of Lublin *1519 - Voivode of Sandomierz *1527 - He received from the Emperor Ferdinand I the hereditary title of Count of the Empire for his family. The Habsburgs as the Roman emperors gave some Polish families titles of princes and counts of the ''Sacri Imperii Romagna'' for gratitude. Thus, the representatives of these families were called ''hrabiami Roman Empire''. *1527 - Voivode of Kraków *1532 - Castellan of Kraków In addition to these titles Andrzej Tęczyński held offices as: starosta of Sandomierz, starosta of Belz, starosta C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
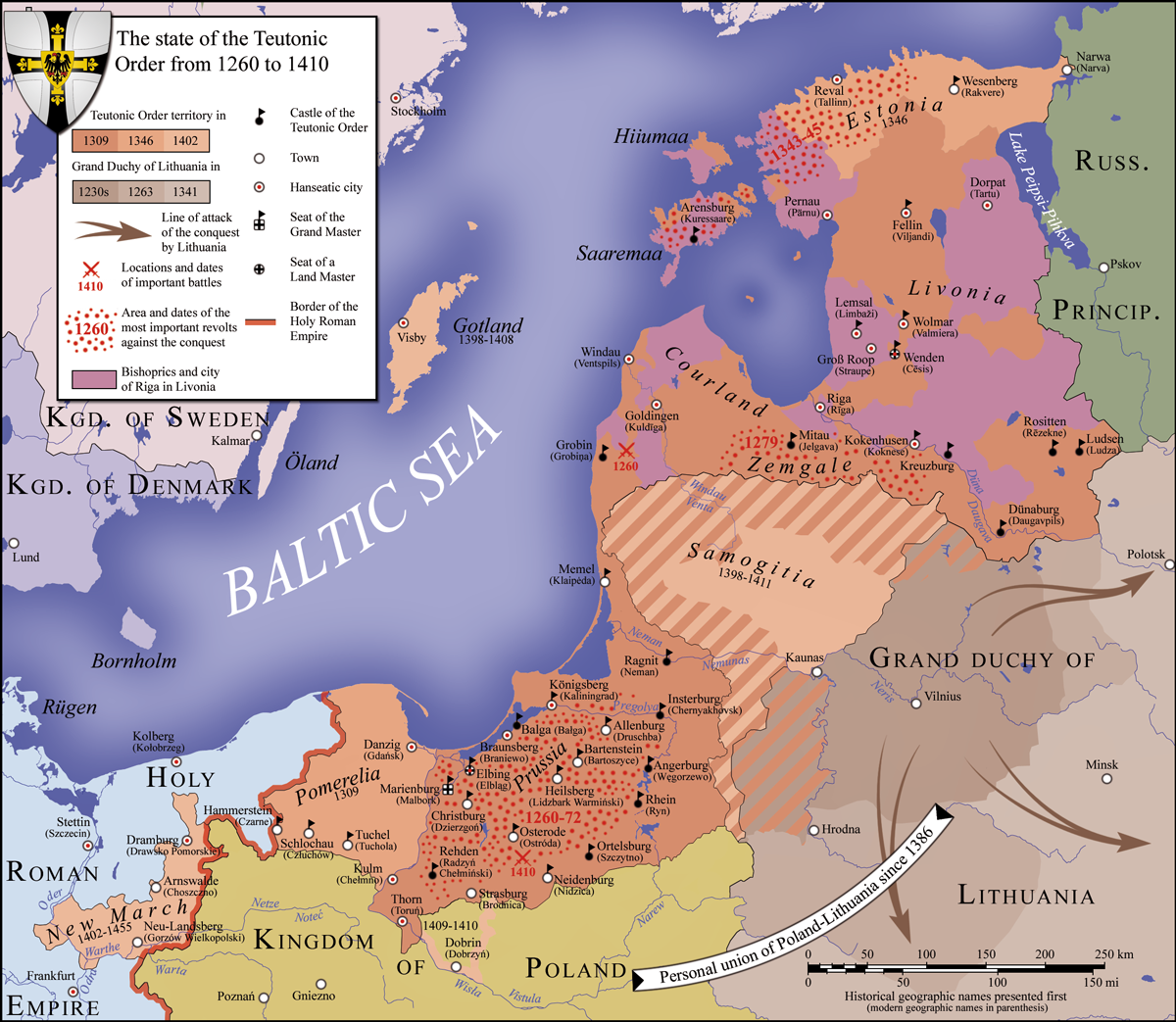
Prussia (region)
Prussia (Old Prussian: ''Prūsa''; german: Preußen; lt, Prūsija; pl, Prusy; russian: Пруссия, tr=Prussiya, ''/Prussia/Borussia'') is a historical region in Europe on the south-eastern coast of the Baltic Sea, that ranges from the Vistula delta in the west to the end of the Curonian Spit in the east and extends inland as far as Masuria. Tacitus's ''Germania'' (98 AD) is the oldest known record of an eyewitness account on the territory and its inhabitants. Pliny the Elder had already confirmed that the Romans had navigated into the waters beyond the ''Cimbric peninsula'' (Jutland). Suiones, Sitones, Goths and other Germanic people had temporarily settled to the east and west of the Vistula River during the Migration Period, adjacent to the Aesti, who lived further to the east. Overview The region's inhabitants of the Middle Ages have first been called ''Bruzi'' in the brief text of the Bavarian Geographer and since been referred to as Old Prussians, who, beginning in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teutonic Order 1410
Teutonic or Teuton(s) may refer to: Peoples and cultures * Teutons, a Germanic tribe or Celtic tribe mentioned by Greek and Roman authors ** ''Furor Teutonicus'', a Latin phrase referring to the proverbial ferocity of the Teutons * Having qualities related to classical Germanic peoples ''(dated)'' * Pertaining to Germanic languages or speakers of those languages ''(dated)'' ; see Theodiscus * Having qualities related to modern Germans or Austrians ''(poetic)'' * Nordic race, a putative sub-race discussed in the 19th to mid-20th centuries Other uses * A German Catholic order, the Teutonic Order **State of the Teutonic Order, the Northern European country it once formed * Teutonic, West Virginia Teutonic was an unincorporated community in Marshall County, West Virginia West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geogr ... * RMS ''Teutonic'', a steam shi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balthasar Of Żagań
Balthasar, Duke of Żagań ( pl, Baltazar żagański; – Przewóz, 15 July 1472), was a Duke of Żagań- Przewóz since 1439 (with his brothers as co-rulers until 1449), from 1449 Duke of Żagań. Deposed during 1461–1468, he recovered the Duchy in this year until shortly before his death. He was the oldest son of Duke Jan I of Żagań by his wife Scholastika, daughter of Rudolf III, Duke of Saxe-Wittemberg and Elector of Saxony. He was named after his maternal great-grandfather, Balthasar, Landgrave of Thuringia (Scholastika's maternal grandfather). Life After his father's death in 1439, he inherited the Duchy of Żagań with his younger brothers Rudolf, Wenceslaus and Jan II the Mad. In 1449 the Duchy was divided into two districts: Żagań and Przewóz. Balthasar and Rudolf received Żagań as co-rulers while Przewóz was given to Jan II and Wenceslaus, also as co-rulers. In 1450, together with Rudolf, Balthasar went on a pilgrimage to Rome. Shortly after his return, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolf Of Żagań
Rudolf of Żagań ( pl, Rudolf żagański) (ca. 1418 – 18 September 1454) was a Duke of Żagań- Przewóz since 1439 (with his brothers as co-rulers until 1449), from 1449 Duke of Żagań (as co-ruler of his older brother). He was the second son of Duke Jan I of Żagań by his wife Scholastika, daughter of Rudolf III, Duke of Saxe-Wittemberg and Elector of Saxony. He was named after his maternal grandfather. Rudolf was born between 1411 and 1418. Life At the time of his father's death (1439), Rudolf inherited the Duchy of Żagań-Przewóz jointly with his older brother Balthasar and his younger brothers Wenceslaus and Jan II the Mad. In 1449 the Duchy was divided in two parts: Żagań and Przewóz. Rudolf and Balthasar received Żagań as co-rulers while Przewóz was given to Jan II and Wenceslaus also as co-rulers. In 1450 Rudolf went along with his older brother on a pilgrimage to Rome. Here, he vowed to fight for the Christian faith, evidencing his strong religious beli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian I Of Denmark
Christian I (February 1426 – 21 May 1481) was a Scandinavian monarch under the Kalmar Union. He was king of Denmark (1448–1481), Norway (1450–1481) and Sweden (1457–1464). From 1460 to 1481, he was also duke of Schleswig (within Denmark) and count (after 1474, duke) of Holstein (within the Holy Roman Empire). He was the first king of the House of Oldenburg. In the power vacuum that arose following the death of King Christopher of Bavaria (1416–1448) without a direct heir, Sweden elected Charles VIII of Sweden (14081470) king with the intent to reestablish the union under a Swedish king. Charles was elected king of Norway in the following year. However the counts of Holstein made the Danish Privy Council appoint Christian as king of Denmark. His subsequent accessions to the thrones of Norway (in 1450) and Sweden (in 1457), restored the unity of the Kalmar Union for a short period. In 1463, Sweden broke away from the union and Christian's attempt at a reconquest res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Von Erlichshausen
Ludwig von Erlichshausen (1410–1467) was the 31st Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights, serving from 1449/1450 to 1467. As did his uncle and predecessor Konrad von Erlichshausen, Ludwig came from Ellrichshausen in Swabia, now part of Satteldorf in Baden-Württemberg. Ludwig was aide to Grand Master Paul von Rusdorf 1436-40, Komtur of Schönsee (Wąbrzeźno) near Thorn (Toruń) (1442–47), and Komtur of Mewe (Gniew) (1446–50). After the death of his more compromising uncle in 1449, Ludwig became Grand Master in 1450, despite being of limited ability and bad temper. His uncompromising stance towards the Prussian Confederation made the Prussian cities ask the Polish king for support, which led to the outbreak of the Thirteen Years' War in 1454 between the Order and Poland, supported by the Prussian Confederation. As the Order was short on cash since the expensive First Peace of Thorn (1411), Ludwig had to hand over the Order's headquarter Marienburg Castle in Malbork t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Reuß Von Plauen
Heinrich Reuß von Plauen (died 2 January 1470) was the 32nd Grand Master of the Teutonic Order, serving from 1467 to 1470. He was the nephew of the previous Grand Master, Ludwig von Erlichshausen, and a distant relative to the 27th Grand Master, Heinrich von Plauen. Biography Reuß von Plauen came from the Reuss family from Plauen, Saxony. Incidentally, the family named every male child Heinrich (Henry). Earlier, the brothers Heinrich Reuss von Plauen the Elder and Heinrich Reuss von Plauen the Younger had served in the Thirteen Years' War. Reuß von Plauen joined the Teutonic Order at a young age. He was first a brother in a monastery in Germany. Reuß von Plauen arrived in Prussia in the 1420s when he became the Vogt of Dirschau. In 1433 he became the Komtur of Balga and in 1440 the Vogt of Natangia. From 1441, Reuß von Plauen held the position of the Grand Hospitaller and the Komtur of Elbing (Elbląg). As the Grand Master's nephew, his influence in the Order grew and he ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernard Szumborski
Bernard Szumborski (german: Bernhard von Zinnenberg, links=no) was a Moravian knight and a mercenary. Szumborski was hired by the Teutonic Knights during the Battle of Chojnice (part of Thirteen Years' War), and was sent with 15,000 men to relieve the besieged city of Chojnice. King Casimir IV of Poland sent cavalry attacks to the rear of the Teutonic lines and Szumborski was captured. However, Teutonic knights rallied up and caused panic. Szumborski managed to escape and organized the pursuit of the fleeing Polish army. On October 24, 1457, together with 2000 mercenaries, Szumborski captured Chełmno (Kulm), and killed its mayor, Michal Segemund, claiming that he was a traitor. His forces captured other towns of Pomerelia and Chełmno Land, and on March 21, 1458, Szumborski with his army approached Toruń (Thorn), burning its suburbs, but failing to capture the heavily fortified city. On September 19, 1460, Szumborski captured the town of Golub-Dobrzyń, but Polish garrison of it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1.jpg)

