|
Occupational Cancer
Occupational cancer is cancer caused by occupational hazards. Several cancers have been directly tied to occupational hazards, including chimney sweeps' carcinoma, mesothelioma, and others. Types of hazards Occupational exposure to chemicals, dusts, radiation, and certain industrial processes have been tied to occupational cancer. Exposure to cancer-causing chemicals (carcinogens) may cause mutations that allow cells to grow out of control, causing cancer. Carcinogens in the workplace may include chemicals like anilines, Chromate ion, chromates, dinitrotoluenes, arsenic and inorganic arsenic compounds, beryllium and beryllium compounds, cadmium compounds, and nickel compounds. Dusts that can cause cancer leather or wood dusts, asbestos, crystalline forms of silica, coal tar pitch volatiles, coke oven emissions, diesel exhaust and environmental tobacco smoke. sunlight; Radon, radon gas; and industrial, medical, or other exposure to ionizing radiation can all cause cancer in the work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occupational Hazard
An occupational hazard is a hazard experienced in the workplace. This encompasses many types of hazards, including chemical hazards, biological hazards (biohazards), psychosocial hazards, and physical hazards. In the United States, the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) conduct workplace investigations and research addressing workplace health and safety hazards resulting in guidelines. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) establishes enforceable standards to prevent workplace injuries and illnesses. In the EU, a similar role is taken by EU-OSHA. Occupational hazard as a term signifies both long-term and short-term risks associated with the workplace environment. It is a field of study within occupational safety and health and public health. Short term risks may include physical injury (e.g., eye, back, head, etc.,), while long-term risks may be an increased risk of developing occupational disease, such as cancer or heart disease. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tobacco Smoke
Tobacco smoke is a sooty aerosol produced by the incomplete combustion of tobacco during the tobacco smoking, smoking of cigarettes and other tobacco products. Temperatures in burning cigarettes range from about 400 °C between puffs to about 900 °C during a puff. During the burning of the cigarette tobacco (itself a complex mixture), thousands of chemical substances are generated by combustion, distillation, pyrolysis and pyrosynthesis. Tobacco smoke is used as a fumigant and inhalant. Composition The particles in tobacco smoke are liquid aerosol droplets (about 20% water), with a mass median aerodynamic diameter (MMAD) that is submicrometer (and thus, fairly "lung-respirable" by humans). The droplets are present in high concentrations (some estimates are as high as 1010 droplets per cm3). Most cigarettes today contain a cigarette filter, which can reduce "Tar (tobacco residue), tar" and nicotine smoke yields up to 50% by several different mechanisms, with an even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ''leukemia cells''. Symptoms may include bleeding and bruising, bone pain, fatigue, fever, and an increased risk of infections. These symptoms occur due to a lack of normal blood cells. Diagnosis is typically made by blood tests or bone marrow biopsy. The exact cause of leukemia is unknown. A combination of genetic factors and environmental (non-inherited) factors are believed to play a role. Risk factors include smoking, ionizing radiation, petrochemicals (such as benzene), prior chemotherapy, and Down syndrome. People with a family history of leukemia are also at higher risk. There are four main types of leukemia— acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and chronic myeloi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laryngeal Cancer
Laryngeal cancers are mostly squamous-cell carcinomas, reflecting their origin from the epithelium of the larynx. Cancer can develop in any part of the larynx. The prognosis is affected by the location of the tumour. For the purposes of staging, the larynx is divided into three anatomical regions: the glottis (true vocal cords, anterior and posterior commissures); the supraglottis (epiglottis, arytenoids and aryepiglottic folds, and false cords); and the subglottis. Most laryngeal cancers originate in the glottis, with supraglottic and subglottic tumours being less frequent. Laryngeal cancer may spread by: direct extension to adjacent structures, metastasis to regional cervical lymph nodes, or via the blood stream. The most common site of distant metastases is the lung. Laryngeal cancer occurred in 177,000 people in 2018, and resulted in 94,800 deaths (an increase from 76,000 deaths in 1990). Five-year survival rates in the United States are 60.3%. Signs and symptoms The symp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
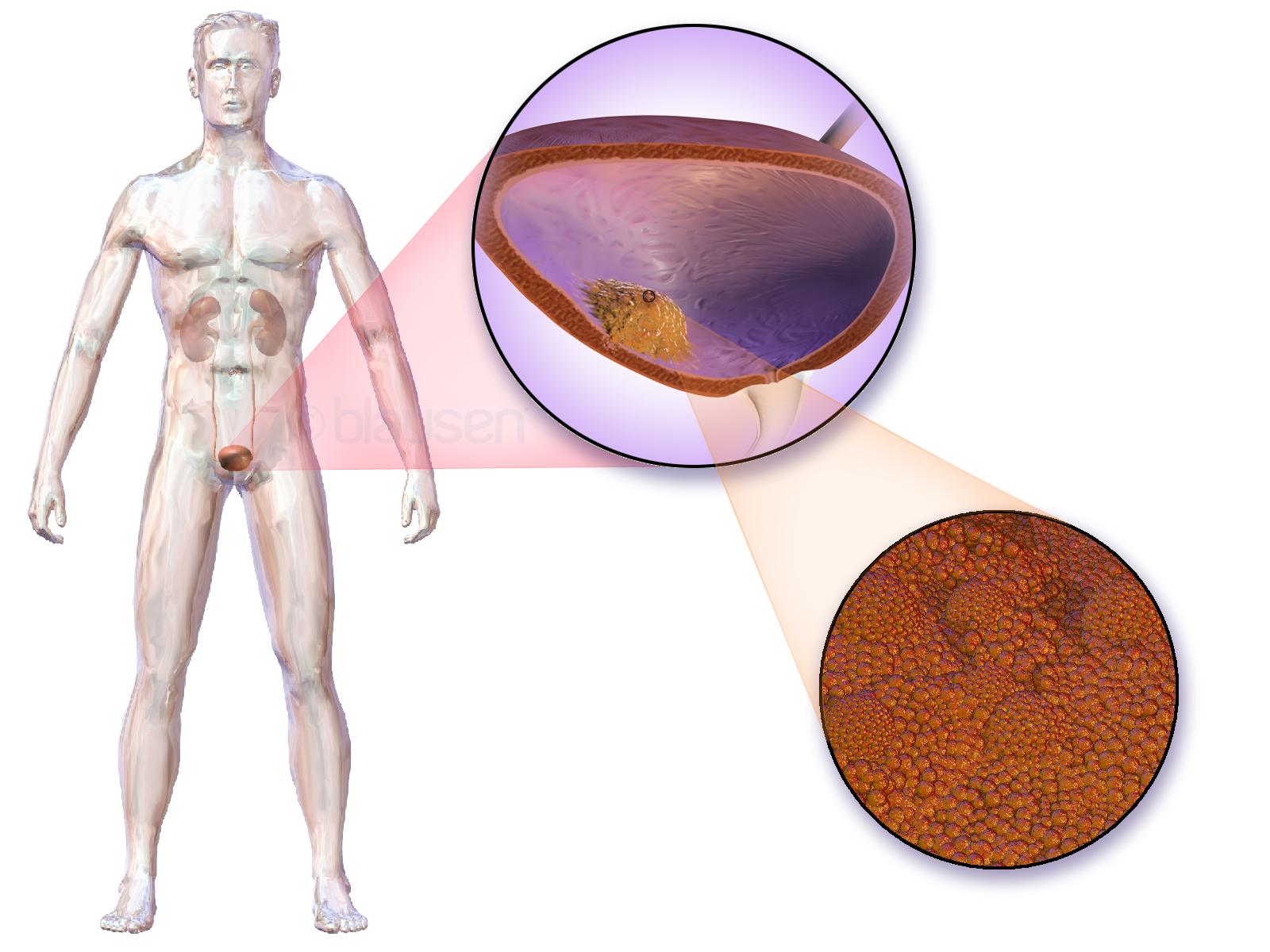
Kidney Cancer
Kidney cancer, also known as renal cancer, is a group of cancers that starts in the kidney. Symptoms may include blood in the urine, lump in the abdomen, or back pain. Fever, weight loss, and tiredness may also occur. Complications can include spread to the lungs or brain. The main types of kidney cancer are renal cell cancer (RCC), transitional cell cancer (TCC), and Wilms tumor. RCC makes up approximately 80% of kidney cancers, and TCC accounts for most of the rest. Risk factors for RCC and TCC include smoking, certain pain medications, previous bladder cancer, being overweight, high blood pressure, certain chemicals, and a family history. Risk factors for Wilms tumor include a family history and certain genetic disorders such as WAGR syndrome. Diagnosis maybe suspected based on symptoms, urine testing, and medical imaging. It is confirmed by tissue biopsy. Treatment may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy. Kidney cancer newly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer is any of several types of cancer arising from the tissues of the urinary bladder. Symptoms include blood in the urine, pain with urination, and low back pain. It is caused when epithelial cells that line the bladder become malignant. Risk factors for bladder cancer include smoking, family history, prior radiation therapy, frequent bladder infections, and exposure to certain chemicals. The most common type is transitional cell carcinoma. Other types include squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Diagnosis is typically by cystoscopy with tissue biopsies. Staging of the cancer is determined by transurethral resection and medical imaging. Treatment depends on the stage of the cancer. It may include some combination of surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy. Surgical options may include transurethral resection, partial or complete removal of the bladder, or urinary diversion. The typical five-year survival rates in the United States i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helicobacter Pylori
''Helicobacter pylori'', previously known as ''Campylobacter pylori'', is a gram-negative, microaerophilic, spiral (helical) bacterium usually found in the stomach. Its helical shape (from which the genus name, helicobacter, derives) is thought to have evolved in order to penetrate the mucoid lining of the stomach and thereby establish infection. The bacterium was first identified in 1982 by the Australian doctors Barry Marshall and Robin Warren. ''H. pylori'' has been associated with cancer of the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue in the stomach, esophagus, colon, rectum, or tissues around the eye (termed extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of the cited organ), and of lymphoid tissue in the stomach (termed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma). ''H. pylori'' infection usually has no symptoms but sometimes causes gastritis (stomach inflammation) or ulcers of the stomach or first part of the small intestine. The infection is also associated with the development of cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
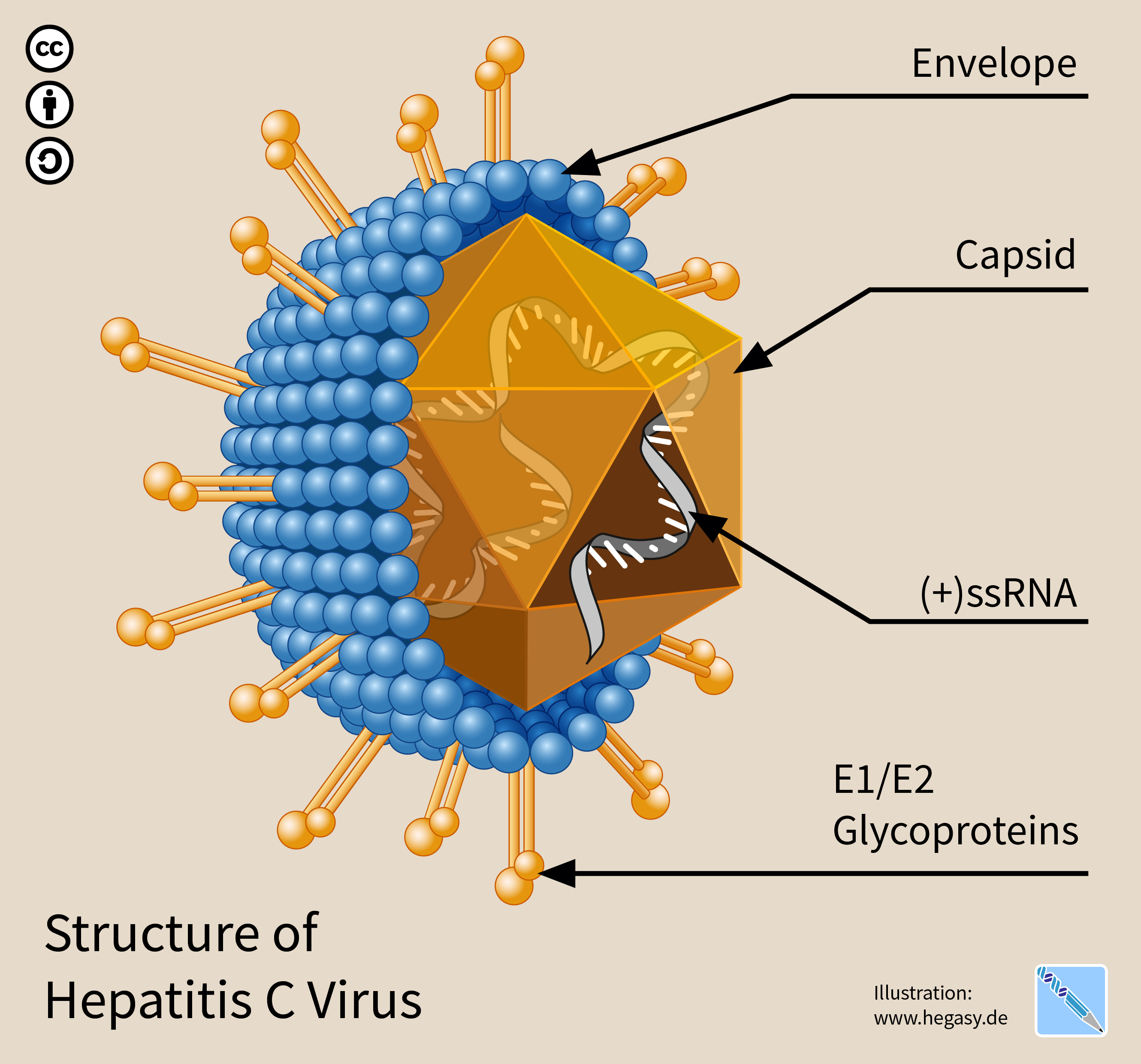
Hepatitis C Virus
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a small (55–65 nm in size), enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus of the family ''Flaviviridae''. The hepatitis C virus is the cause of hepatitis C and some cancers such as liver cancer ( hepatocellular carcinoma, abbreviated HCC) and lymphomas in humans. Taxonomy The hepatitis C virus belongs to the genus ''Hepacivirus'', a member of the family ''Flaviviridae''. Before 2011, it was considered to be the only member of this genus. However a member of this genus has been discovered in dogs: canine hepacivirus. There is also at least one virus in this genus that infects horses. Several additional viruses in the genus have been described in bats and rodents. Structure The hepatitis C virus particle consists of a lipid membrane envelope that is 55 to 65 nm in diameter. Two viral envelope glycoproteins, E1 and E2, are embedded in the lipid envelope. They take part in viral attachment and entry into the cell. Within the envel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis B Virus
''Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, a species of the genus ''Orthohepadnavirus'' and a member of the ''Hepadnaviridae'' family of viruses. This virus causes the disease hepatitis B. Disease Despite there being a vaccine to prevent Hepatitis B, HBV remains a global health problem. Hepatitis B can be acute and later become chronic, leading to other diseases and health conditions. In addition to causing hepatitis, infection with HBV can lead to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. It has also been suggested that it may increase the risk of pancreatic cancer. Roles in disease Viral infection by ''Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) causes many hepatocyte changes due to the direct action of a protein encoded by the virus, HBx, and to indirect changes due to a large increase in intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) after infection. HBx appears to dysregulate a number of cellular pathways. HBx causes dysregulation in part by binding to genomic DNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epstein–Barr Virus
The Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), formally called ''Human gammaherpesvirus 4'', is one of the nine known human herpesvirus types in the herpes family, and is one of the most common viruses in humans. EBV is a double-stranded DNA virus. It is best known as the cause of infectious mononucleosis ("mono" or "glandular fever"). It is also associated with various non-malignant, premalignant, and malignant Epstein–Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative diseases such as Burkitt lymphoma, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, and Hodgkin's lymphoma; non-lymphoid malignancies such as gastric cancer and nasopharyngeal carcinoma; and conditions associated with human immunodeficiency virus such as hairy leukoplakia and central nervous system lymphomas. The virus is also associated with the childhood disorders of Alice in Wonderland syndrome and acute cerebellar ataxia and, by some evidence, higher risks of developing certain autoimmune diseases, especially dermatomyositis, systemic lu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
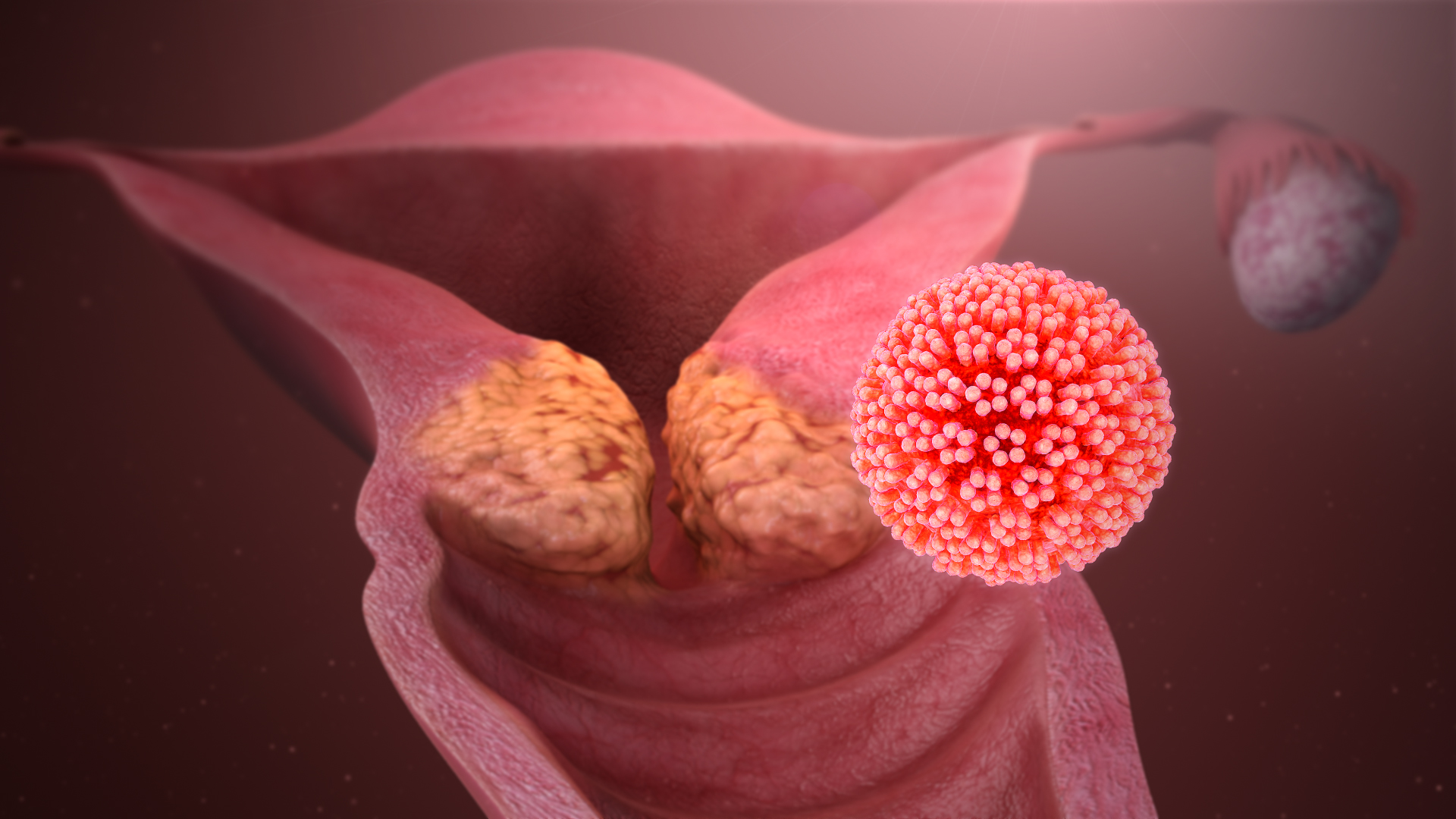
Human Papillomavirus Infection
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and results in either warts or precancerous lesions. These lesions, depending on the site affected, increase the risk of cancer of the cervix, vulva, vagina, penis, anus, mouth, tonsils, or throat. Nearly all cervical cancer is due to HPV and two strains – HPV16 and HPV18 – account for 70% of cases. HPV16 is responsible for almost 90% of HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers. Between 60% and 90% of the other cancers listed above are also linked to HPV. HPV6 and HPV11 are common causes of genital warts and laryngeal papillomatosis. An HPV infection is caused by ''human papillomavirus'', a DNA virus from the papillomavirus family. Over 170 types have been described. An individual can become infected with more than one type of HPV, and the disea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circadian Rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural, internal process that regulates the sleep–wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. It can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., Endogeny (biology), endogenous) and responds to the environment (Entrainment (chronobiology), entrained by the environment). These 24-hour rhythms are driven by a circadian clock, and they have been widely observed in animals, plants, fungi and cyanobacteria. The term ''circadian'' comes from the Latin ''wikt:circa#Latin, circa'', meaning "approximately", and ''dies'', meaning "day". Processes with 24-hour cycles are more generally called diurnal rhythms; diurnal rhythms should not be called circadian rhythms unless they can be confirmed as endogenous, and not environmental. Although circadian rhythms are endogenous, they are adjusted to the local environment by external cues called zeitgebers (German for "time givers"), which include light, temperature and redox cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |