|
Spatial Music
Spatial music is composed music that intentionally exploits sound localization. Though present in Western music from biblical times in the form of the antiphon, as a component specific to new musical techniques the concept of spatial music (''Raummusik'', usually translated as "space music") was introduced as early as 1928 in Germany. The term ''spatialisation'' is connected especially with electroacoustic music to denote the projection and localization of sound sources in physical or virtual space or sound's spatial movement in space. Context The term "spatial music" indicates music in which the location and movement of sound sources is a primary compositional parameter and a central feature for the listener. It may involve a single, mobile sound source, or multiple, simultaneous, stationary or mobile sound events in different locations. There are at least three distinct categories when plural events are treated spatially: #essentially independent events separated in space, like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound Localization
Sound localization is a listener's ability to identify the location or origin of a detected sound in direction and distance. The sound localization mechanisms of the mammalian auditory system have been extensively studied. The auditory system uses several cues for sound source localization, including time difference and level difference (or intensity difference) between the ears, and spectral information. Other animals, such as birds and reptiles, also use them but they may use them differently, and some also have localization cues which are absent in the human auditory system, such as the effects of ear movements. Animals with the ability to localize sound have a clear evolutionary advantage. How sound reaches the brain Sound is the perceptual result of mechanical vibrations traveling through a medium such as air or water. Through the mechanisms of compression and rarefaction, sound waves travel through the air, bounce off the Pinna (anatomy), pinna and concha of the exter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Tallis
Thomas Tallis (; also Tallys or Talles; 23 November 1585) was an English composer of High Renaissance music. His compositions are primarily vocal, and he occupies a primary place in anthologies of English choral music. Tallis is considered one of England's greatest composers, and is honoured for his original voice in English musicianship. Life Youth As no records about the birth, family or childhood of Thomas Tallis exist, almost nothing is known about his early life or origins. Historians have calculated that he was born in the early part of the 16th century, towards the end of the reign of Henry VII of England, and estimates for the year of his birth range from 1500 to 1520. His only known relative was a cousin called John Sayer. As the surnames ''Sayer'' and ''Tallis'' both have strong connections with Kent, Thomas Tallis is usually thought to have been born somewhere in the county. [Baidu] |
The Journal Of Musicology
''The Journal of Musicology'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal of musicology published by University of California Press The University of California Press, otherwise known as UC Press, is a publishing house associated with the University of California that engages in academic publishing. It was founded in 1893 to publish scholarly and scientific works by faculty .... The journal was established in 1982 by Marian C. Green. External links * {{DEFAULTSORT:Journal of Musicology Music journals University of California Press academic journals Quarterly journals English-language journals Academic journals established in 1981 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henryk Górecki
Henryk Mikołaj Górecki ( , ; 6 December 1933 – 12 November 2010) was a Polish composer of contemporary classical music. According to critic Alex Ross, no recent classical composer has had as much commercial success as Górecki. He became a leading figure of the Polish avant-garde during the post-Stalin cultural thaw. His Anton Webern-influenced serialist works of the 1950s and 1960s were characterized by adherence to dissonant modernism and influenced by Luigi Nono, Karlheinz Stockhausen, Krzysztof Penderecki and Kazimierz Serocki. He continued in this direction throughout the 1960s, but by the mid-1970s had changed to a less complex sacred minimalist sound, exemplified by the transitional Symphony No. 2 and the Symphony No. 3 (''Symphony of Sorrowful Songs''). This later style developed through several other distinct phases, from such works as his 1979 ''Beatus Vir'', to the 1981 choral hymn '' Miserere'', the 1993 '' Kleines Requiem für eine Polka'' and his requiem ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
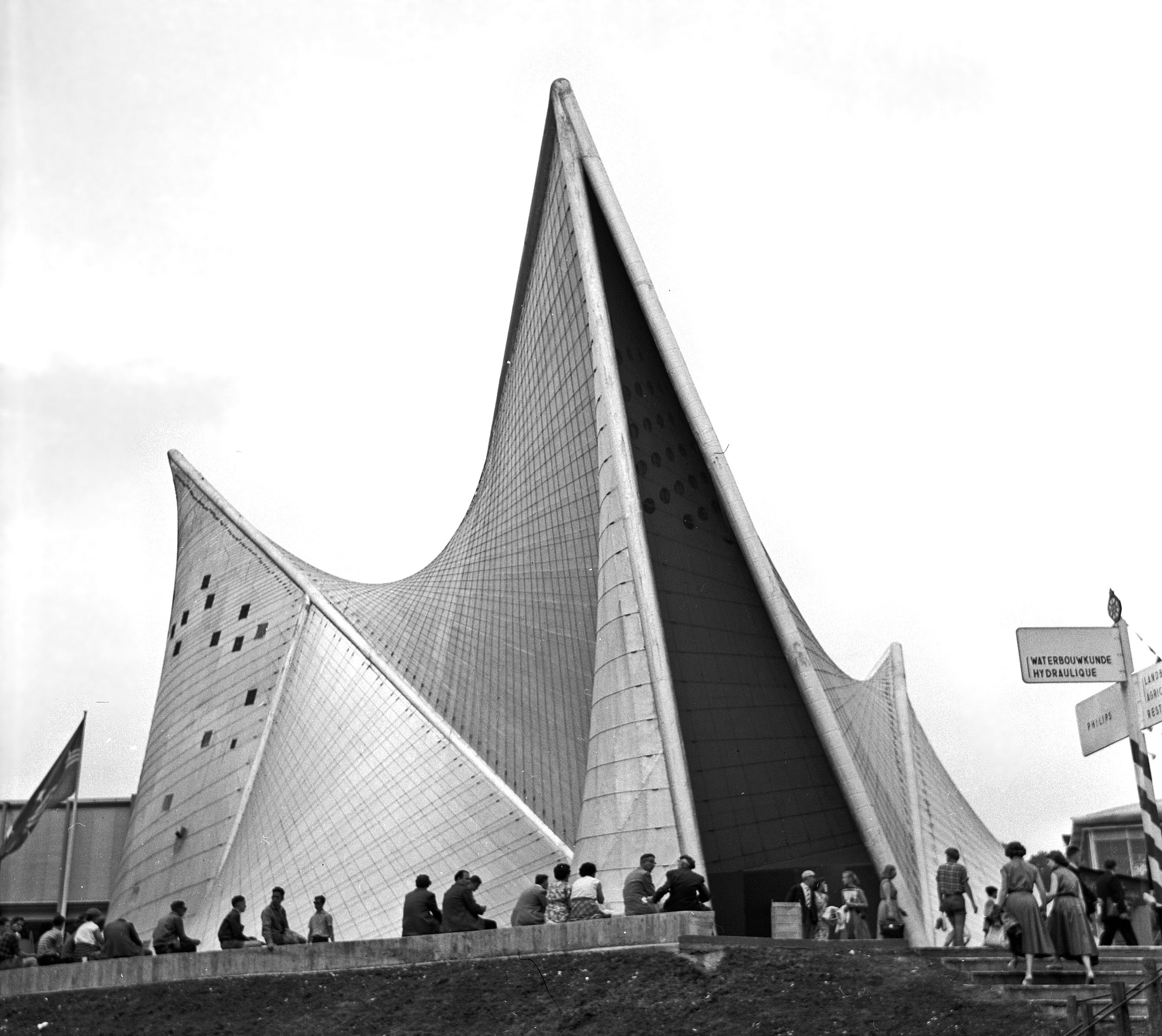
Expo 58
Expo 58, also known as the 1958 Brussels World's Fair (; ), was a world's fair held on the Heysel/Heizel Plateau in Brussels, Belgium, from 17 April to 19 October 1958. It was the first major world's fair registered under the Bureau International des Expositions (BIE) after World War II and the fifth in Brussels overall. Expo 58 left a deep impression on Belgium. It was also the pretext for major upheavals and works in Brussels, whose boulevards were transformed into urban motorways. The Atomium, built for the occasion, has become one of the city's must-see landmarks. Background Expo 58 was the eleventh world's fair hosted by Belgium, and the fifth in Brussels, following the fairs in 1888, 1897, 1910 and 1935. In 1953, Belgium won the bid for the next world's fair, winning out over other European capitals such as Paris and London. Nearly 15,000 workers spent three years building the site on the Heysel/Heizel Plateau, north-west of central Brussels. Many of the building ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poème électronique
''Poème électronique'' (English Translation: "Electronic Poem") is an 8-minute piece of electronic music by composer A composer is a person who writes music. The term is especially used to indicate composers of Western classical music, or those who are composers by occupation. Many composers are, or were, also skilled performers of music. Etymology and def ... Edgard Varèse, written for the Philips Pavilion at the 1958 Brussels World's Fair. The Philips corporation commissioned Le Corbusier to design the pavilion, which was intended as a showcase of their engineering progress. Le Corbusier came up with the title ''Poème électronique'', saying he wanted to create a "poem in a bottle". Varèse composed the piece with the intention of creating a liberation between sounds and as a result uses noises not usually considered "musical" throughout the piece. Original performance The pavilion was shaped like a stomach, with a narrow entrance and exit on either side of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edgard Varèse
Edgard Victor Achille Charles Varèse (; also spelled Edgar; December 22, 1883 – November 6, 1965) was a French and American composer who spent the greater part of his career in the United States. Varèse's music emphasizes timbre and rhythm; he coined the term "organized sound" in reference to his own musical aesthetic. Varèse's conception of music reflected his vision of "sound as living matter" and of "musical space as open rather than bounded". He conceived the elements of his music in terms of "Sound mass, sound-masses", likening their organization to the natural phenomenon of crystallization. Varèse thought that "to stubbornly conditioned ears, anything new in music has always been called Noise in music, noise", and he posed the question, "what is music but organized noises?" Although his complete surviving works only last about three hours, he has been recognized as an influence by several major composers of the late 20th century. Varèse saw potential in using electron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Daily Telegraph
''The Daily Telegraph'', known online and elsewhere as ''The Telegraph'', is a British daily broadsheet conservative newspaper published in London by Telegraph Media Group and distributed in the United Kingdom and internationally. It was founded by Arthur B. Sleigh in 1855 as ''The Daily Telegraph and Courier''. ''The Telegraph'' is considered a newspaper of record in the UK. The paper's motto, "Was, is, and will be", was included in its emblem which was used for over a century starting in 1858. In 2013, ''The Daily Telegraph'' and ''The Sunday Telegraph'', which started in 1961, were merged, although the latter retains its own editor. It is politically conservative and supports the Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party. It was moderately Liberalism, liberal politically before the late 1870s.Dictionary of Nineteenth Century Journalismp 159 ''The Telegraph'' has had a number of news scoops, including the outbreak of World War II by rookie reporter Clare Hollingworth, desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoffrey Norris
Geoffrey Norris (born 19 September 1947) is an English musicologist and music critic. His scholarship focuses on Russian composers; in particular, Norris is a leading scholar on the life and music of Sergei Rachmaninoff, about whom he has written in numerous articles and a 1976 book-length study. He was chief classical music critic of ''The Daily Telegraph'' from 1995 to 2009. Life and career Geoffrey Norris was born in London, England in 19 September 1947. An enthusiast for Russian culture since his youth, Norris attended the University of Durham where his undergraduate dissertation was on The Five, a leading group of 19th-century Russian composers. Original froMiamiPianoFest He continued his studies of Russian music at the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Of The Spheres (Langgaard)
''Music of the Spheres'' (in Danish: ), BVN 128, is a multi- movement composition for soprano, mixed choir, orchestra (including a second, smaller "orchestra at a distance"), and organ written from 1916 to 1918 by the Danish composer Rued Langgaard. The piece was inspired by a line from a Danish poem translated as, "The stars seem to twinkle kindly at us, yet the writing of the stars is cold and merciless." Analysis The work incorporates innovations that were ahead of their time, including some of the earliest examples of string piano (playing directly on the strings of the piano). The piece's extensive use of slow-moving string clusters prompted the composer György Ligeti to proclaim himself a "Langgaard-epigone" when presented with the score in the late 1960s. According to the music researcher Eric Christensen – in an analysis of works utilizing the "spatial dimension" as a fundamental concept – the space of ''Music of the Spheres'' is limited at the upper level ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rued Langgaard
Rued Langgaard (; born Rud Immanuel Langgaard; 28 July 1893 – 10 July 1952) was a late-Romantic Danish composer and organist. His then-unconventional music was at odds with that of his Danish contemporaries but was recognized 16 years after his death. Life Born in Copenhagen, Rued Langgaard was the only son of composer and Royal Chamber musician Siegfried Langgaard and Emma Langgaard (née Foss), both of whom were pianists. At the age of five Rued began taking piano lessons with his mother, and later with his father and a private teacher. His talent emerged quickly, and at seven he was able to play Robert Schumann, Schumann's ''Davidsbündlertänze'' and Frédéric Chopin, Chopin's mazurkas. By then he had begun to compose short pieces for the piano and play the organ. At 10 he began to study the organ under Gustav Helsted, organist at the Jesus Church, Valby, Jesuskirken in Valby, and the violin under Chr. Petersen, formerly of the Royal Orchestra. At the age of 11 he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jan Swafford
Jan Swafford (born September 10, 1946) is an American author and composer. He earned his Bachelor of Arts ''magna cum laude'' from Harvard College and his M.M.A. and D.M.A. from the Yale School of Music. His teachers included Earl Kim at Harvard, Jacob Druckman at Yale, and Betsy Jolas at Tanglewood. The Scott Chamber Players (album notes), He has written respected musical biographies of , |