|
Rax-Schneeberg Group
The Rax-Schneeberg Group (german: Rax-Schneeberg-Gruppe) is a mountain range in the Northern Limestone Alps on the Styrian-Lower Austrian border in Austria. Location According to the official classification of the Eastern Alps by the Alpine Club (''Alpenvereinseinteilung der Ostalpen''), the Rax-Schneeberg Group is bounded by the following divisions to neighbouring groups of mountains: * to the north by the Klostertaler Gscheid – Klausgraben – Mamauwiese – Sebastiansbach – Puchberg * to the northeast by the valley of the River Sierning as far as Ternitz * to the south by the line: Ternitz – Schwarza near Gloggnitz – Schottwien – Semmering – Mürzzuschlag – Mürz near Kapellen * to the west by the Altenberg valley – Naßkamm – Naßbach – Schwarza – Voisbach as far as the Klostertaler Gscheid. Summits The highest point in the limestone massif of the Schneeberg is the ''Klosterwappen'' at . Its nearby twin peak is known as the '' Kaiserstein'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mürzzuschlag
Mürzzuschlag is a town in northeastern Styria, Austria, the capital of the former Mürzzuschlag District. It is located on the Mürz river near the Semmering Pass Semmering () is a mountain pass in the Eastern Northern Limestone Alps connecting Lower Austria and Styria, between which it forms a natural border. Location Semmering Pass is located west of Sonnwendstein and Hirschenkogel and east of the P ..., the border with the state of Lower Austria, about southwest of Vienna. The population is 8,684 (1 January 2016). Originally an industrial area, the nearby mountains are today a popular ski resort. History The settlement in the Duchy of Styria was first documented in 1227. The minnesinger Ulrich von Liechtenstein in his 1265 poem ''Frauendienst'' mentioned ''Murzuslage'', which he passed on his journey from Venice to Vienna. In 1360 the House of Habsburg, Habsburg duke Rudolf IV, Duke of Austria, Rudolf IV confirmed the inhabitants' privilege of iron production, competi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prigglitz
Prigglitz is a town in the district of Neunkirchen in the Austrian state of Lower Austria Lower Austria (german: Niederösterreich; Austro-Bavarian: ''Niedaöstareich'', ''Niedaestareich'') is one of the nine states of Austria, located in the northeastern corner of the country. Since 1986, the capital of Lower Austria has been Sankt P .... Population References Cities and towns in Neunkirchen District, Austria {{LowerAustria-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Payerbach
Payerbach is a town in the district of Neunkirchen in the Austrian state of Lower Austria Lower Austria (german: Niederösterreich; Austro-Bavarian: ''Niedaöstareich'', ''Niedaestareich'') is one of the nine states of Austria, located in the northeastern corner of the country. Since 1986, the capital of Lower Austria has been Sankt P .... Population References Payerbach - Kirche.JPG, Parish church St. James the Greater Payerbach-Reichenau-Bahnhof-01.jpg, Train station Payerbach-Reichenau Cities and towns in Neunkirchen District, Austria {{LowerAustria-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cog Railway
A rack railway (also rack-and-pinion railway, cog railway, or cogwheel railway) is a steep grade railway with a toothed rack rail, usually between the running rails. The trains are fitted with one or more cog wheels or pinions that mesh with this rack rail. This allows the trains to operate on steep grades above 10%, which is the maximum for friction-based rail. Most rack railways are mountain railways, although a few are transit railways or tramways built to overcome a steep gradient in an urban environment. The first cog railway was the Middleton Railway between Middleton and Leeds in West Yorkshire, England, United Kingdom, where the first commercially successful steam locomotive, ''Salamanca'', ran in 1812. This used a rack and pinion system designed and patented in 1811 by John Blenkinsop. The first mountain cog railway was the Mount Washington Cog Railway in the U.S. state of New Hampshire, which carried its first fare-paying passengers in 1868. The track was comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
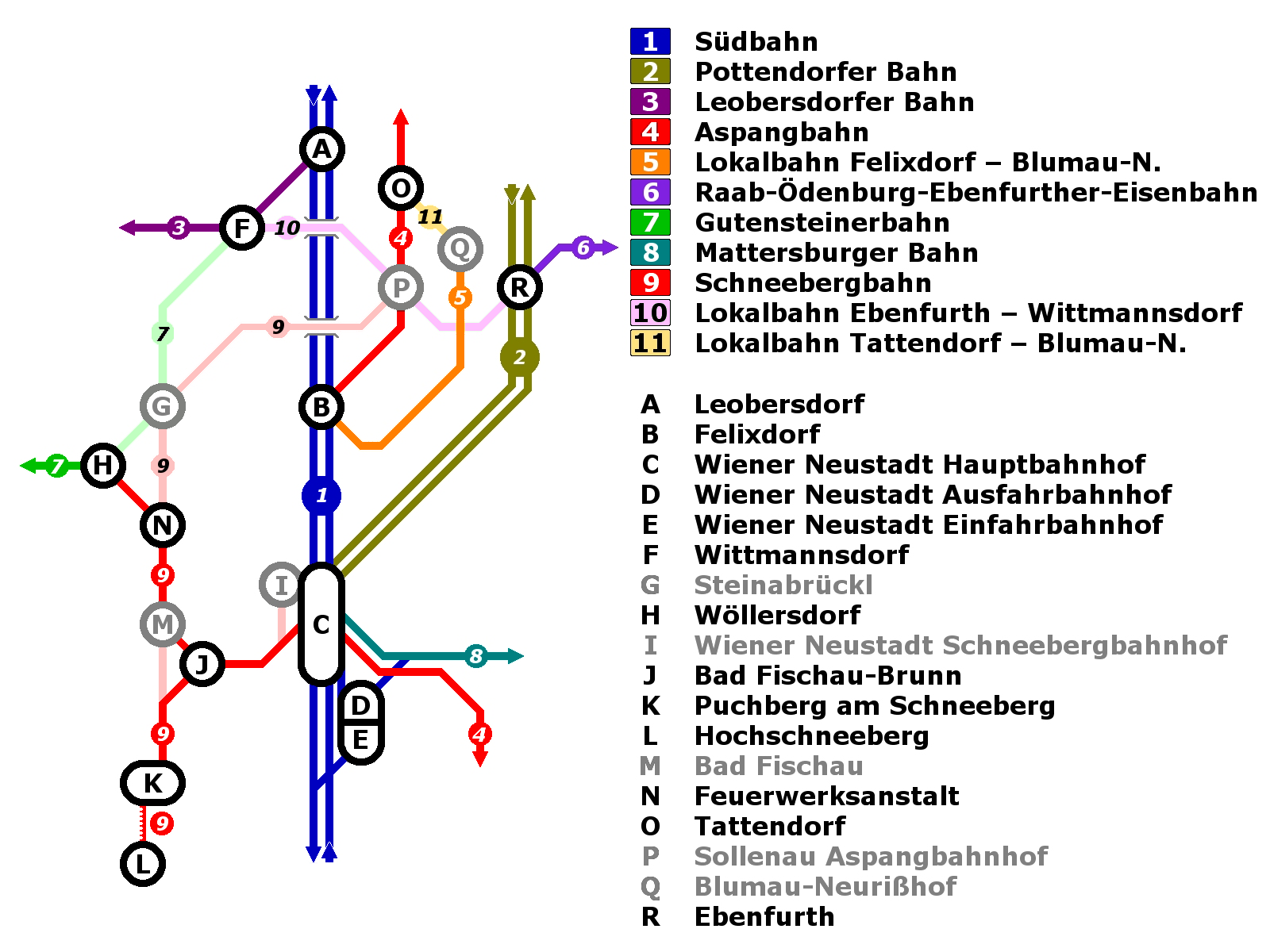
Schneeberg Railway
The Schneeberg Railway (german: Schneebergbahn) is a local railway line in Lower Austria running from Wiener Neustadt to the Hochschneeberg mountain. From Wiener Neustadt to Puchberg am Schneeberg it runs as a standard gauge, adhesion railway (main section) and from Puchberg am Schneeberg to the Hochschneeberg as a narrow-gauge, cog railway (extension). The main section from Wiener Neustadt to Puchberg am Schneeberg had a branch to Wöllersdorf from the outset. The section built later from Sollenau to Feuerwerksanstalt (extension) is now closed and renaturalised. The line's name - the Schneeberg Railway (''Schneebergbahn'') - was not only used in the title of the original operating company, the Schneeberg Railway Company Limited, (''Actiengesellschaft der Schneebergbahn''), but has also been adopted by its latest operator, the Lower Austrian Schneeberg Railway Company (''Niederösterreichsche Schneebergbahn GmbH'' or NÖSBB) founded on 1 January 1997. However, the NÖS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vienna Hausberge
Vienna's Hausberge (german: Wiener Hausberge) are the mountains of Raxalpe, Schneeberg and Hohe Wand in the south of the state of Lower Austria. These mountains may be reached from Vienna in about an hour and are therefore a popular recreation area for the Viennese. Accessibility The Viennese ''Hausberge'' - a ''Hausberg'' is a local mountain associated with a town or city - may be reached by car on the Southern Autobahn (A2). There are also good public transport links between Vienna and the mountains. For the Raxalpe, the visitor can catch a train on the Southern Railway to Payerbach-Reichenau, then a ''Retter'' bus to Hirschwang, Hinternaßwald or the Preiner Gscheid. For the Schneeberg, Southern Railway trains run to Wr. Neustadt, then the visitor can catch a diesel railcar on the Schneebergbahn to Puchberg and continue on the rack railway up the Hochschneeberg or catch a train to Neunkirchen and the ''Retter'' bus to Losenheim. For the Hohe Wand, visitors may also take the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
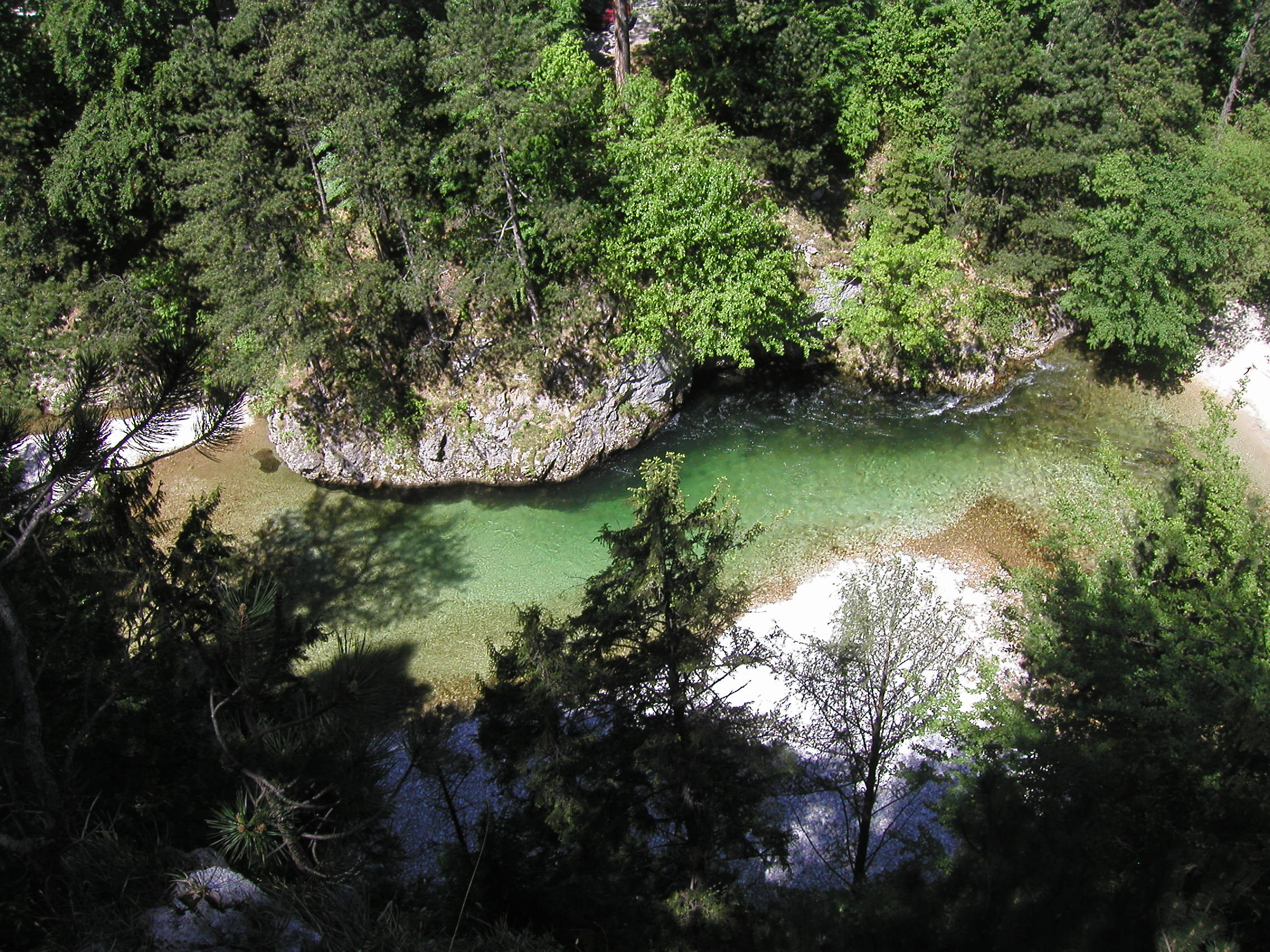
Höllental (Lower Austria)
The Höllental ("Hell Valley") in Lower Austria is a narrow valley between the steep limestone massifs of the Schneeberg and Rax through which the River Schwarza flows. It stretches for a total of 16.5 km between Schwarzau im Gebirge and Hirschwang and, because of its natural beauty, it belongs to the Natura 2000 region of Northeastern Border Alps: Hohe Wand - Schneeberg - Rax (''Nordöstliche Randalpen: Hohe Wand - Schneeberg - Rax''). It biggest side valleys are the Weich valley, the Großes Höllental (which is much smaller however), the Kesselgraben, the Nasswald and Voisbach valleys. A well-developed road, the Höllental Straße (B 27), follows the course of the river and is especially popular with motorcyclists. In the valley and its side valleys are important sources of drinking water supply (The Fuchs Pass Spring, Kaiserbrunn and Wasseralm Spring), whose water is delivered to the Austria's capital city of Vienna over the First Vienna Mountain Spring Pipeline (''I. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Vienna Mountain Spring Pipeline
The First Vienna Mountain Spring Pipeline (I. Wiener Hochquellenwasserleitung) is a major part of Vienna's water supply and was the first source of safe drinking water for that city. The 95 km long line was opened on 24 October 1873, after four years of construction. Today, it delivers 62 million cubic meters of water per year (53% of Vienna's total supply in 2007). The water comes from high springs in the Rax and Schneeberg areas in Southern Lower Austria and Styria. History Beginnings to 1910 The reason for its creation Vienna's water supply originally came from private wells. In the absence of a functioning sewer system, the quality of the groundwater went from bad to worse, triggering disease and epidemics. Reinforced water pipes were built, but these primarily benefitted the wealthy and large institutions. Most of the population had to rely on spouts or fountains attached to wells. The first water pipe that provided greater coverage was built in 1803-1804, brin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heukuppe
The Rax is a mountain range in the Northern Limestone Alps on the border of the Austrian federal provinces of Lower Austria and Styria. Its highest peak is the ''Heukuppe'' (2,007 m). The Rax, together with the nearby Schneeberg, are a traditional mountaineering and mountain walking area, and are called the ''Wiener Hausberge'' (Vienna's local mountains). They are separated by the deep ''Höllental'' ("Hell Valley"). A cable car, the ''Raxseilbahn'', starting at Hirschwang at the north-eastern foot of the mountains and the first in Austria (construction began in 1925), takes visitors to the extensive, high plateau of the Rax at a height of about 1,500 m. This area is a particular favourite with hikers from Lower Austria and Vienna. The steep sides of the plateau offer climbing tours of various difficulty. These ''steige'' (mountain trails) and the ''hütten'', alpine huts offering basic accommodation, were built and are maintained kept by various Austrian Alpine Clubs. They w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massif
In geology, a massif ( or ) is a section of a planet's crust that is demarcated by faults or flexures. In the movement of the crust, a massif tends to retain its internal structure while being displaced as a whole. The term also refers to a group of mountains formed by such a structure. In mountaineering and climbing literature, a massif is frequently used to denote the main mass of an individual mountain. The massif is a smaller structural unit of the crust than a tectonic plate, and is considered the fourth-largest driving force in geomorphology. The word is taken from French (in which the word also means "massive"), where it is used to refer a large mountain mass or compact group of connected mountains forming an independent portion of a range. One of the most notable European examples of a massif is the Massif Central of the Auvergne region of France. The Face on Mars is an example of an extraterrestrial massif. Massifs may also form underwater, as with the Atlanti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twin Peak
Twin Peak may refer to: *Twin Peaks, television series *The Twins, two mountains in Canada known as: **North Twin Peak **South Twin Peak See also * Twin peak * Double summit * Double Peak (other) A double summit, double peak, twin summit, or twin peak refers to a mountain or hill that has two summits, separated by a col or saddle. One well-known double summit is Austria’s highest mountain, the Großglockner, where the main summit of ... * Twin peak sign in obstetric ultrasonography {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |