|
Surgical Oncology
Surgical oncology is the branch of surgery applied to oncology; it focuses on the surgical management of tumors, especially cancerous tumors. As one of several modalities in the management of cancer, the specialty of surgical oncology has evolved in steps similar to medical oncology ( pharmacotherapy for cancer), which grew out of hematology, and radiation oncology, which grew out of radiology. The Ewing Society known today as the Society of Surgical Oncology was started by surgeons interested in promoting the field of oncology. Complex General Surgical Oncology was ratified by a specialty Board certification in 2011 from the American Board of Surgery. The proliferation of cancer centers will continue to popularize the field, as will developments in minimally invasive techniques, palliative surgery, and neo-adjuvant treatments. Debate Whether surgical oncology constitutes a medical specialty ''per se'' is the topic of a heated debate. Today, some would agree that it is simpl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specialty (medicine)
A medical specialty is a branch of medical practice that is focused on a defined group of patients, diseases, skills, or philosophy. Examples include those branches of medicine that deal exclusively with children (paediatrics), cancer (oncology), laboratory medicine (pathology), or primary care ( family medicine). After completing medical school or other basic training, physicians or surgeons and other clinicians usually further their medical education in a specific specialty of medicine by completing a multiple-year residency to become a specialist. History of medical specialization To a certain extent, medical practitioners have long been specialized. According to Galen, specialization was common among Roman physicians. The particular system of modern medical specialties evolved gradually during the 19th century. Informal social recognition of medical specialization evolved before the formal legal system. The particular subdivision of the practice of medicine into various sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
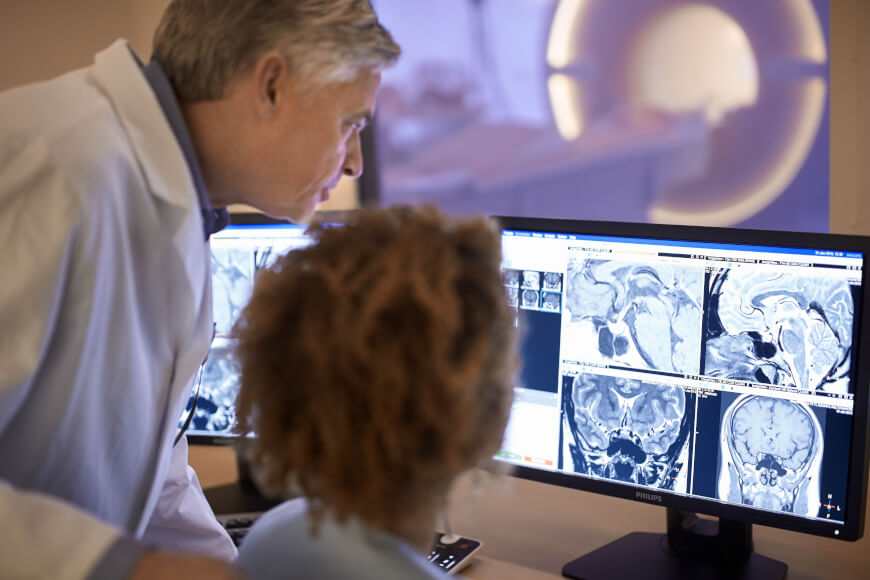
Radiology
Radiology ( ) is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiation), but today it includes all imaging modalities, including those that use no electromagnetic radiation (such as ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging), as well as others that do, such as computed tomography (CT), fluoroscopy, and nuclear medicine including positron emission tomography (PET). Interventional radiology is the performance of usually minimally invasive medical procedures with the guidance of imaging technologies such as those mentioned above. The modern practice of radiology involves several different healthcare professions working as a team. The radiologist is a medical doctor who has completed the appropriate post-graduate training and interprets medical images, communicates these findings to other physicians b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer Staging
Cancer staging is the process of determining the extent to which a cancer has developed by growing and spreading. Contemporary practice is to assign a number from I to IV to a cancer, with I being an isolated cancer and IV being a cancer that has spread to the limit of what the assessment measures. The stage generally takes into account the size of a tumor, whether it has invaded adjacent organs, how many regional (nearby) lymph nodes it has spread to (if any), and whether it has appeared in more distant locations ( metastasized). The staging system is not applicable to astrocytoma, which is instead expressed as "grade I–IV". Grade IV astrocytoma, more commonly referred to as glioblastoma multiforme, is a universally fatal primary brain cancer most commonly seen in the seventh decade of life. TNM staging system Cancer staging can be divided into a clinical stage and a pathologic stage. In the TNM (Tumor, Node, Metastasis) system, clinical stage and pathologic stage are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a red or scaly patch of skin. In those with distant spread of the disease, there may be bone pain, swollen lymph nodes, shortness of breath, or yellow skin. Risk factors for developing breast cancer include obesity, a lack of physical exercise, alcoholism, hormone replacement therapy during menopause, ionizing radiation, an early age at first menstruation, having children late in life or not at all, older age, having a prior history of breast cancer, and a family history of breast cancer. About 5–10% of cases are the result of a genetic predisposition inherited from a person's parents, including BRCA1 and BRCA2 among others. Breast cancer most commonly develops in cells from the lining of milk ducts and the lobules that supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Diseases
Breast diseases make up a number of conditions. The most common symptoms are a breast mass, breast pain, and nipple discharge. A majority of breast diseases are noncancerous. Tumor A breast tumor is an abnormal mass of tissue in the breast as a result of neoplasia. A breast neoplasm may be benign, as in fibroadenoma, or it may be malignant, in which case it is termed breast cancer. Either case commonly presents as a breast lump. Approximately 7% of breast lumps are fibroadenomas and 10% are breast cancer, the rest being other benign conditions or no disease.Page 739 in: 8th edition. Phyllodes tumor is a fibroepithelial tumor which can be benign, borderline or malignant. Breast cancer Breast cancer is cancer of the breast tissues, most commonly arising from the milk ducts. Worldwide, breast cancer is the leading type of cancer in women, accounting for 25% of all cases. It is most common in women over age 50. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a red or scaly patch of skin. In those with distant spread of the disease, there may be bone pain, swollen lymph nodes, shortness of breath, or yellow skin. Risk factors for developing breast cancer include obesity, a lack of physical exercise, alcoholism, hormone replacement therapy during menopause, ionizing radiation, an early age at first menstruation, having children late in life or not at all, older age, having a prior history of breast cancer, and a family history of breast cancer. About 5–10% of cases are the result of a genetic predisposition inherited from a person's parents, including BRCA1 and BRCA2 among others. Breast cancer most commonly develops in cells from the lining of milk ducts and the lobules that supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Diseases
Breast diseases make up a number of conditions. The most common symptoms are a breast mass, breast pain, and nipple discharge. A majority of breast diseases are noncancerous. Tumor A breast tumor is an abnormal mass of tissue in the breast as a result of neoplasia. A breast neoplasm may be benign, as in fibroadenoma, or it may be malignant, in which case it is termed breast cancer. Either case commonly presents as a breast lump. Approximately 7% of breast lumps are fibroadenomas and 10% are breast cancer, the rest being other benign conditions or no disease.Page 739 in: 8th edition. Phyllodes tumor is a fibroepithelial tumor which can be benign, borderline or malignant. Breast cancer Breast cancer is cancer of the breast tissues, most commonly arising from the milk ducts. Worldwide, breast cancer is the leading type of cancer in women, accounting for 25% of all cases. It is most common in women over age 50. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphadenectomy
Lymphadenectomy or lymph node dissection is the surgical removal of one or more groups of lymph nodes. It is almost always performed as part of the surgical management of cancer. In a regional lymph node dissection, some of the lymph nodes in the tumor area are removed; in a radical lymph node dissection, most or all of the lymph nodes in the tumor area are removed. Indications It is usually done because many types of cancer have a marked tendency to produce lymph node metastasis early in their natural history. This is particularly true of melanoma, head and neck cancer, differentiated thyroid cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, gastric cancer and colorectal cancer. Famed British surgeon Berkeley Moynihan once remarked that "the surgery of cancer is not the surgery of organs; it is the surgery of the lymphatic system". The better-known examples of lymphadenectomy are '' axillary lymph node dissection'' for breast cancer; ''radical neck dissection'' for head and neck cancer and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrectomy
A gastrectomy is a partial or total surgical removal of the stomach. Indications Gastrectomies are performed to treat stomach cancer and perforations of the stomach wall. In severe duodenal ulcers it may be necessary to remove the lower portion of the stomach called the pylorus and the upper portion of the small intestine called the duodenum. If there is a sufficient portion of the upper duodenum remaining a Billroth I procedure is performed, where the remaining portion of the stomach is reattached to the duodenum before the bile duct and the duct of the pancreas. If the stomach cannot be reattached to the duodenum a Billroth II is performed, where the remaining portion of the duodenum is sealed off, a hole is cut into the next section of the small intestine called the jejunum and the stomach is reattached at this hole. As the pylorus is used to grind food and slowly release the food into the small intestine, removal of the pylorus can cause food to move into the small int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancreaticoduodenectomy
A pancreaticoduodenectomy, also known as a Whipple procedure, is a major surgical operation most often performed to remove cancerous tumours from the head of the pancreas. It is also used for the treatment of pancreatic or duodenal trauma, or chronic pancreatitis. Due to the shared blood supply of organs in the proximal gastrointestinal system, surgical removal of the head of the pancreas also necessitates removal of the duodenum, proximal jejunum, gallbladder, and, occasionally, part of the stomach. Anatomy involved in the procedure The most common technique of a pancreaticoduodenectomy consists of the en bloc removal of the distal segment (antrum) of the stomach, the first and second portions of the duodenum, the head of the pancreas, the common bile duct, and the gallbladder. Lymph nodes in the area are often removed during the operation as well (lymphadenectomy). However, not all lymph nodes are removed in the most common type of pancreaticoduodenectomy because studies sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Cancer Surgery
The breast is one of two prominences located on the upper ventral region of a primate's torso. Both females and males develop breasts from the same embryological tissues. In females, it serves as the mammary gland, which produces and secretes milk to feed infants. Subcutaneous fat covers and envelops a network of ducts that converge on the nipple, and these tissues give the breast its size and shape. At the ends of the ducts are lobules, or clusters of alveoli, where milk is produced and stored in response to hormonal signals. During pregnancy, the breast responds to a complex interaction of hormones, including estrogens, progesterone, and prolactin, that mediate the completion of its development, namely lobuloalveolar maturation, in preparation of lactation and breastfeeding. Humans are the only animals with permanent breasts. At puberty, estrogens, in conjunction with growth hormone, cause permanent breast growth in female humans. This happens only to a much lesser e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, drugs, dietary choices, dietary supplements, and medical devices) and known interventions that warrant further study and comparison. Clinical trials generate data on dosage, safety and efficacy. They are conducted only after they have received health authority/ethics committee approval in the country where approval of the therapy is sought. These authorities are responsible for vetting the risk/benefit ratio of the trial—their approval does not mean the therapy is 'safe' or effective, only that the trial may be conducted. Depending on product type and development stage, investigators initially enroll volunteers or patients into small pilot studies, and subsequently conduct progressively larger scale comparative studies. Clinical trials can vary i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)