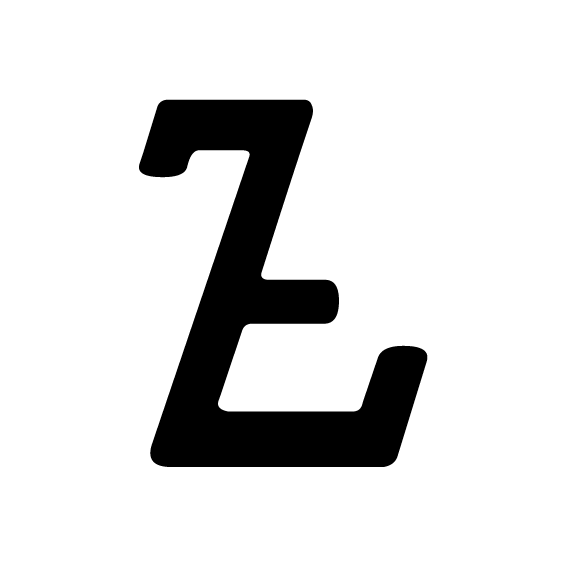|
Sundanese Script
Standard Sundanese script (''Aksara Sunda Baku'', ) is a traditional writing system used by Sundanese people to write Sundanese language. It is built based on Old Sundanese script (''Aksara Sunda Kuno'') which was used from the 14th to the 18th centuries. History Old Sundanese was developed based on the Pallava script of India, and was used from the 14th until the 18th centuries. The last manuscript written in Old Sundanese script was ''Carita Waruga Guru.'' From the 17th to the 19th centuries, Sundanese was mostly spoken and not written. Javanese script, Javanese and Pegon script, Pegon scripts were used to write Sundanese during this period. In 1996, the government of West Java announced a plan to introduce an official Sundanese script, and in October 1997, the Old Sundanese script was chosen and renamed to ''Aksara Sunda.'' Typology The standardized script has 32 basic characters-- seven vowels, 23 consonants, and thirteen phonetic diacriticals (). There are also numerals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Sundanese Language
Old Sundanese (Sundanese script: , Old Sundanese script: , Buda script: , Roman script: ) is the earliest recorded stage of the Sundanese language which is spoken in the western part of Java, Indonesia. The evidence is recorded in inscriptions from around the 12th to 14th centuries and ancient palm-leaf manuscripts from the 15th to 17th centuries AD. Old Sundanese is no longer used today, but has developed into its descendant, Sundanese language, modern Sundanese. Written evidence Old Sundanese is recorded in stone inscriptions such as the Astana Gede inscriptions, Kawali inscription in Ciamis Regency, Ciamis, and the Batutulis inscription in Bogor, as well as in inscriptions made from copper plates such as the Kabantenan inscription from the Bekasi Regency. Other remains documenting the use of Old Sundanese are palm-leaf manuscripts from the Bandung, Garut, and Bogor regions. The manuscripts are now stored in several institutions, including Kabuyutan Ciburuy in Bayongbong Garu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Sundanese Script
Old Sundanese script () is a script that developed in West Java in the 14th–18th centuries which was originally used to write Old Sundanese language. The Old Sundanese script is a development of the Pallava script which has reached the stage of modifying its distinctive form as used in lontar texts in the 16th century. History The use of Old Sundanese script in its earliest form is found in the inscriptions found in Astana Gede inscriptions, Astana Gede, Kawali District, Ciamis Regency, and the Kebantenan Inscription in Jati Asih, Jatiasih District, Bekasi City. According to Edi S. Ekajati, the existence of the Old Sundanese script had been gradually displaced due to the expansion of the Mataram Sultanate into the Parahyangan, Priangan region, except for Sultanate of Cirebon, Cirebon and Banten Sultanate, Banten. At that time the Sundanese people, Sundanese conquerors made Javanese culture their role model and ideal type. As a result, Sundanese culture was displaced by Jav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Kawi
The Kawi script or the Old Javanese script (, ) is a Brahmic script found primarily in Java and used across much of Maritime Southeast Asia between the 8th century and the 16th century.Aditya Bayu Perdana and Ilham Nurwansah 2020Proposal to encode Kawi/ref> The script is an abugida, meaning that characters are read with an inherent vowel. Diacritics are used, either to suppress the vowel and represent a pure consonant, or to represent other vowels.De Casparis, J. G. ''Indonesian Palaeography: A History of Writing in Indonesia from the beginnings to c. AD 1500'', Leiden/Koln, 1975, pp. 35-42 with footnotes History The Kawi script is related to the Nāgarī script, Nagari or old-Devanagari script in India. Also called the Prae-Nagari in Dutch publications after the classic work of F.D.K. Bosch on early Indonesian scripts, the early-Nagari form of script was primarily used in the Kawi script form to write southeast Asian Sanskrit and Old Javanese language in central and eastern J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abugida
An abugida (; from Geʽez: , )sometimes also called alphasyllabary, neosyllabary, or pseudo-alphabetis a segmental Writing systems#Segmental writing system, writing system in which consonant–vowel sequences are written as units; each unit is based on a consonant letter, and vowel notation is secondary, similar to a diacritical mark. This contrasts with a full alphabet, in which vowels have status equal to consonants, and with an abjad, in which vowel marking is absent, Abjad#Impure abjads, partial, or optional – in less formal contexts, all three types of the script may be termed "alphabets". The terms also contrast them with a syllabary, in which a single symbol denotes the combination of one consonant and one vowel. Related concepts were introduced independently in 1948 by James Germain Février (using the term ) and David Diringer (using the term ''semisyllabary''), then in 1959 by Fred Householder (introducing the term ''pseudo-alphabet''). The Ethiopian Semitic langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
14th-century Introductions
The 14th century lasted from 1 January 1301 (represented by the Roman numerals MCCCI) to 31 December 1400 (MCD). It is estimated that the century witnessed the death of more than 45 million lives from political and natural disasters in both Europe and the Mongol Empire. West Africa experienced economic growth and prosperity. In Europe, the Black Death claimed 25 million lives wiping out one third of the European population while the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of France fought in the protracted Hundred Years' War after the death of King Charles IV of France led to a claim to the French throne by King Edward III of England. This period is considered the height of chivalry and marks the beginning of strong separate identities for both England and France as well as the foundation of the Italian Renaissance and the Ottoman Empire. In Asia, Tamerlane (Timur), established the Timurid Empire, history's third largest empire to have been ever established by a single conqueror. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sundanese Numerals
Sundanese numerals (Sundanese language: ''Wilangan'') is a number system used by Sundanese people and contains a sequence of 10 digits ( ) in Sundanese script. The Wilangan writing system is the same as in Arabic numerals, i.e. the writing is directed to the right, only there is a difference in terms of marking, namely that the writing of numbers in Sundanese script must use a pipe sign ( , ), because some forms of Sundanese numerals are similar to consonant letters ( ''ngalagéna''), it is feared that ambiguity will occur. Example: , , = 2020 However, because the writing system that is more often used in Sundanese is the Latin alphabet, it is more common to write numbers in Sundanese using Arabic numerals and the use of numbers in Sundanese script Standard Sundanese script (''Aksara Sunda Baku'', ) is a traditional writing system used by Sundanese people to write Sundanese language. It is built based on Old Sundanese script (''Aksara Sunda Kuno'') which was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lontar Manuscript
Palm-leaf manuscripts are manuscripts made out of dried palm leaves. Palm leaves were used as writing materials in the Indian subcontinent and in Southeast Asia dating back to the 5th century BCE. Their use began in South Asia and spread to other regions, as texts on dried and smoke-treated palm leaves of the Palmyra or talipot palm. Their use continued until the 19th century when printing presses replaced hand-written manuscripts. One of the oldest surviving palm leaf manuscripts of a complete treatise is a Sanskrit Shaivism text from the 9th century, discovered in Nepal, and now preserved at the Cambridge University Library.Pārameśvaratantra (MS Add.1049.1) with images , Puṣkarapārameśvaratantra, University of Cambridge (2015) The |
Unicode
Unicode or ''The Unicode Standard'' or TUS is a character encoding standard maintained by the Unicode Consortium designed to support the use of text in all of the world's writing systems that can be digitized. Version 16.0 defines 154,998 Character (computing), characters and 168 script (Unicode), scripts used in various ordinary, literary, academic, and technical contexts. Unicode has largely supplanted the previous environment of a myriad of incompatible character sets used within different locales and on different computer architectures. The entire repertoire of these sets, plus many additional characters, were merged into the single Unicode set. Unicode is used to encode the vast majority of text on the Internet, including most web pages, and relevant Unicode support has become a common consideration in contemporary software development. Unicode is ultimately capable of encoding more than 1.1 million characters. The Unicode character repertoire is synchronized with Univers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Declaration Of Human Rights
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) is an international document adopted by the United Nations General Assembly that enshrines the Human rights, rights and freedoms of all human beings. Drafted by a UN Drafting of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, committee chaired by Eleanor Roosevelt, it was accepted by the General Assembly as United Nations General Assembly Resolution 217, Resolution 217 during Third session of the United Nations General Assembly, its third session on 10 December 1948 at the Palais de Chaillot in Paris, France. Of the 58 members of the United Nations at the time, 48 voted in favour, none against, eight abstentions, abstained, and two did not vote. A foundational text in the History of human rights, history of human and civil rights, the Declaration consists of 30 articles detailing an individual's "basic rights and fundamental freedoms" and affirming their universal character as inherent, inalienable, and applicable to all human beings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciamis Sundanese Lexicon Kanjat
Ciamis (, ) is a district and a town; it is the regency seat of Ciamis Regency in West Java, Indonesia. It covers an area of . It had a population of 93,744 as of the 2010 Census, 98,610 as of the 2020 Census, and 99,750 as of a mid-2022 official estimate.Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2023. History The process of determining the history of the Ciamis Regency was born with the decree of the Regional House of Representatives of Ciamis Regency of October 6, 1970, concerning the formation of the committee for the preparation of a history of the Galuh Kingdom, where the committee was advised by a team of historians from Ikip Bandung led by Said Raksanegara. The committee preparing of the history of Galuh intends to explore and study the history of Galuh as a whole, considering that there are several alternatives in determining the date of its inception. Titimangsa Rahyangta in Medang Jati, namely the establishment of the Galuh Kingdom by on March 23, 612 AD, or the Rakean Ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virama
Virama ( ्, ) is a Sanskrit phonological concept to suppress the inherent vowel that otherwise occurs with every consonant letter, commonly used as a generic term for a codepoint in Unicode, representing either # halanta, hasanta or explicit virāma, a diacritic in many Brahmic scripts, including the Devanagari and Bengali scripts, or # saṃyuktākṣara (Sanskrit: संयुक्ताक्षर) or implicit virama, a conjunct consonant or ligature. Unicode schemes of scripts writing Mainland Southeast Asia languages, such as that of Burmese script and of Tibetan script, generally do not group the two functions together. Names The name is Sanskrit for "cessation, termination, end". As a Sanskrit word, it is used in place of several language-specific terms, such as: Usage In Devanagari and many other Indic scripts, a virama is used to cancel the inherent vowel of a consonant letter and represent a consonant without a vowel, a "dead" consonant. For example, in Dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |