|
Sprigginidae
Sprigginidae is an extinct family of cephalozoans characterized by having a greater number of isomers than its sister taxon, Yorgiidae. They lived approximately 635 million years ago, in the Ediacaran period. Distribution Fossils are found within the Ediacaran sediments of South Australia. Taxonomy Sprigginidae presents 4 genera: *†''Spriggina'' (type genus). *†''Marywadea'' *†''Cyanorus'' *†''Praecambridium'', sometimes included into Yorgiidae. Gallery Spriggina_flounensi_C.jpg , ''Spriggina floundersi'' Cyanorus_singularis.jpg , ''Cyanorus singularis'' Praecambridium_sigillum.jpg , ''Praecambridium sigillum'' See also *Cephalozoa *Yorgiidae Yorgiidae is an extinct family of cephalozoans, which lived 635 million years ago. They were filter fed. Description Like most proarticulates, they present semi-bilateral symmetry. They had a discoid appearance, with the body segmented by isome ... References Ediacaran life {{Ediacaran-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sprigginidae
Sprigginidae is an extinct family of cephalozoans characterized by having a greater number of isomers than its sister taxon, Yorgiidae. They lived approximately 635 million years ago, in the Ediacaran period. Distribution Fossils are found within the Ediacaran sediments of South Australia. Taxonomy Sprigginidae presents 4 genera: *†''Spriggina'' (type genus). *†''Marywadea'' *†''Cyanorus'' *†''Praecambridium'', sometimes included into Yorgiidae. Gallery Spriggina_flounensi_C.jpg , ''Spriggina floundersi'' Cyanorus_singularis.jpg , ''Cyanorus singularis'' Praecambridium_sigillum.jpg , ''Praecambridium sigillum'' See also *Cephalozoa *Yorgiidae Yorgiidae is an extinct family of cephalozoans, which lived 635 million years ago. They were filter fed. Description Like most proarticulates, they present semi-bilateral symmetry. They had a discoid appearance, with the body segmented by isome ... References Ediacaran life {{Ediacaran-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
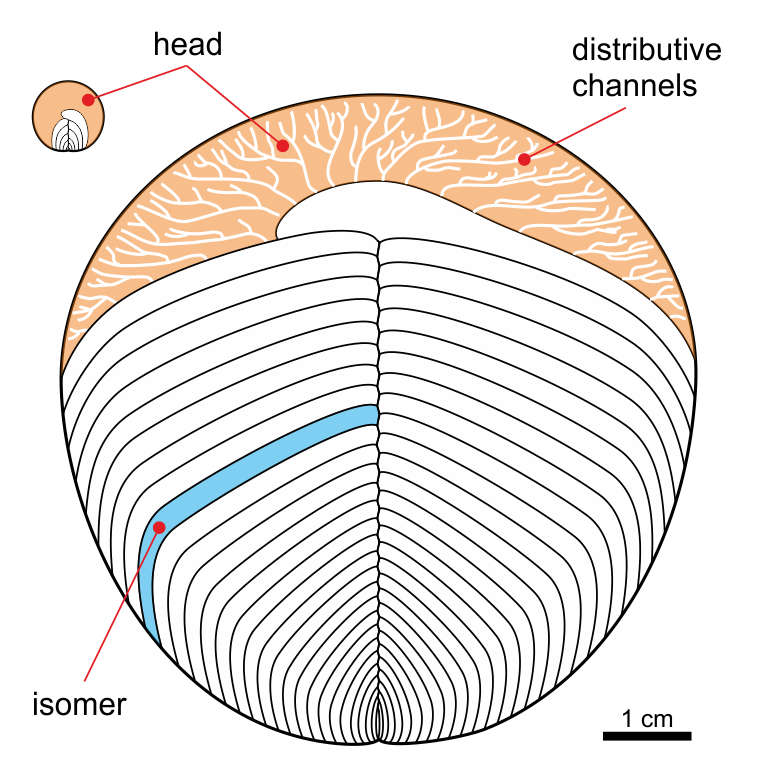
Cephalozoa
Cephalozoa are an extinct class of primitive segmented marine organisms within the Phylum Proarticulata from the Ediacaran period. They possessed bilateral symmetry and were characterized by a thin, rounded body. Description Unlike the other classes of proarticulates, the segmentation of the body is not complete and shows a "head" with fine distribution channels. Some species of the Yorgiidae family also show some asymmetry.Ivantsov, A. Y. (2004"Vendian Animals in the Phylum Proarticulata" The Rise and Fall of the Vendian Biota. IGSP Project 493. Abstracts. Prato, Italy, . They were discovered in Russia near the White Sea in the Arkhangelsk region, where they lived during the Ediacaran, approximately 635 to 540 Ma (millions of years ago). Taxonomy Cephalozoa includes the families Yorgiidae and Sprigginidae: Yorgiidae *† ''Archaeaspinus'' Ivantsov, 2007 (synonym of ''Archaeaspis'') **† ''Archaeaspinus fedonkini'' Ivantsov, 2001 *† ''Yorgia'' Ivantsov, 1999 **† ''Yorgi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalozoa
Cephalozoa are an extinct class of primitive segmented marine organisms within the Phylum Proarticulata from the Ediacaran period. They possessed bilateral symmetry and were characterized by a thin, rounded body. Description Unlike the other classes of proarticulates, the segmentation of the body is not complete and shows a "head" with fine distribution channels. Some species of the Yorgiidae family also show some asymmetry.Ivantsov, A. Y. (2004"Vendian Animals in the Phylum Proarticulata" The Rise and Fall of the Vendian Biota. IGSP Project 493. Abstracts. Prato, Italy, . They were discovered in Russia near the White Sea in the Arkhangelsk region, where they lived during the Ediacaran, approximately 635 to 540 Ma (millions of years ago). Taxonomy Cephalozoa includes the families Yorgiidae and Sprigginidae: Yorgiidae *† ''Archaeaspinus'' Ivantsov, 2007 (synonym of ''Archaeaspis'') **† ''Archaeaspinus fedonkini'' Ivantsov, 2001 *† ''Yorgia'' Ivantsov, 1999 **† ''Yorgi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
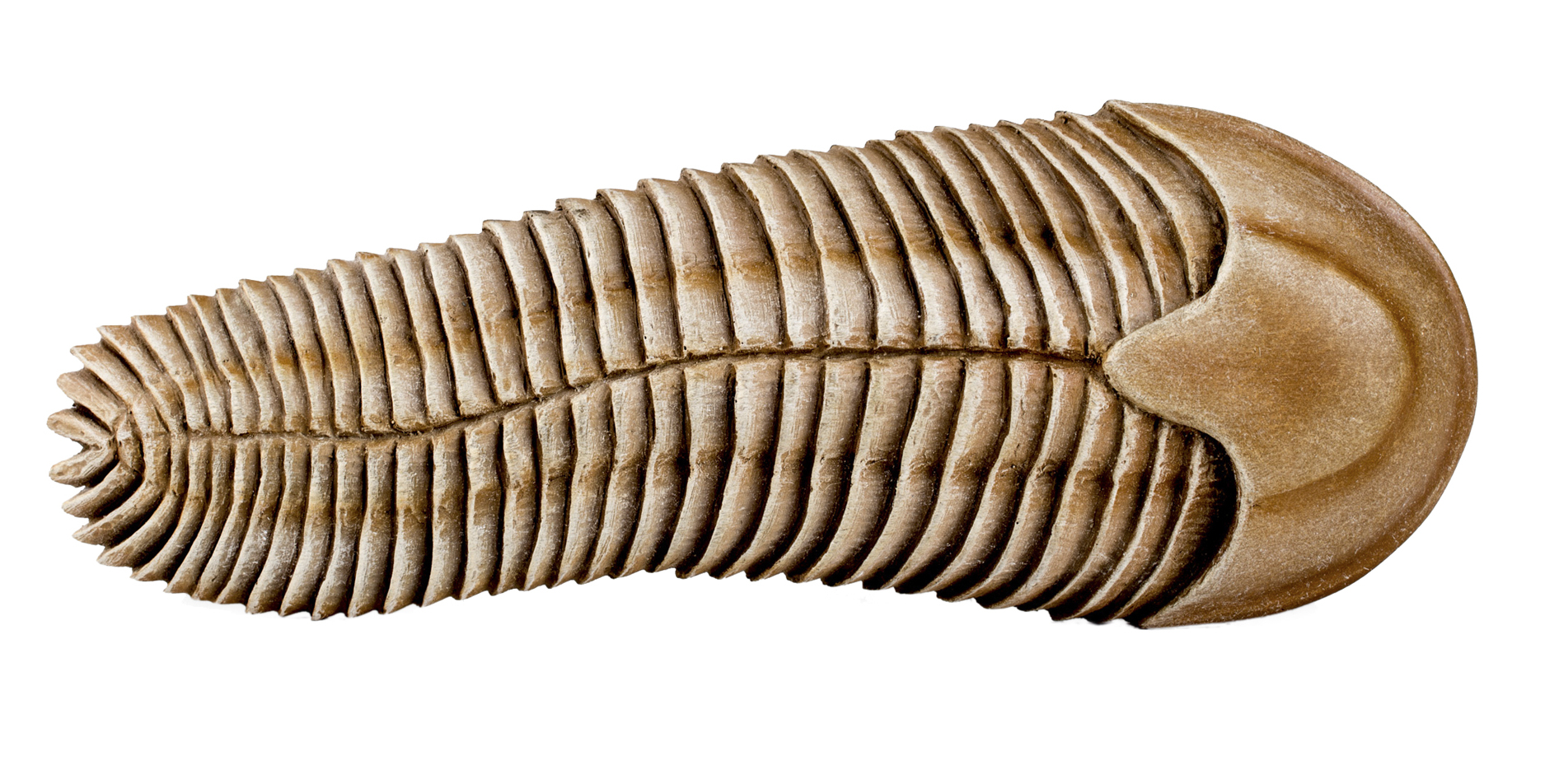
Spriggina Floundersi
''Spriggina'' is a genus of early bilaterian animals whose relationship to living animals is unclear. Fossils of ''Spriggina'' are known from the late Ediacaran period in what is now South Australia. ''Spriggina floundersi'' is the official fossil emblem of South Australia. It has been found nowhere else. The organism reached about in length and may have been predatory. Its bottom was covered with two rows of tough interlocking plates, while one row covered its top; its front few segments fused to form a "head." ''Spriggina'' affinity is currently unknown; it has been variously classified as an annelid worm, a rangeomorph-like frond, a variant of ''Charniodiscus'', a proarticulatan, or an arthropod perhaps related to the trilobites, or even an extinct phylum. Lack of known segmented legs or limbs, and glide reflection instead of symmetric segments, suggest an arthropod classification is unlikely despite some superficial resemblance. The genus ''Spriggina'' may have originally co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yorgiidae
Yorgiidae is an extinct family of cephalozoans, which lived 635 million years ago. They were filter fed. Description Like most proarticulates, they present semi-bilateral symmetry. They had a discoid appearance, with the body segmented by isomers. Distribution Ediacaran of Russian Federation and South Australia. Gallery Archaeaspinus_fedonkini.jpg , ''Archaeaspinus fedonkini'' Photo_of_"Archaeaspinus_fedonkini"_fossil_Ivantsov_2007.png , ''Other fossil of Archaeaspinus fedonkini'' Yorgia_trace.jpg , ''Epibaion waggoneri, possible ichnofossil of Yorgia waggoneri'' See also * Cephalozoa References Cephalozoa Yorgiidae Ediacaran life Fossils of Russia {{Ediacaran-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spriggina
''Spriggina'' is a genus of early bilaterian animals whose relationship to living animals is unclear. Fossils of ''Spriggina'' are known from the late Ediacaran period in what is now South Australia. ''Spriggina floundersi'' is the official fossil emblem of South Australia. It has been found nowhere else. The organism reached about in length and may have been predatory. Its bottom was covered with two rows of tough interlocking plates, while one row covered its top; its front few segments fused to form a "head." ''Spriggina'' affinity is currently unknown; it has been variously classified as an annelid worm, a rangeomorph-like frond, a variant of ''Charniodiscus'', a proarticulatan, or an arthropod perhaps related to the trilobites, or even an extinct phylum. Lack of known segmented legs or limbs, and glide reflection instead of symmetric segments, suggest an arthropod classification is unlikely despite some superficial resemblance. The genus ''Spriggina'' may have originally co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marywadea
''Marywadea'' is a genus of Ediacaran biota shaped like an oval with a central ridge. It is a bilaterian organism as evidenced by its symmetry, vaguely resembling a very primitive trilobite. The fossil has an asymmetrical first chamber of the quilt. It has transverse ridges away from the central axis that may be gonads. The head is shaped as a semicircle and is the same width as the rest of the body. The ridges number about 50. There are two oval shapes below the head. ''Marywadea ovata'' is the only described species of the genus. Originally ''M. ovata'' was grouped under the genus ''Spriggina'', but recent research has moved the species into its own genus. It is most often interpreted as an early arthropod, annelid, or a member of Proarticulata, but as with all Ediacarian fauna its phylogeny remains uncertain. Initially, it was described as the second species of ''Spriggina''. The genus was established by Martin Glaessner in 1976, who named it after fellow paleontologist M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanorus
''Cyanorus singularis'' is a small proarticulatan, closely related to ''Spriggina'' and '' Marywadea''. Its two largest pairs of appendages are located on the anterior part of the body. The anterior part of the body was most likely not segmented. The axial structure of it combines features of the ''Vendia'' species and ''Dickinsonia'' species. It was found in the Upper Vendian of the White Sea area, Arkhangel'sk Region. It is a White Sea Ediacaran fossil and it became extinct during the Late Precambrian The Precambrian (or Pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pꞒ, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of the .... Notes References {{Taxonbar, from=Q60760937 Ediacaran life Sprigginidae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praecambridium
''Praecambridium sigillum'' is an extinct organism that superficially resembles a segmented trilobite-like arthropod. It was originally described as being a trilobite-like arthropod, though the majority of experts now place it within the Proarticulata as a close relative of the much larger ''Yorgia''. It is from the Late Ediacaran deposit of Ediacara Hills, Australia, about 555 million years ago. On average, ''P. sigillum'' had at least 5 pairs of segments, with each unit becoming progressively larger as they approach the cephalon-like head. Etymology The generic name is a compound word, with the Latin prefix ''prae'' "before" and a reference to the Cambrian mollusc genus '' Cambridium'', in reference to how the appearance of the various segments are reminiscent of the muscle-scars on the inner surface of the shells of '' Cambridium''. The specific name is from Latin ''sigillum'' "a sigil". Classification and interpretations Originally, Runnegar and M.A. Fedokin (1992) suggested ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ediacaran
The Ediacaran Period ( ) is a geological period that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period 635 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Cambrian Period 538.8 Mya. It marks the end of the Proterozoic Eon, and the beginning of the Phanerozoic Eon. It is named after the Ediacara Hills of South Australia. The Ediacaran Period's status as an official geological period was ratified in 2004 by the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), making it the first new geological period declared in 120 years. Although the period takes its name from the Ediacara Hills where geologist Reg Sprigg first discovered fossils of the eponymous Ediacaran biota in 1946, the type section is located in the bed of the Enorama Creek within Brachina Gorge in the Flinders Ranges of South Australia, at . The Ediacaran marks the first appearance of widespread multicellular fauna following the end of Snowball Earth glaciation events, the so-called Ediacaran biota, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isomer (Proarticulata)
Isomer (Greek ''isos'' = "equal", ''méros'' = "part") is an element of transverse body articulation of the bilateral fossil animals of the Phylum Proarticulata from the Ediacaran (Vendian) period. This term has been proposed by Andrey Yu. Ivantsov, a Russian paleontologist from the Laboratory of the Precambrian organisms, Paleontological Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences. Morphology Proarticulatan isomers are distinct from the segments of the Annelida and Panarthropoda, as each of these elements occupies only half of width of a body and are organized in an alternating pattern relatively to the axis of the body. In other words, although proarticulatans are bilaterally symmetrical, one side is not the direct mirror image of its opposite. Opposite isomers of left and right side are located with displacement of half of its width. This phenomenon is described as the symmetry of gliding reflection.M. A. Fedonkin (1985). "Systematic Description of Vendian Metazoa". In Sokolov, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ediacaran Period
The Ediacaran Period ( ) is a geological period that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period 635 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Cambrian Period 538.8 Mya. It marks the end of the Proterozoic Eon, and the beginning of the Phanerozoic Eon. It is named after the Ediacara Hills of South Australia. The Ediacaran Period's status as an official geological period was ratified in 2004 by the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), making it the first new geological period declared in 120 years. Although the period takes its name from the Ediacara Hills where geologist Reg Sprigg first discovered fossils of the eponymous Ediacaran biota in 1946, the type section is located in the bed of the Enorama Creek within Brachina Gorge in the Flinders Ranges of South Australia, at . The Ediacaran marks the first appearance of widespread multicellular fauna following the end of Snowball Earth glaciation events, the so-called Ediacaran biota, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |