|
Struma Basin
{{disambiguation, geo ...
Struma may refer to: * Struma (medicine), a swelling in the neck due to an enlarged thyroid gland * Struma (skin disease), a mycobacterial skin disease * Struma (river), a river in Bulgaria and Greece * Struma motorway, a Bulgarian motorway * Struma (village), a village in Bulgaria * , a ship chartered to carry Jewish refugees from Axis-allied Romania to British-controlled Palestine in World War II sunken in the ''Struma'' disaster, the largest civilian Black Sea naval disaster of World War II * Struma Glacier, a glacier in Antarctica See also * Struma Corps, of the Ottoman Empire * Struma Offensive in the First World War * Stroma (other) Stroma may refer to: Biology * Stroma (tissue), the connective, functionally supportive framework of a biological cell, tissue, or organ (in contrast, the parenchyma is the functional aspect of a tissue) ** Stroma of ovary, a soft tissue, we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Struma (medicine)
A goitre, or goiter, is a swelling in the neck resulting from an enlarged thyroid gland. A goitre can be associated with a thyroid that is not functioning properly. Worldwide, over 90% of goitre cases are caused by iodine deficiency. The term is from the Latin ''gutturia'', meaning throat. Most goitres are not cancerous (benign), though they may be potentially harmful. Signs and symptoms A goitre can present as a palpable or visible enlargement of the thyroid gland at the base of the neck. A goitre, if associated with hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, may be present with symptoms of the underlying disorder. For hyperthyroidism, the most common symptoms are associated with adrenergic stimulation: tachycardia (increased heart rate), palpitations, nervousness, tremor, increased blood pressure and heat intolerance. Clinical manifestations are often related to hypermetabolism, (increased metabolism), excessive thyroid hormone, an increase in oxygen consumption, metabolic changes in pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Struma (skin Disease)
The disease mycobacterial cervical lymphadenitis, also known as scrofula and historically as king's evil, involves a lymphadenitis of the cervical lymph nodes associated with tuberculosis as well as nontuberculous (atypical) mycobacteria. Disease Scrofula is the term used for lymphadenopathy of the neck, usually as a result of an infection in the lymph nodes, known as lymphadenitis. It can be caused by tuberculous or nontuberculous mycobacteria. About 95% of the scrofula cases in adults are caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', most often in immunocompromised patients (about 50% of cervical tuberculous lymphadenopathy). In immunocompetent children, scrofula is often caused by atypical mycobacteria ('' Mycobacterium scrofulaceum)'' and other nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM). Unlike the adult cases, only 8% of cases in children are tuberculous. With the stark decrease of tuberculosis in the second half of the 20th century, scrofula became a less common disease in adults, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Struma (river)
The Struma or Strymónas ( bg, Струма ; el, Στρυμόνας ; tr, (Struma) Karasu , 'black water') is a river in Bulgaria and Greece. Its ancient name was Strymṓn (Greek: Στρυμών ). Its drainage area is , of which in Bulgaria, in Greece and the remaining in North Macedonia and Serbia. It takes its source from the Vitosha Mountain in Bulgaria, runs first westward, then southward, forming a number of gorges, enters Greek territory at the Kula village. In Greece it is the main waterway feeding and exiting from Lake Kerkini, a significant centre for migratory wildfowl. The river flows into the Strymonian Gulf in Aegean Sea, near Amphipolis in the Serres regional unit. The river's length is (of which in Bulgaria, making it the country's fifth-longest and one of the longest rivers that run solely in the interior of the Balkans. Parts of the river valley belong to a Bulgarian (Pirin Macedonia) coal-producing area, more significant in the past than nowadays; the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Struma Motorway
The Struma Motorway (, ) is a motorway currently under construction in Bulgaria. The motorway is located in the Yugozapaden area in South West Bulgaria, and follows the route Sofia-Pernik-Dupnitsa-Blagoevgrad-Sandanski to Kulata on the border with in Greece. It is part of the Pan-European Corridor IV and also is part of Е79, that runs from Miskolc (Hungary) to Thessaloniki (Greece), via the Romanian cities of Deva and Craiova. This project is under the European Union's Ten-T Priority Projects. The road is also part of the proposed Via Carpatia route. The Struma motorway forms a connection between Sofia and Kulata at the Bulgaria-Greece border with a total planned length of 172.8 km. As of December 2018, about 129.46 km of the motorway, from Sofia to Blagoevgrad, and from Kresna to Kulata have already been completed and are in service. The highway has a total width of 29 m, and has two asphalt-surfaced lanes in each direction, two emergency halt lanes, and a 3.5m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Struma (village)
Struma (village) is a village in Sandanski municipality, Blagoevgrad Province, Bulgaria. Accessed May 5, 2010 References Villages in Blagoevgrad Province {{Blagoevgrad-geo-stub ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Struma Disaster
The ''Struma'' disaster was the sinking on 24 February 1942 of a ship, , that had been trying to take nearly 800 Jewish refugees from Romania in World War II, Axis-allied Romania to Mandatory Palestine. She was a small iron-hulled ship of only that had been built in 1867 as a Marine steam engine, steam-powered schooner but had recently been re-engined with an unreliable second-hand Marine propulsion#Reciprocating, diesel engine. ''Struma'' was only long, had a Beam (nautical), beam of only and a Draft (hull), draught of only but an estimated 781 refugees and 10 crew were crammed into her. ''Struma''s diesel engine failed several times between her departure from Constanţa on the Black Sea on 12 December 1941 and her arrival in Istanbul on 15 December. She had to be towed by a tug boat to leave Constanţa and to enter Istanbul. On 23 February 1942, with her engine still inoperable and her refugee passengers aboard, Turkish authorities towed ''Struma'' from Istanbul through the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Struma Glacier
Struma Glacier ( bg, ледник Струма, lednik Struma, ) is a glacier in eastern Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica situated south of lower Kaliakra Glacier and north of Huron Glacier. Bounded by Melnik Ridge to the north, Yankov Gap to the west and Bowles Ridge to the south, it is 4.8 km long and 1.5 km wide, and flows eastwards into Moon Bay south of Sindel Point. First crossed by the Bulgarians Lyubomir Ivanov and Doychin Vasilev from Camp Academia on 28 December 2004, as part of Tangra 2004/05 survey. The glacier is named after the Struma River in Bulgaria and forms part of the overland route between Pirdop Gate and Yankov Gap. Location The midpoint is located at . Bulgarian topographic survey Tangra 2004/05 and mapping in 2005 and 2009. See also * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * Glaciology Maps * L.L. Ivanov et al. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich Island, South Shetland Islands. Scale 1:100000 topographic ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Struma Corps
The Struma Corps or Usturma Corps of the Ottoman Empire ( Turkish: ''Usturma Kolordusu'') was one of the corps under the command of the Ottoman Western Army. It was formed in Ustruma ( Struma) area during the First Balkan War The First Balkan War ( sr, Први балкански рат, ''Prvi balkanski rat''; bg, Балканска война; el, Αʹ Βαλκανικός πόλεμος; tr, Birinci Balkan Savaşı) lasted from October 1912 to May 1913 and invo .... Balkan Wars Order of Battle, October 19, 1912 On October 19, 1912, the detachment was structured as follows:Edward J. Erickson, ''Defeat in Detail, The Ottoman Army in the Balkans, 1912–1913'', Westport, Praeger, 2003, p. 170. *Struma Corps HQ (Bulgarian Front, under the command of the Western Army) ** 14th Division **Serez Redif Division **Nevrekop Detachment Sources {{Ottoman Forces during the Balkan Wars Corps of the Ottoman Empire Military units and formations of the Ottoman Empire in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
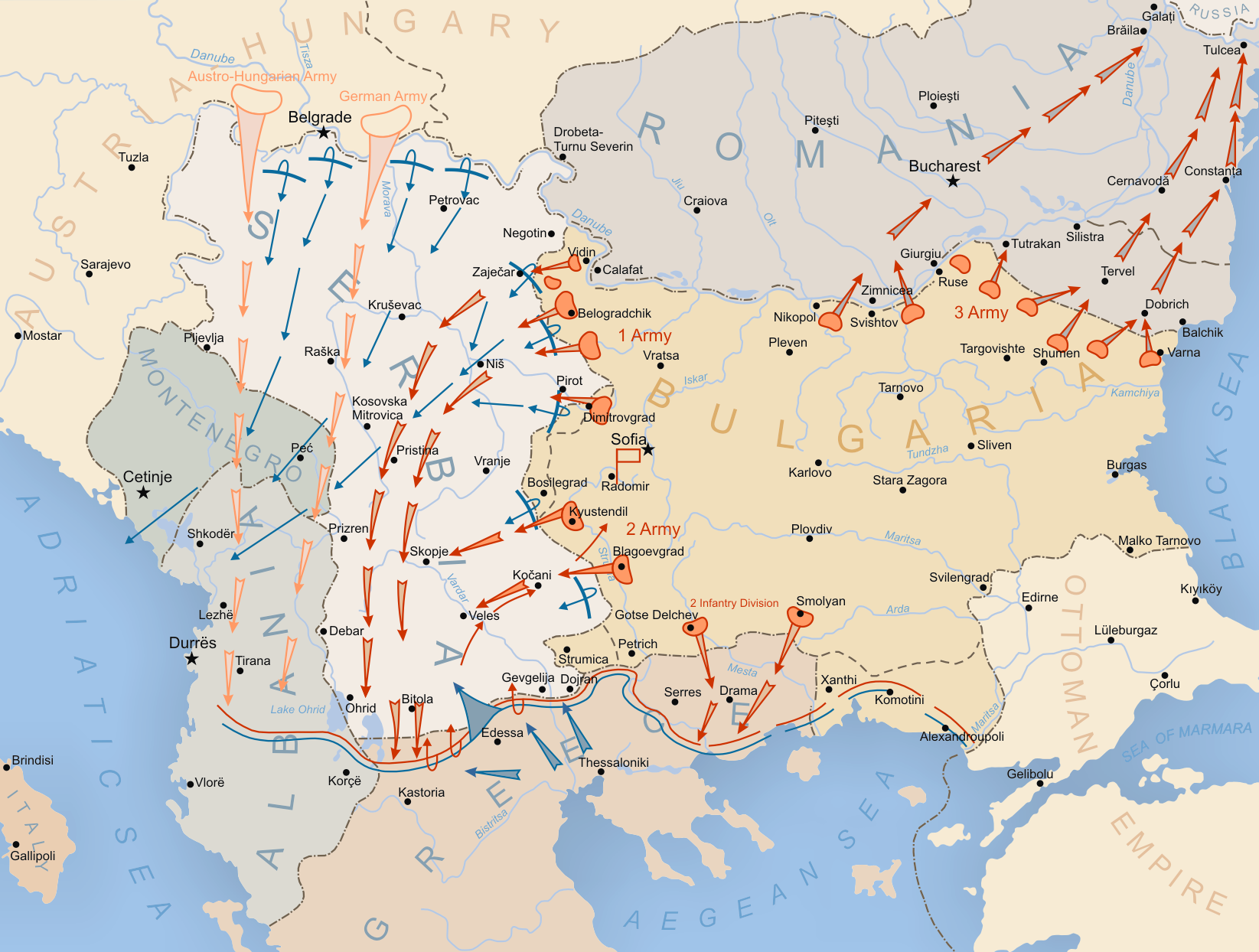
Struma Offensive
The Struma operation was the occupation of a part of northeastern mainland Greece by the Bulgarian army, during the First World War between 17–23 August 1916. It was named after the Struma (Strymonas) river. Background In August 1916 Romania chose to join the war effort on the side of the Allies. The Allies planned a large offensive in the Macedonian front for the middle of August in order to support Romania's entry in the war and pin down as many Bulgarian forces as possible. The Bulgarian high command suspected an impending offensive and the fighting around Doiran that erupted on 9 August only confirmed these suspicions. On their part the Bulgarians had urged for an offensive in Macedonia since the beginning of the year and now planned a strike with the First Army and Second Army on both Allied flanks. On the western flank, the Chegan Offensive resulted in the conquest of Florina, but the First Army failed to take Chegan (today Agios Athanasios). The plan on the easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |