|
Osteostraci
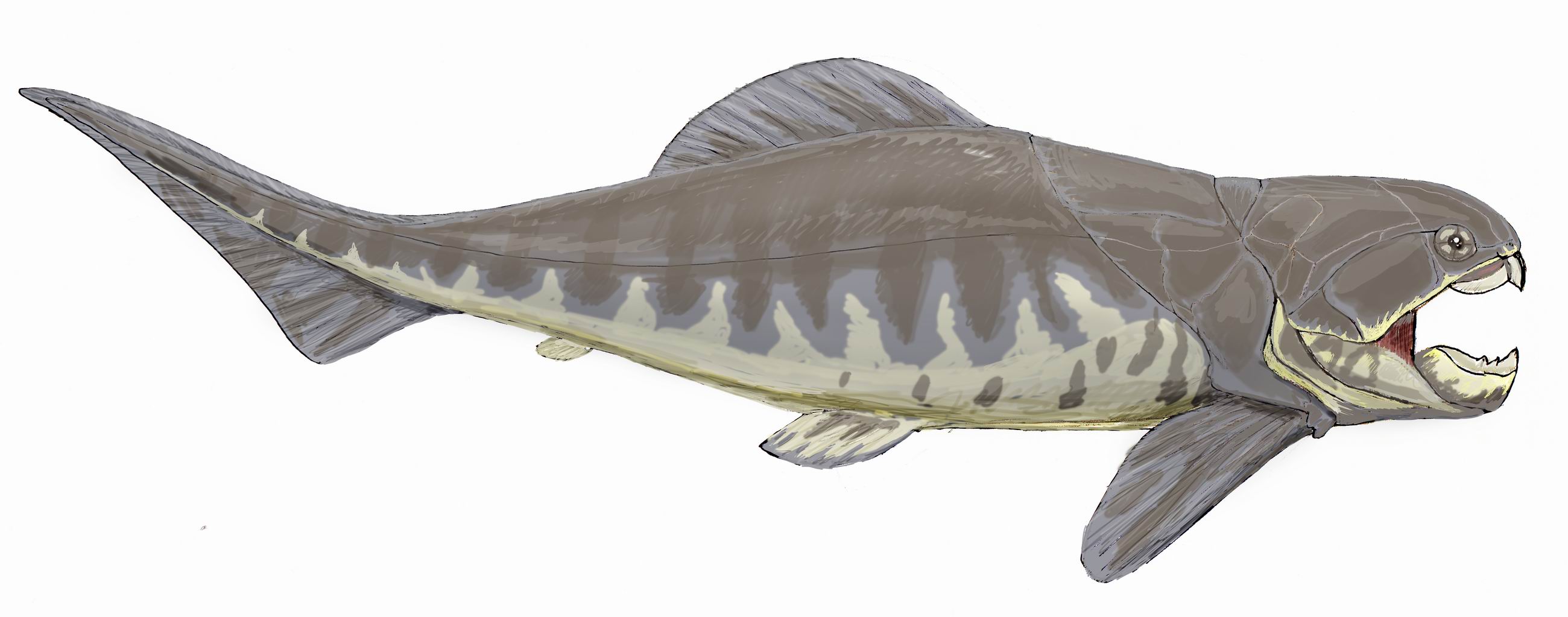
The class Osteostraci (meaning "bony shells") is an extinct taxon of bony-armored jawless fish, termed "ostracoderms", that lived in what is now North America, Europe and Russia from the Middle Silurian to Late Devonian. Anatomically speaking, the osteostracans, especially the Devonian species, were among the most advanced of all known agnathans. This is due to the development of paired fins, and their complicated cranial anatomy. The osteostracans were more similar to lampreys than to jawed vertebrates in possessing two pairs of semicircular canals in the inner ear, as opposed to the three pairs found in the inner ears of jawed vertebrates. They are thought to be the sister-group to pituriaspids, and together, these two taxa of jawless vertebrates are the sister-group of gnathostomes. Several synapomorphies support this hypothesis, such as the presence of: sclerotic ossicles, paired pectoral fins, a dermal skeleton with three layers (a basal layer of isopedin, a middle layer of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteostraci Janvier
The class (biology), class Osteostraci (meaning "bony shells") is an extinct taxon of bony-armored jawless fish, termed "ostracoderms", that lived in what is now North America, Europe and Russia from the Wenlock epoch, Middle Silurian to Late Devonian. Anatomically speaking, the osteostracans, especially the Devonian species, were among the most advanced of all known Agnatha, agnathans. This is due to the development of paired fins, and their complicated cranial anatomy. The osteostracans were more similar to lampreys than to jawed vertebrates in possessing two pairs of semicircular canals in the inner ear, as opposed to the three pairs found in the inner ears of jawed vertebrates. They are thought to be the sister-group to Pituriaspida, pituriaspids, and together, these two taxa of jawless vertebrates are the sister-group of Gnathostomata, gnathostomes. Several synapomorphies support this hypothesis, such as the presence of: sclerotic ossicles, paired pectoral fins, a dermal skel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostracoderm
Ostracoderms () are the armored jawless fish of the Paleozoic Era. The term does not often appear in classifications today because it is paraphyletic (excluding jawed fishes) (may also be polyphyletic if anaspids are closer to cyclostomes) and thus does not correspond to one evolutionary lineage. However, the term is still used as an informal way of loosely grouping together the armored jawless fishes. An innovation of ostracoderms was the use of gills not for feeding, but exclusively for respiration. Earlier chordates with gill precursors used them for both respiration and feeding. Ostracoderms had separate pharyngeal gill pouches along the side of the head, which were permanently open with no protective operculum. Unlike invertebrates that use ciliated motion to move food, ostracoderms used their muscular pharynx to create a suction that pulled small and slow moving prey into their mouths. Swiss anatomist Louis Agassiz received some fossils of bony armored fish from Scotland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyestiida
Thyestiida is an order of bony-armored jawless fish in the extinct vertebrate class Osteostraci The class Osteostraci (meaning "bony shells") is an extinct taxon of bony-armored jawless fish, termed "ostracoderms", that lived in what is now North America, Europe and Russia from the Middle Silurian to Late Devonian. Anatomically speaking, ....The origin and early evolution of the Osteostraci (Vertebrata): A phylogeny for the Thyestiida. Robert S. Sansom, Journal of Systematic Palaeontology, Volume 6, Issue 3, 2008, pages 317-332, References External links Thyestiidaat fossilworks.org (retrieved 21 April 2016) Osteostraci Prehistoric jawless fish orders {{Paleo-jawless-fish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benneviaspidida
Benneviaspidida is an order of osteostracan jawless fishes which lived in the Early Devonian. The fishes in this order have a flat headshield and are dorsoventrally depressed. The first canal to lateral sensory field bifurcates near the orbit. Phylogeny The cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to d ... below is adapted from Sansom (2009): References External links Benneviaspidida at PalaeosOsteostraci by Philippe JanvierEarly Devonian osteostracans from Russia {{Taxonbar, from=Q4889790 Osteostraci Prehistoric jawless fish orders Devonian jawless fish Early Devonian first appearances Early Devonian taxonomic orders Early Devonian extinctions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalaspis
''Cephalaspis'' (from el, κεφαλή , 'head' and el, ἀσπίς , 'shield') is a possibly monotypic genus of extinct osteostracan agnathan vertebrate. It was a trout-sized detritivorous fish that lived in the early Devonian. Description Like its relatives, ''Cephalaspis'' was heavily armored, presumedly to defend against predatory placoderms and eurypterids, as well as to serve as a source of calcium for metabolic functions in calcium-poor freshwater environments. It had sensory patches along the rim and center of its head shield, which were used to sense for worms and other burrowing organisms in the mud. Diet Because its mouth was situated directly beneath its head, ''Cephalaspis'' was thought of as being a bottom-feeder, akin to a heavily armoured catfish or sturgeon. It moved its plow-like head from side to side, ''Cephalaspis'' easily stirring sand and dust into the water, along with revealing the hiding places of its prey, digging up worms or crustaceans hidden in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ateleaspididae
Ateleaspididae is a prehistoric jawless fish family in the class Osteostraci The class Osteostraci (meaning "bony shells") is an extinct taxon of bony-armored jawless fish, termed "ostracoderms", that lived in what is now North America, Europe and Russia from the Middle Silurian to Late Devonian. Anatomically speaking, ....Sansom, R. S. (2009). "Phylogeny, classification and character polarity of the Osteostraci (Vertebrata)". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology 7: 95–11. References External links Osteostraci Prehistoric jawless fish families {{Paleo-jawless-fish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
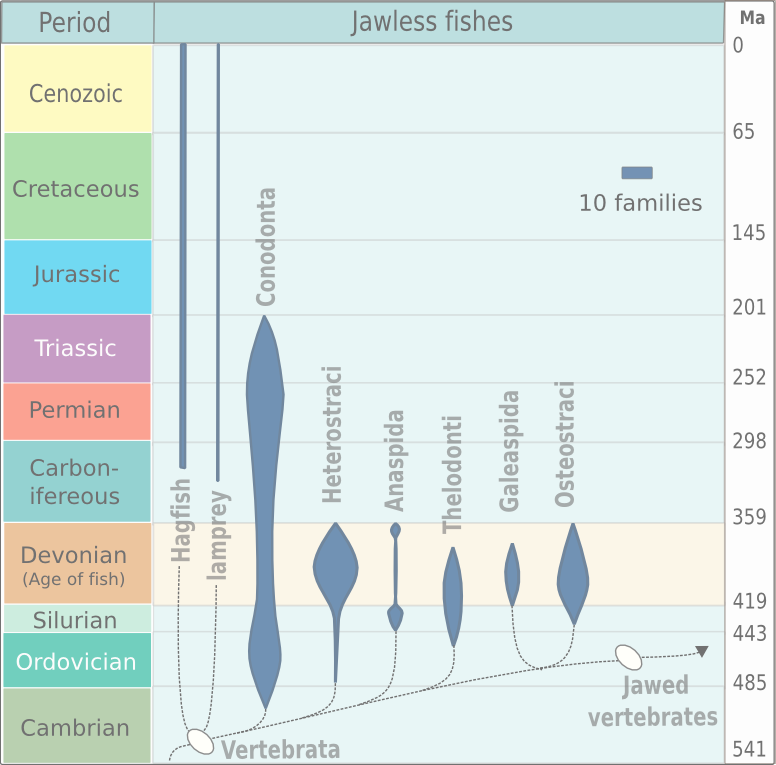
Jawless Fish
Agnatha (, Ancient Greek 'without jaws') is an infraphylum of jawless fish in the phylum Chordata, subphylum Vertebrata, consisting of both present (cyclostomes) and extinct (conodonts and ostracoderms) species. Among recent animals, cyclostomes are sister to all vertebrates with jaws, known as gnathostomes. Recent molecular data, both from rRNA and from mtDNA as well as embryological data, strongly supports the hypothesis that living agnathans, the cyclostomes, are monophyletic. The oldest fossil agnathans appeared in the Cambrian, and two groups still survive today: the lampreys and the hagfish, comprising about 120 species in total. Hagfish are considered members of the subphylum Vertebrata, because they secondarily lost vertebrae; before this event was inferred from molecular and developmental data, the group Craniata was created by Linnaeus (and is still sometimes used as a strictly morphological descriptor) to reference hagfish plus vertebrates. While a few scientist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zenaspida
Zenaspidida is an extinct order of osteostracans, a group of jawless stem-gnathostomes. They possessed a distinct headshield, which varied in width to length ratio by species. Description The head shield is dome-shaped and extremely large in comparison to the main body. The abdominal section of this shield has a less developed median dorsal crest. As a rule for this order, the nasohypophysial opening is larger than the nasal division. The pineal plate seen in other osteostracans is barely developed or completely absent. The median dorsal field is notably broad, and the lateral fields are widened in the posterior, but reach back no further than the proximal section of the dorsal surface of the cornual processes. The ornamentation on the head shield can have singular, large tubercles, or groups of tubercles which range in size. This is often used to speciate. Classification The cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agnatha
Agnatha (, Ancient Greek 'without jaws') is an infraphylum of jawless fish in the phylum Chordata, subphylum Vertebrata, consisting of both present (cyclostomes) and extinct ( conodonts and ostracoderms) species. Among recent animals, cyclostomes are sister to all vertebrates with jaws, known as gnathostomes. Recent molecular data, both from rRNA and from mtDNA as well as embryological data, strongly supports the hypothesis that living agnathans, the cyclostomes, are monophyletic. The oldest fossil agnathans appeared in the Cambrian, and two groups still survive today: the lampreys and the hagfish, comprising about 120 species in total. Hagfish are considered members of the subphylum Vertebrata, because they secondarily lost vertebrae; before this event was inferred from molecular and developmental data, the group Craniata was created by Linnaeus (and is still sometimes used as a strictly morphological descriptor) to reference hagfish plus vertebrates. While a few scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ateleaspis
''Ateleaspis'' is an extinct genus of primitive ostracoderm fish that lived in the Early Silurian to Early Devonian periods. Like other ostracoderms, ''Ateleaspis'' had a head shield similar to that of ''Cephalaspis''. Species from Silurian period were found in Norway and Scotland, but now has been found also in Siberia Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ... from Early Devonian period. Description ''Ateleaspis'' possibly is the most basal vertebrate with paired fins. ''Ateleaspis'' was a small fish (about 15 – 20 cm) and had a flat headshield and a narrow trunk covered by brick-like scales. References External links Ateleaspis at PalaeosAteleaspis species location & chronology Osteostraci genera Paleozoic jawless fish Fossils of Norway Fossils of Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemicyclaspis
''Hemicyclaspis'' ( or 'semicircle plate') is an extinct genus of primitive jawless fish, closely related to ''Cephalaspis'', that lived in the Late Silurian ( Pridoli) to Devonian period in what is now Europe and North America. A typical cephalaspid, ''Hemicyclaspis'' had a heavily armored, shovel-shaped headshield. It is thought to have been a better swimmer than most of its relatives because of its powerful tail, stabilizing dorsal fin and the keel-shaped hydrodynamic In physics and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids—liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including ''aerodynamics'' (the study of air and other gases in motion) and ... edges of its head shield. ''Hemicyclaspis'' probably foraged the ocean floor for food. ''Hemicyclaspis'' grew to a length of 5 inches (13 centimeters) and would most likely have fed on particles from the muddy sea bed. References * Parker, Steve. Dinosaurus: th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnathostomata
Gnathostomata (; from Greek: (') "jaw" + (') "mouth") are the jawed vertebrates. Gnathostome diversity comprises roughly 60,000 species, which accounts for 99% of all living vertebrates, including humans. In addition to opposing jaws, living gnathostomes have true teeth (a characteristic which has subsequently been lost in some), paired appendages (pectoral and pelvic fins, arms, legs, wings, etc.), the elastomeric protein of elastin, and a horizontal semicircular canal of the inner ear, along with physiological and cellular anatomical characters such as the myelin sheaths of neurons, and an adaptive immune system that has the discrete lymphoid organs of spleen and thymus, and uses V(D)J recombination to create antigen recognition sites, rather than using genetic recombination in the variable lymphocyte receptor gene. It is now assumed that Gnathostomata evolved from ancestors that already possessed a pair of both pectoral and pelvic fins. Until recently these ancestors, know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |