|
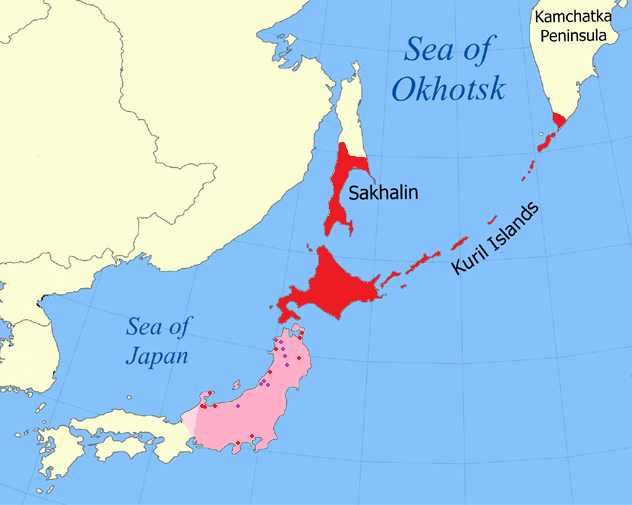
Sakhalin
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, r=Sakhalín, p=səxɐˈlʲin; ja, 樺太 ''Karafuto''; zh, c=, p=Kùyèdǎo, s=库页岛, t=庫頁島; Manchu: ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ, ''Sahaliyan''; Orok: Бугата на̄, ''Bugata nā''; Nivkh: Yh-mif) is the largest island of Russia. It is north of the Japanese archipelago, and is administered as part of the Sakhalin Oblast. Sakhalin is situated in the Pacific Ocean, sandwiched between the Sea of Okhotsk to the east and the Sea of Japan to the west. It is located just off Khabarovsk Krai, and is north of Hokkaido in Japan. The island has a population of roughly 500,000, the majority of which are Russians. The indigenous peoples of the island are the Ainu, Oroks, and Nivkhs, who are now present in very small numbers. The Island's name is derived from the Manchu word ''Sahaliyan'' (ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ). Sakhalin was once part of China during the Qing dynasty, although Chinese control was relaxed at times. Sakhalin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Lopatin (Sakhalin)
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, r=Sakhalín, p=səxɐˈlʲin; ja, 樺太 ''Karafuto''; zh, c=, p=Kùyèdǎo, s=库页岛, t=庫頁島; Manchu: ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ, ''Sahaliyan''; Orok: Бугата на̄, ''Bugata nā''; Nivkh: Yh-mif) is the largest island of Russia. It is north of the Japanese archipelago, and is administered as part of the Sakhalin Oblast. Sakhalin is situated in the Pacific Ocean, sandwiched between the Sea of Okhotsk to the east and the Sea of Japan to the west. It is located just off Khabarovsk Krai, and is north of Hokkaido in Japan. The island has a population of roughly 500,000, the majority of which are Russians. The indigenous peoples of the island are the Ainu, Oroks, and Nivkhs, who are now present in very small numbers. The Island's name is derived from the Manchu word ''Sahaliyan'' (ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ). Sakhalin was once part of China during the Qing dynasty, although Chinese control was relaxed at times. Sakhalin was l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakhalin Oblast
Sakhalin Oblast ( rus, Сахали́нская о́бласть, r=Sakhalínskaya óblast', p=səxɐˈlʲinskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast) comprising the island of Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands in the Russian Far East. The oblast has an area of . Its administrative center and largest city is Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk. As of the 2010 Census, the oblast has a population of roughly 500,000. The vast majority of the oblast's residents are ethnic Russians, with a small minority of Koreans. Sakhalin Oblast is rich in natural gas and oil, and is Russia's fourth wealthiest federal subject and wealthiest oblast. It borders by sea Khabarovsk Krai to the west and Kamchatka Krai to the north, along with Hokkaido, Japan to the south. Demographics Population: ;Vital statistics for 2012 *Births: 6,316 (12.8 per 1,000) *Deaths: 6,841 (13.8 per 1,000) Total fertility rate: Ethnic groups: 409,786 ethnic Russians are the largest group, followed by 24,993 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk
Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk ( rus, Ю́жно-Сахали́нск, a=Ru-Южно-Сахалинск.ogg, p=ˈjuʐnə səxɐˈlʲinsk, literally "South Sakhalin City") is a city on Sakhalin island, and the administrative center of Sakhalin Oblast, Russia. It is located in the Far East part of Russia, situated north of Japan. Gas and oil extraction as well as processing are amongst the main industries on the island. It was called Vladimirovka () from 1882 to 1905, then during its period of Imperial Japanese control from 1905 to 1946. As of the 2010 Census, its population was 181,728. History Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk began as a small Russian settlement called Vladimirovka, founded by convicts in 1882. The Treaty of Portsmouth in 1905, which brought an end to the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905, awarded the southern half of the Sakhalin Island to Japan. Vladimirovka was renamed Toyohara (meaning "bountiful plain"), and was the prefect capital of the Japanese Karafuto Prefecture. During t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nivkh People
The Nivkh, or Gilyak (also Nivkhs or Nivkhi, or Gilyaks; ethnonym: Нивхгу, ''Nʼivxgu'' (Amur) or Ниғвңгун, ''Nʼiɣvŋgun'' (E. Sakhalin) "the people"), are an indigenous ethnic group inhabiting the northern half of Sakhalin Island and the lower Amur River and coast on the adjacent Russian mainland and historically possibly parts of Manchuria. Nivkh were traditionally fishermen, hunters, and dog breeders. They were semi-nomadic, living near the coasts in the summer and wintering inland along streams and rivers to catch salmon. The land the Nivkh inhabit is characterized as taiga forest with cold snow-laden winters and mild summers with sparse tree cover. The Nivkh are believed to be the original inhabitants of the region, and to derive from a proposed Neolithic people that migrated from the Transbaikal region during the Late Pleistocene.Fitzhugh, William, and Durbreui pp.39, 40 The Nivkh had long maintained trade and cultural relations with neighboring China a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ainu People
The Ainu are the indigenous people of the lands surrounding the Sea of Okhotsk, including Hokkaido Island, Northeast Honshu Island, Sakhalin Island, the Kuril Islands, the Kamchatka Peninsula and Khabarovsk Krai, before the arrival of the Yamato Japanese and Russians. These regions are referred to as in historical Japanese texts. Official estimates place the total Ainu population of Japan at 25,000. Unofficial estimates place the total population at 200,000 or higher, as the near-total assimilation of the Ainu into Japanese society has resulted in many individuals of Ainu descent having no knowledge of their ancestry. As of 2000, the number of "pure" Ainu was estimated at about 300 people. In 1966, there were about 300 native Ainu speakers; in 2008, however, there were about 100. Names This people's most widely known ethnonym, "Ainu" ( ain, ; ja, アイヌ; russian: Айны) means "human" in the Ainu language, particularly as opposed to , divine beings. Ainu also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nivkh Languages
Nivkh (; occasionally also Nivkhic; self-designation: Нивхгу диф, ''Nivxgu dif'', ), or Gilyak (), or Amuric, is a small language family, often portrayed as a language isolate, of two or three mutually unintelligible languages spoken by the Nivkh people in Outer Manchuria, in the basin of the Amgun (a tributary of the Amur), along the lower reaches of the Amur itself, and on the northern half of Sakhalin. "Gilyak" is the Russian rendering of terms derived from the Tungusic "Gileke" and Manchu-Chinese "Gilemi" (Gilimi, Gilyami) for culturally similar peoples of the Amur River region, and was applied principally to the Nivkh in Western literature. The population of ethnic Nivkhs has been reasonably stable over the past century, with 4,549 Nivkhs counted in 1897 and 4,673 in 1989. However, the number of native speakers of the Nivkh language among these dropped from 100% to 23.3% in the same period, so by the 1989 census there were only 1,079 first-language speakers left. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
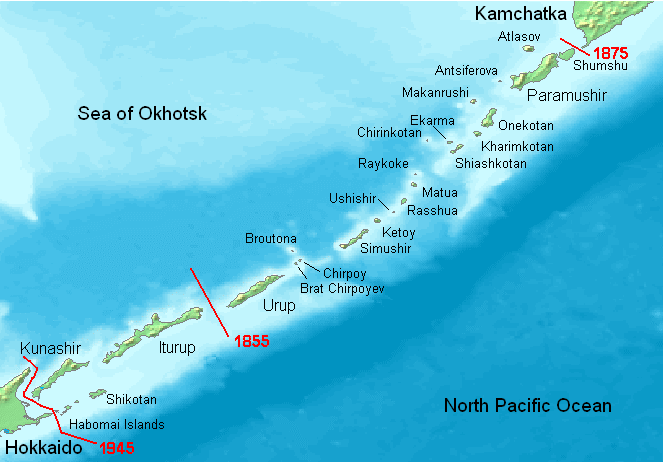
Kuril Islands
The Kuril Islands or Kurile Islands (; rus, Кури́льские острова́, r=Kuril'skiye ostrova, p=kʊˈrʲilʲskʲɪjə ɐstrɐˈva; Japanese: or ) are a volcanic archipelago currently administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast in the Russian Far East. It stretches approximately northeast from Hokkaido in Japan to Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the north Pacific Ocean. There are 56 islands and many minor rocks. The Kuril Islands consist of the Greater Kuril Chain and the Lesser Kuril Chain. They cover an area of around , with a population of roughly 20,000. The islands have been under Russian administration since their 1945 invasion as the Soviet Union towards the end of World War II. Japan claims the four southernmost islands, including two of the three largest ( Iturup and Kunashir), as part of its territory, as well as Shikotan and the Habomai islets, which has led to the ongoing Kuril Islands dispute. The disputed islands ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuril Islands Dispute
The Kuril Islands dispute, known as the Northern Territories dispute in Japan, is a territorial dispute between Japan and Russia over the ownership of the four southernmost Kuril Islands. The Kuril Islands are a chain of islands that stretch between the Japanese island of Hokkaido at their southern end and the Russian Kamchatka Peninsula at their northern end. The islands separate the Sea of Okhotsk from the Pacific Ocean. The four disputed islands, like other islands in the Kuril chain that are not in dispute, were unilaterally annexed by the Soviet Union following the Kuril Islands landing operation at the end of World War II. The disputed islands are under Russian administration as the South Kuril District and part of Kuril District of the Sakhalin Oblast (Сахалинская область, ''Sakhalinskaya oblast''). They are claimed by Japan, which refers to them as its Northern Territories or Southern Chishima, and considers them part of the Nemuro Subprefecture o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oroks
Oroks (''Ороки'' in Russian; self-designation: ''Ulta, Ulcha''), sometimes called Uilta, are a people in the Sakhalin Oblast (mainly the eastern part of the island) in Russia. The Orok language belongs to the Southern group of the Tungusic language family. According to the 2002 Russian census, there were 346 Oroks living in Northern Sakhalin by the Okhotsk Sea and Southern Sakhalin in the district by the city of Poronaysk. According to the 2010 census there were 295 Oroks in Russia. Etymology The name Orok is believed to derive from the exonym ''Oro'' given by a Tungusic group meaning "a domestic reindeer". The Orok self-designation endonym is ''Ul'ta'', probably from the root ''Ula'' (meaning "domestic reindeer" in Orok). Another self-designation is ''Nani''. Occasionally, the Oroks, as well as the Orochs and Udege, are erroneously called Orochons. The Uilta Association in Japan claims that the term Orok has a derogatory connotation. Population and settlement The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orok People
Oroks (''Ороки'' in Russian; self-designation: ''Ulta, Ulcha''), sometimes called Uilta, are a people in the Sakhalin Oblast (mainly the eastern part of the island) in Russia. The Orok language belongs to the Southern group of the Tungusic language family. According to the 2002 Russian census, there were 346 Oroks living in Northern Sakhalin by the Okhotsk Sea and Southern Sakhalin in the district by the city of Poronaysk. According to the 2010 census there were 295 Oroks in Russia. Etymology The name Orok is believed to derive from the exonym ''Oro'' given by a Tungusic group meaning "a domestic reindeer". The Orok self-designation endonym is ''Ul'ta'', probably from the root ''Ula'' (meaning "domestic reindeer" in Orok). Another self-designation is ''Nani''. Occasionally, the Oroks, as well as the Orochs and Udege, are erroneously called Orochons. The Uilta Association in Japan claims that the term Orok has a derogatory connotation. Population and settlement The to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Of Okhotsk
The Sea of Okhotsk ( rus, Охо́тское мо́ре, Ohótskoye móre ; ja, オホーツク海, Ohōtsuku-kai) is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean. It is located between Russia's Kamchatka Peninsula on the east, the Kuril Islands on the southeast, Japan's island of Hokkaido on the south, the island of Sakhalin along the west, and a stretch of eastern Siberian coast along the west and north. The northeast corner is the Shelikhov Gulf. The sea is named after the Okhota river, which in turn named after the Even word () meaning "river". Geography The Sea of Okhotsk covers an area of , with a mean depth of and a maximum depth of . It is connected to the Sea of Japan on either side of Sakhalin: on the west through the Sakhalin Gulf and the Gulf of Tartary; on the south through the La Pérouse Strait. In winter, navigation on the Sea of Okhotsk is impeded by ice floes. Ice floes form due to the large amount of freshwater from the Amur River, lowering the sal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orok Language
Uilta ( oaa, ульта, also called Ulta, Uilta, Ujlta, or Orok) is a Tungusic language spoken in the Poronaysky and Nogliksky Administrative Divisions of Sakhalin Oblast, in the Russian Federation, by the Uilta people. The northern Uilta who live along the river of Tym’ and around the village of Val have reindeer herding as one of their traditional occupations. The southern Uilta live along the Polonay near city of Polonask. The two dialects come from northern and eastern groups, however they have very few differences. Classification Uilta is closely related to Nanai, and is classified within the southern branch of the Tungusic languages. Classifications which recognize an intermediate group between the northern and southern branch of Manchu-Tungus classify Uilta (and Nanai) as Central Tungusic. Within Central Tungusic, Glottolog groups Uilta with Ulch as "Ulchaic", and Ulchaic with Nanai as "Central-Western Tungusic" (also known as the "Nanai group"), while Oro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |