|
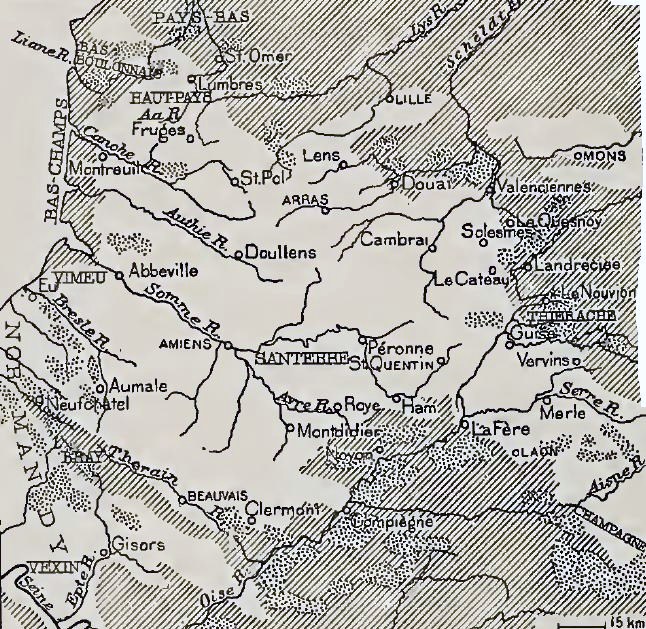
Ovillers-la-Boisselle
Ovillers-la-Boisselle is a commune in the Somme department in Hauts-de-France in northern France. Geography The commune of Ovillers-la-Boisselle is situated northeast of Amiens and extends to the north and south of the D 929 Albert–Bapaume road. The constituent village of Ovillers-la-Boisselle (commonly shortened to "Ovillers") lies on the north of the D 929 road, north-east of Aveluy and south-west of Pozières. The constituent village of La Boisselle, which had in 1914, lies across the D 929, to the south-west of Ovillers at the junction of the D 104 to Contalmaison. Population History The village of La Boisselle is a settlement dating back to pre-Roman times,''The La Boisselle Project'': project details access date: 4 November 2016 and the D 929 Albert–Bapaume road follows the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovillers-la-Boisselle In World War I
In World War I, the small commune of Ovillers-la-Boisselle, located some north-east of Amiens in the Somme department in Hauts-de-France in northern France, was the site of intense and sustained fighting between German and Allied forces. Between 1914 and 1916, the Western Front ran through the commune, and the villages were completely destroyed. After the Armistice of 11 November 1918, the former inhabitants returned and gradually rebuilt most of the infrastructure as it had been before the war. The commune extends to the north and south of the D 929 Albert–Bapaume road, a former Roman road. The constituent village of Ovillers-la-Boisselle (commonly shortened to "Ovillers") lies to the north of the road. The constituent village of La Boisselle, which had in 1914, lies to the south-west of Ovillers at the junction of the D 929 and the D 104 to Contalmaison. To avoid confusion, the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) in its documents referred to Ovillers-la-Boisselle north of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
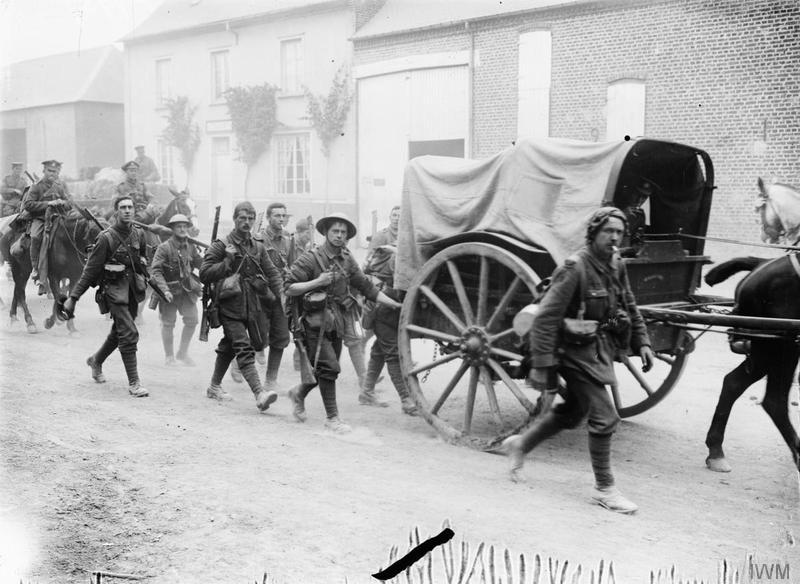
Capture Of La Boisselle
The Capture of La Boisselle (1–6 July 1916) was a tactical incident during the Battle of Albert, the name given by the British to the first two weeks of the Battle of the Somme. The village of La Boisselle forms part of the small commune of Ovillers-la-Boisselle about north-east of Amiens in the Somme department in Picardie in northern France. To the north-east of La Boisselle lies Ovillers; by 1916, the village was called Ovillers by the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) to avoid confusion with La Boisselle, south of the road. On 1 July 1916, the first day on the Somme, La Boisselle was attacked by the 34th Division, III Corps but the bombardment had not damaged the German deep-mined dug-outs () and a German listening post overheard a British telephone conversation the day before, which gave away the attack. The III Corps divisions suffered more than and failed to capture La Boisselle or Ovillers, gaining only small footholds near the boundary with XV Corps to the south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capture Of Ovillers
The Capture of Ovillers (1–16 July 1916) was a British local operation during the Battle of Albert, the name given by the British to the first two weeks of the Battle of the Somme. The village of Ovillers-la-Boisselle (commonly shortened to Ovillers) forms part of the small commune of Ovillers-la-Boisselle, about north-east of Amiens in the Somme department in Picardie in northern France. By 1916, the village was called Ovillers by the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) to avoid confusion with La Boisselle south of the road. To the south-west of Ovillers lies La Boisselle. On 1 July 1916, the first day on the Somme, Ovillers was attacked by the 8th Division, part of the III Corps. The attack was a disaster and the division lost the defending Infantry Regiment 180 had and Reserve Infantry Regiment 110 The 8th Division was withdrawn and replaced by the 12th (Eastern) Division, which resumed the attack on Ovillers on 3 July and lost by the time it was relieved. Attacks by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sausage Valley
The Capture of La Boisselle (1–6 July 1916) was a tactical incident during the Battle of Albert, the name given by the British to the first two weeks of the Battle of the Somme. The village of La Boisselle forms part of the small commune of Ovillers-la-Boisselle about north-east of Amiens in the Somme department in Picardie in northern France. To the north-east of La Boisselle lies Ovillers; by 1916, the village was called Ovillers by the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) to avoid confusion with La Boisselle, south of the road. On 1 July 1916, the first day on the Somme, La Boisselle was attacked by the 34th Division, III Corps but the bombardment had not damaged the German deep-mined dug-outs () and a German listening post overheard a British telephone conversation the day before, which gave away the attack. The III Corps divisions suffered more than and failed to capture La Boisselle or Ovillers, gaining only small footholds near the boundary with XV Corps to the sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L'îlot De La Boisselle
L'îlot de La Boisselle (french: ilôt meaning "small island") is a small, historic site in the commune of Ovillers-la-Boisselle in the Somme department in Picardie in northern France. was heavily fought over during the First World War, when it was known as Granathof (German: "shell farm") to the Germans and as Glory Hole to British soldiers. The site is private property and opens to the public by appointment with Claudie Llewellyn (who lives in Montauban-de-Picardie: 06 11 30 76 35). Geography Located in the small village of La Boisselle, the site lies south of the D 929 Albert–Bapaume road and occupies a small area in the southeast of the village see photographs. Once the location of a small number of houses, is now covered with grass and shrubs and separated from the built over areas of the village by the ''rue Georges Cuvillier'' (D 104) leading to Contalmaison in the north and the ''route de Bécourt'' leading to Bécordel-Bécourt in the east. History La Boissell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of The Somme Department
The following is a list of the 772 communes of the Somme department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):BANATIC Périmètre des EPCI à fiscalité propre. Accessed 3 July 2020. * * * |
William Orpen
Major Sir William Newenham Montague Orpen, (27 November 1878 – 29 September 1931) was an Irish artist who worked mainly in London. Orpen was a fine draughtsman and a popular, commercially successful painter of portraits for the well-to-do in Edwardian society, though many of his most striking paintings are self-portraits. During World War I, he was the most prolific of the official war artists sent by Britain to the Western Front. There he produced drawings and paintings of ordinary soldiers, dead men, and German prisoners of war, as well as portraits of generals and politicians. Most of these works, 138 in all, he donated to the British government; they are now in the collection of the Imperial War Museum. His connections to the senior ranks of the British Army allowed him to stay in France longer than any of the other official war artists, and although he was made a Knight Commander of the Order of the British Empire in the 1918 Birthday Honours, and also elected a membe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lochnagar Crater
The Lochnagar mine south of the village of La Boisselle in the Somme was an underground explosive charge, secretly planted by the British during the First World War, to be ready for 1 July 1916, the first day on the Somme. The mine was dug by the Tunnelling Companies of the Royal Engineers under a German field fortification known as (Swabian Height). The British named the mine after Lochnagar Street, the trench from which the gallery was driven. The charge at Lochnagar was one of 19 mines that were dug under the German lines on the British section of the Somme front, to assist the infantry advance at the start of the battle. The mine was sprung at on 1 July 1916 and left a crater deep and wide, which was captured and held by British troops. The attack on either flank was defeated by German small arms and artillery fire, except on the extreme right flank and just south of La Boisselle, north of the Lochnagar Crater. The crater has been preserved as a memorial and a religio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Barton (historian)
Peter Arthur Barton (born 28 March 1955) is a British military historian, author and filmmaker specialising in trench warfare during World War I. He has published extensively on military mining and aspects of battlefield archaeology on the Western Front, and led archaeological excavations that have been featured in several ''Time Team'' episodes. His work has led to the rediscovery of many tunnels, wartime panoramas and mass graves of soldiers. Career In 2005, Barton published ''Beneath Flanders Fields'', a history of the British tunnellers fighting in the Ypres Salient from 1914 to 1918, for which he collaborated with Peter Doyle and Johan Vandewalle. Between 2006 and 2011, Barton rediscovered and published several panoramic perspectives of the Western Front which allow readers to view the battlefields from the Belgian coast to the British lines at the Somme. With his colleagues Simon Jones and Jeremy Banning, he has been involved in several large-scale archaeological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Somme (1916)
The Battle of the Somme (French: Bataille de la Somme), also known as the Somme offensive, was a battle of the First World War fought by the armies of the British Empire and French Third Republic against the German Empire. It took place between 1 July and 18 November 1916 on both sides of the upper reaches of the Somme, a river in France. The battle was intended to hasten a victory for the Allies. More than three million men fought in the battle of whom one million were wounded or killed, making it one of the deadliest battles in human history. The French and British had committed themselves to an offensive on the Somme during the Chantilly Conference in December 1915. The Allies agreed upon a strategy of combined offensives against the Central Powers in 1916 by the French, Russian, British and Italian armies, with the Somme offensive as the Franco-British contribution. Initial plans called for the French army to undertake the main part of the Somme offensive, supported on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Somme
The Battle of the Somme ( French: Bataille de la Somme), also known as the Somme offensive, was a battle of the First World War fought by the armies of the British Empire and French Third Republic against the German Empire. It took place between 1 July and 18 November 1916 on both sides of the upper reaches of the Somme, a river in France. The battle was intended to hasten a victory for the Allies. More than three million men fought in the battle of whom one million were wounded or killed, making it one of the deadliest battles in human history. The French and British had committed themselves to an offensive on the Somme during the Chantilly Conference in December 1915. The Allies agreed upon a strategy of combined offensives against the Central Powers in 1916 by the French, Russian, British and Italian armies, with the Somme offensive as the Franco-British contribution. Initial plans called for the French army to undertake the main part of the Somme offensive, supported on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mines On The First Day Of The Somme
Mine, mines, miners or mining may refer to: Extraction or digging *Miner, a person engaged in mining or digging *Mining, extraction of mineral resources from the ground through a mine Grammar *Mine, a first-person English possessive pronoun Military * Anti-tank mine, a land mine made for use against armored vehicles * Antipersonnel mine, a land mine targeting people walking around, either with explosives or poison gas * Bangalore mine, colloquial name for the Bangalore torpedo, a man-portable explosive device for clearing a path through wire obstacles and land mines * Cluster bomb, an aerial bomb which releases many small submunitions, which often act as mines * Land mine, explosive mines placed under or on the ground * Mining (military), digging under a fortified military position to penetrate its defenses * Naval mine, or sea mine, a mine at sea, either floating or on the sea bed, often dropped via parachute from aircraft, or otherwise lain by surface ships or submarines * Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |