|
Pre-Indo-Europeans
Pre-Indo-European means "preceding Indo-European languages". Pre-Indo-European may refer to: * Pre-Indo-European languages, several (not necessarily related) ancient languages in prehistoric Europe and South Asia before the arrival of Indo-European languages * Pre-Proto-Indo-European, theoretical reconstruction of language earlier than the Proto-Indo-European language * Old Europe (archaeology), a Neolithic culture in southeastern Europe before the arrival of speakers of Indo-European languages See also *Pre-Germanic (other) *Indo-European (other) *Neolithic Europe, the period when Neolithic technology was present in Europe, roughly 7000 BCE to 1700 BCE *Proto-Indo-European Urheimat hypotheses, proposed homeland of the common ancestor of Indo-European languages * Pre-Greek substrate, unknown language(s) spoken in prehistoric Greece before the Proto-Greek language *Pre-Celtic, prehistory of Central and Western Europe before the expansion of the Celts *Vasconic subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-Indo-European Languages
The Pre-Indo-European languages are any of several ancient languages, not necessarily related to one another, that existed in Prehistoric Europe and Southern Asia before the arrival of speakers of Indo-European languages. The oldest Indo-European language texts date from the 19th century BC in Kültepe (modern Turkey), and while estimates vary widely, the spoken Indo-European languages are believed to have developed at the latest by the 3rd millennium BC (see Proto-Indo-European Urheimat hypotheses). Thus, the Pre-Indo-European languages must have developed earlier than or, in some cases, alongside the Indo-European languages that ultimately displaced them. A handful of the pre-Indo-European languages still survive; in Europe, Basque retains a localised strength, with fewer than a million native speakers, but the Dravidian languages remain very widespread in the Indian subcontinent, with over 200 million native speakers (the four major languages being Telugu, Tamil, Kannada and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Europe (archaeology)
Old Europe is a term coined by the Lithuanian archaeologist Marija Gimbutas to describe what she perceived as a relatively homogeneous pre-Indo-European Neolithic and Copper Age cultural horizon or civilisation in Southeastern Europe and part of Central-Eastern Europe, centred in the Danube River valley. Old Europe is also referred to in some literature as the Danube civilisation. The term 'Danubian culture' was earlier coined by the archaeologist Vere Gordon Childe to describe early farming cultures (e.g. the Linear Pottery culture) which spread westwards and northwards from the Danube valley into Central and Eastern Europe. Old Europe Old Europe, or Neolithic Europe, refers to the time between the Mesolithic and Bronze Age periods in Europe, roughly from 7000 BCE (the approximate time of the first farming societies in Greece) to c. 2000 BCE (the beginning of the Bronze Age in Scandinavia). The duration of the Neolithic varies from place to place: in Southeastern Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic Europe
The European Neolithic is the period when Neolithic (New Stone Age) technology was present in Europe, roughly between 7000 BCE (the approximate time of the first farming societies in Greece) and c.2000–1700 BCE (the beginning of the Bronze Age in Scandinavia). The Neolithic overlaps the Mesolithic and Bronze Age periods in Europe as cultural changes moved from the southeast to northwest at about 1 km/year – this is called the Neolithic Expansion. The duration of the Neolithic varies from place to place, its end marked by the introduction of bronze tools: in southeast Europe it is approximately 4,000 years (i.e. 7000 BCE–3000 BCE) while in parts of Northwest Europe it is just under 3,000 years (c. 4500 BCE–1700 BCE). In parts of Europe, notably the Balkans, the period after c. 5000 BC is known as the Chalcolithic (Copper Age), due to the invention of copper smelting and the prevalence of copper tools, weapons and other artefacts. The spread of the Neolithic from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-Greek Substrate
The Pre-Greek substrate (or Pre-Greek substratum) consists of the unknown pre-Indo-European language(s) spoken in prehistoric Greece before the coming of the Proto-Greek language in the Greek peninsula during the Bronze Age. It is possible that Greek acquired approximately one thousand words and proper names from such a language or group of languages, because some of its vocabulary cannot be satisfactorily explained as deriving from Proto-Greek and a Proto-Indo-European reconstruction is almost certainly impossible for such terms. Introduction Linguistic situation Based upon toponymic and lexical evidence, it is generally assumed that one or several languages were once spoken in both the Greek peninsula and western Asia Minor before Mycenaean Greek and the attested Anatolian languages ( Hittite and Luwian) became predominant in the region. Various explanations for this phenomenon have been given by scholars. One substrate language, whose influence is observable on Ancient Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
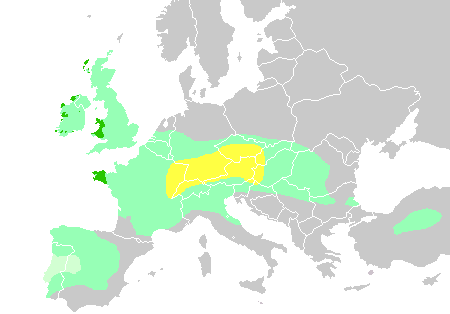
Pre-Celtic
The pre-Celtic period in the prehistory of Central Europe and Western Europe occurred before the expansion of the Celts or their culture in Iron Age Europe and Anatolia (9th to 6th centuries BC), but after the emergence of the Proto-Celtic language and cultures. The area involved is that of the maximum extent of the Celtic languages in about the mid 1st century BC. The extent to which Celtic language, culture and genetics coincided and interacted during this period remains very uncertain and controversial. Languages Proto-Celtic is mainly dated to approximately 800 BC, coincident with the Hallstatt culture, while the earliest possible divergence of pre-proto-Celtic dialects from Proto-Indo-European is mainly dated to between 3000 BC and 2000 BC. In continental Europe, pre-Celtic languages of the European Bronze Age may be taken to comprise two distinct groups. * Non-Indo-European languages (i.e. pre-Indo-European languages); these include Basque, Rhaetic, Etrus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-European Languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch, and Spanish, have expanded through colonialism in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divided into several branches or sub-families, of which there are eight groups with languages still alive today: Albanian, Armenian, Balto-Slavic, Celtic, Germanic, Hellenic, Indo-Iranian, and Italic; and another nine subdivisions that are now extinct. Today, the individual Indo-European languages with the most native speakers are English, Hindi–Urdu, Spanish, Bengali, French, Russian, Portuguese, German, and Punjabi, each with over 100 million native speakers; many others are small and in danger of extinction. In total, 46% of the world's population (3.2 billion people) speaks an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo-European exists. Far more work has gone into reconstructing PIE than any other proto-language, and it is the best understood of all proto-languages of its age. The majority of linguistic work during the 19th century was devoted to the reconstruction of PIE or its daughter languages, and many of the modern techniques of linguistic reconstruction (such as the comparative method) were developed as a result. PIE is hypothesized to have been spoken as a single language from 4500 BC to 2500 BC during the Late Neolithic to Early Bronze Age, though estimates vary by more than a thousand years. According to the prevailing Kurgan hypothesis, the original homeland of the Proto-Indo-Europeans may have been in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-Germanic (other)
{{disambig ...
Pre-Germanic may refer to *the predecessor of Common Germanic, see Germanic parent language *a language spoken before the arrival of Germanic speakers during the Migration period, see **Germanic substrate hypothesis **Pre-Indo-European (other) Pre-Indo-European means "preceding Indo-European languages". Pre-Indo-European may refer to: * Pre-Indo-European languages, several (not necessarily related) ancient languages in prehistoric Europe and South Asia before the arrival of Indo-Europea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-European (other)
Indo-European is a major language family of Europe, the Middle East and South Asia. Indo-European may also refer to: * Proto-Indo-European language, the reconstructed common ancestor of all Indo-European languages * Proto-Indo-Europeans (or “Indo-Europeans”), a hypothetical prehistoric ethnolinguistic group of Eurasia who spoke Proto-Indo-European * Indo people ( nl, Indo-Europeaan, links=no), people of Dutch East Indies and European descent See also * Indo-European migrations * Indo-European studies, an academic field involving linguistics, anthropology, history, archaeology * Indo-European vocabulary, a table of the most fundamental Proto-Indo-European language words and roots * Pre-Indo-European (other) * Proto-Indo-European religion, the hypothetical religion of the Proto-Indo-Europeans * Proto-Indo-European society Proto-Indo-European society is the reconstructed culture of Proto-Indo-Europeans, the ancient speakers of the Proto-Indo-European language, anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Indo-European Urheimat Hypotheses
The Proto-Indo-European homeland (or Indo-European homeland) was the prehistoric linguistic homeland of the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE). From this region, its speakers migrated east and west, and went on to form the proto-communities of the different branches of the Indo-European language family. The most widely accepted proposal about the location of the Proto-Indo-European homeland is the steppe hypothesis, which puts the archaic, early and late PIE homeland in the Pontic–Caspian steppe around 4,000 BC. The leading competitor is the Anatolian hypothesis, which puts it in Anatolia around 8,000 BC. A notable third possibility, which has gained renewed attraction due to recent aDNA research, is the Armenian hypothesis which situates the homeland for archaic PIE south of the Caucasus. Several other explanations have been proposed, including the outdated but historically prominent North European hypothesis, the Neolithic creolisation hypothesis, the Paleolithic continuit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |