|
Ogham Letters
Ogham (Modern Irish: ; mga, ogum, ogom, later mga, ogam, label=none ) is an Early Medieval alphabet used primarily to write the early Irish language (in the "orthodox" inscriptions, 4th to 6th centuries AD), and later the Old Irish language (scholastic ogham, 6th to 9th centuries). There are roughly 400 surviving orthodox inscriptions on stone monuments throughout Ireland and western Britain, the bulk of which are in southern Munster. The largest number outside Ireland are in Pembrokeshire, Wales. The vast majority of the inscriptions consist of personal names. According to the High Medieval ''Bríatharogam'', the names of various trees can be ascribed to individual letters. For this reason, ogam is sometimes known as the Celtic tree alphabet. The etymology of the word ''ogam'' or ''ogham'' remains unclear. One possible origin is from the Irish ''og-úaim'' 'point-seam', referring to the seam made by the point of a sharp weapon. Origins It is generally thought that th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphabet
An alphabet is a standardized set of basic written graphemes (called letters) that represent the phonemes of certain spoken languages. Not all writing systems represent language in this way; in a syllabary, each character represents a syllable, and logographic systems use characters to represent words, morphemes, or other semantic units. The first fully phonemic script, the Proto-Sinaitic script, later known as the Phoenician alphabet, is considered to be the first alphabet and is the ancestor of most modern alphabets, including Arabic, Cyrillic, Greek, Hebrew, Latin, and possibly Brahmic. It was created by Semitic-speaking workers and slaves in the Sinai Peninsula (as the Proto-Sinaitic script), by selecting a small number of hieroglyphs commonly seen in their Egyptian surroundings to describe the sounds, as opposed to the semantic values of the Canaanite languages. However, Peter T. Daniels distinguishes an abugida, a set of graphemes that represent consonantal base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Carney (scholar)
James Patrick Carney (17 May 1914 – 7 July 1989) was a noted Irish Celtic scholar. He was born in Portlaoise, County Laois and was educated at the Christian Brothers school in Synge Street, Dublin. He took his degree at University College Dublin in 1935, before going to Bonn University to study under Rudolf Thurneysen. On returning to Dublin, Carney worked under Osborn Bergin, Gerard Murphy, Richard Irvine Best and T. F. O'Rahilly. He pioneered an approach to early Irish texts which focused on their literary merit and their affinities with the other literatures of the medieval world. His ''Studies in Irish Literature and History'' which appeared in 1956 challenged the 'nativist' approach to Irish literature which had dominated the scholarship of the previous decades. His work on Saint Patrick also proved controversial. Carney had controversial views that Christianity had in fact been an overthrow of the pagan druidic order. The 1955 publication of James Carney's ‘Studies in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Ballymote 170r
A book is a medium for recording information in the form of writing or images, typically composed of many pages (made of papyrus, parchment, vellum, or paper) bound together and protected by a cover. The technical term for this physical arrangement is '' codex'' (plural, ''codices''). In the history of hand-held physical supports for extended written compositions or records, the codex replaces its predecessor, the scroll. A single sheet in a codex is a leaf and each side of a leaf is a page. As an intellectual object, a book is prototypically a composition of such great length that it takes a considerable investment of time to compose and still considered as an investment of time to read. In a restricted sense, a book is a self-sufficient section or part of a longer composition, a usage reflecting that, in antiquity, long works had to be written on several scrolls and each scroll had to be identified by the book it contained. Each part of Aristotle's ''Physics'' is called a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonology
Phonology is the branch of linguistics that studies how languages or dialects systematically organize their sounds or, for sign languages, their constituent parts of signs. The term can also refer specifically to the sound or sign system of a particular language variety. At one time, the study of phonology related only to the study of the systems of phonemes in spoken languages, but may now relate to any linguistic analysis either: Sign languages have a phonological system equivalent to the system of sounds in spoken languages. The building blocks of signs are specifications for movement, location, and handshape. At first, a separate terminology was used for the study of sign phonology ('chereme' instead of 'phoneme', etc.), but the concepts are now considered to apply universally to all human languages. Terminology The word 'phonology' (as in 'phonology of English') can refer either to the field of study or to the phonological system of a given language. This is one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Europe
Continental Europe or mainland Europe is the contiguous continent of Europe, excluding its surrounding islands. It can also be referred to ambiguously as the European continent, – which can conversely mean the whole of Europe – and, by some, simply as the Continent. When Eurasia is regarded as a single continent, Europe is treated as a subcontinent, and called as European subcontinent. The old notion of Europe as a cultural term was centred on core Europe (''Kerneuropa''), the continental territory of the historical Carolingian Empire, corresponding to modern France, Italy, German-speaking Europe and the Benelux states (historical Austrasia). This historical core of "Carolingian Europe" was consciously invoked in the 1950s as the historical ethno-cultural basis for the prospective European integration (see also Multi-speed Europe). Usage The most common definition of Mainland Europe excludes these continental islands: the Greek Islands, Cyprus, Malta, Sicily, Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the period in classical antiquity when large parts of the island of Great Britain were under occupation by the Roman Empire. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. During that time, the territory conquered was raised to the status of a Roman province. Julius Caesar invaded Britain in 55 and 54 BC as part of his Gallic Wars. According to Caesar, the Britons had been overrun or culturally assimilated by other Celtic tribes during the British Iron Age and had been aiding Caesar's enemies. He received tribute, installed the friendly king Mandubracius over the Trinovantes, and returned to Gaul. Planned invasions under Augustus were called off in 34, 27, and 25 BC. In 40 AD, Caligula assembled 200,000 men at the Channel on the continent, only to have them gather seashells ('' musculi'') according to Suetonius, perhaps as a symbolic gesture to proclaim Caligula's victory over the sea. Three years later, Claudius directed four legi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digamma
Digamma or wau (uppercase: Ϝ, lowercase: ϝ, numeral: ϛ) is an archaic letter of the Greek alphabet. It originally stood for the sound but it has remained in use principally as a Greek numeral for 6. Whereas it was originally called ''waw'' or ''wau'', its most common appellation in classical Greek is ''digamma''; as a numeral, it was called ''episēmon'' during the Byzantine era and is now known as '' stigma'' after the Byzantine ligature combining σ-τ as ϛ. Digamma or wau was part of the original archaic Greek alphabet as initially adopted from Phoenician. Like its model, Phoenician waw, it represented the voiced labial-velar approximant and stood in the 6th position in the alphabet between epsilon and zeta. It is the consonantal doublet of the vowel letter upsilon (), which was also derived from waw but was placed near the end of the Greek alphabet. Digamma or wau is in turn the ancestor of the Latin letter F. As an alphabetic letter, it is attested in archaic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Alphabet
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BCE. It is derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and was the earliest known alphabetic script to have distinct letters for vowels as well as consonants. In Archaic Greece, Archaic and early Classical Greece, Classical times, the Greek alphabet existed in Archaic Greek alphabets, many local variants, but, by the end of the 4th century BCE, the Euclidean alphabet, with 24 letters, ordered from alpha to omega, had become standard and it is this version that is still used for Greek writing today. The letter case, uppercase and lowercase forms of the 24 letters are: : , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , /ς, , , , , , . The Greek alphabet is the ancestor of the Latin script, Latin and Cyrillic scripts. Like Latin and Cyrillic, Greek originally had only a single form of each letter; it developed the letter case distinction between uppercase and lowercase in parallel with Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
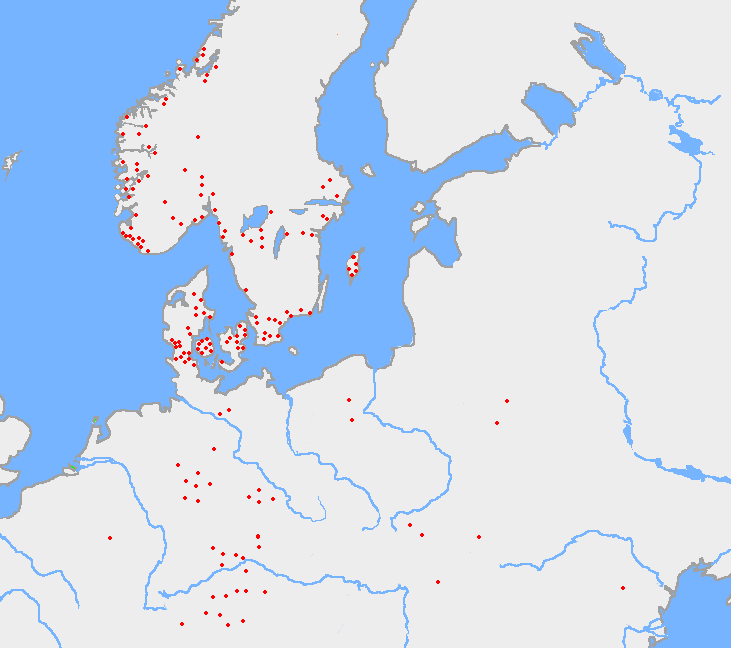
Elder Futhark
The Elder Futhark (or Fuþark), also known as the Older Futhark, Old Futhark, or Germanic Futhark, is the oldest form of the runic alphabets. It was a writing system used by Germanic peoples for Northwest Germanic dialects in the Migration Period. Inscriptions are found on artifacts including jewelry, amulets, plateware, tools, and weapons, as well as runestones in Scandinavia, from the 2nd to the 10th centuries. In Scandinavia, beginning in the late 8th century, the script was simplified to the Younger Futhark, while the Anglo-Saxons and Frisians instead extended it, giving rise to the Anglo-Saxon futhorc. Both the Anglo-Saxon futhorc and the Younger Futhark remained in use during the Early and the High Middle Ages respectively, but knowledge of how to read the Elder Futhark was forgotten until 1865, when it was deciphered by Norwegian scholar Sophus Bugge. Description The Elder Futhark (named after the initial phoneme of the first six rune names: F, U, Þ, A, R and K) has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Alphabet
The Latin alphabet or Roman alphabet is the collection of letters originally used by the ancient Romans to write the Latin language. Largely unaltered with the exception of extensions (such as diacritics), it used to write English and the other modern European languages. With modifications, it is also used for other alphabets, such as the Vietnamese alphabet. Its modern repertoire is standardised as the ISO basic Latin alphabet. Etymology The term ''Latin alphabet'' may refer to either the alphabet used to write Latin (as described in this article) or other alphabets based on the Latin script, which is the basic set of letters common to the various alphabets descended from the classical Latin alphabet, such as the English alphabet. These Latin-script alphabets may discard letters, like the Rotokas alphabet, or add new letters, like the Danish and Norwegian alphabets. Letter shapes have evolved over the centuries, including the development in Medieval Latin of lower-case, fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cipher Runes
Cipher runes, or cryptic runes, are the cryptographical replacement of the letters of the runic alphabet. Preservation The knowledge of cipher runes was best preserved in Iceland, and during the 17th–18th centuries, Icelandic scholars produced several treatises on the subject. The most notable of these is the manuscript ''Runologia'' by Jón Ólafsson (1705–1779), which he wrote in Copenhagen (1732–1752). It thoroughly treats numerous cipher runes and runic ciphers, and it is now preserved in the Arnamagnæan Institute in Copenhagen. Jón Ólafsson's treatise presents the Younger Futhark in the Viking Age order, which means that the m-rune precedes the l-rune. This small detail was of paramount importance for the interpretation of Viking Age cipher runes because in the 13th century the two runes had changed places through the influence of the Latin alphabet where ''l'' precedes ''m''. Since the medieval runic calendar used the post-13th-century order, the early runolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(14760479206).jpg)