|
Nobber Gaelic Footballers
Nobber ( – referring to the description by the local native Irish population, to the development of moat around a Norman castle) is a village in north County Meath, Ireland. The village is located near a river called the Dee () and near Whitewood Lake, which is situated in the townland of Whitewood. It is on the Navan–Kingscourt road ( R162) about north of Navan. This places the village about from the M50 motorway ; the orbital motorway of Dublin. The town of Kells is to the west and the town of Ardee to the east and the town of Kingscourt is to the north. Villages that border the parish are Kilmainhamwood, Moynalty and Kilbeg to the west, Castletown-Kilpatrick to the south and Drumconrath and Lobinstown to the east. The village of Nobber is built on the river Dee, the course of which was diverted around the village in the 19th century. A feature of the local geography is how the village is set within rolling hills called drumlins formed in the last glacial period. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 UN member states, 2 UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a special political status (2 states, both in free association with New Zealand). Compiling a list such as this can be a complicated and controversial process, as there is no definition that is binding on all the members of the community of nations concerni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilbert De Angulo
Gilbert de Angulo was an Anglo-Norman knight, . Biography A son of Jocelyn de Angulo, 1st Baron of Navan, Gilbert held the barony of Machaire Gaileng (Morgallion and Ratoath). Upon his rebellion in 1195, all his lands were forfeited - given by Walter de Lacy to his brother, Hugh, about 1198 - and Gilbert and his brothers Phillip and William outlawed. Gilbert fled English jurisdiction and sought service with King Cathal Crobhdearg Ua Conchobair of Connacht. In return, Cathal granted him lands at Máenmaige, in western Uí Maine. Upon his pardon in 1206, King John of England confirmed him in lands granted by King Cathal and made him a grant of other lands. Brought back into John's favour, he assisted Cathal in the construction of Caeluisce, near Ballyshannon, in 1212. It was attacked and burned the following year, and Gilbert was killed during the attack. Gilbert also appears to have held land in Uí Lomain and Cineal Fheicin/Muntir Mailfinnain. However, as all his lands wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
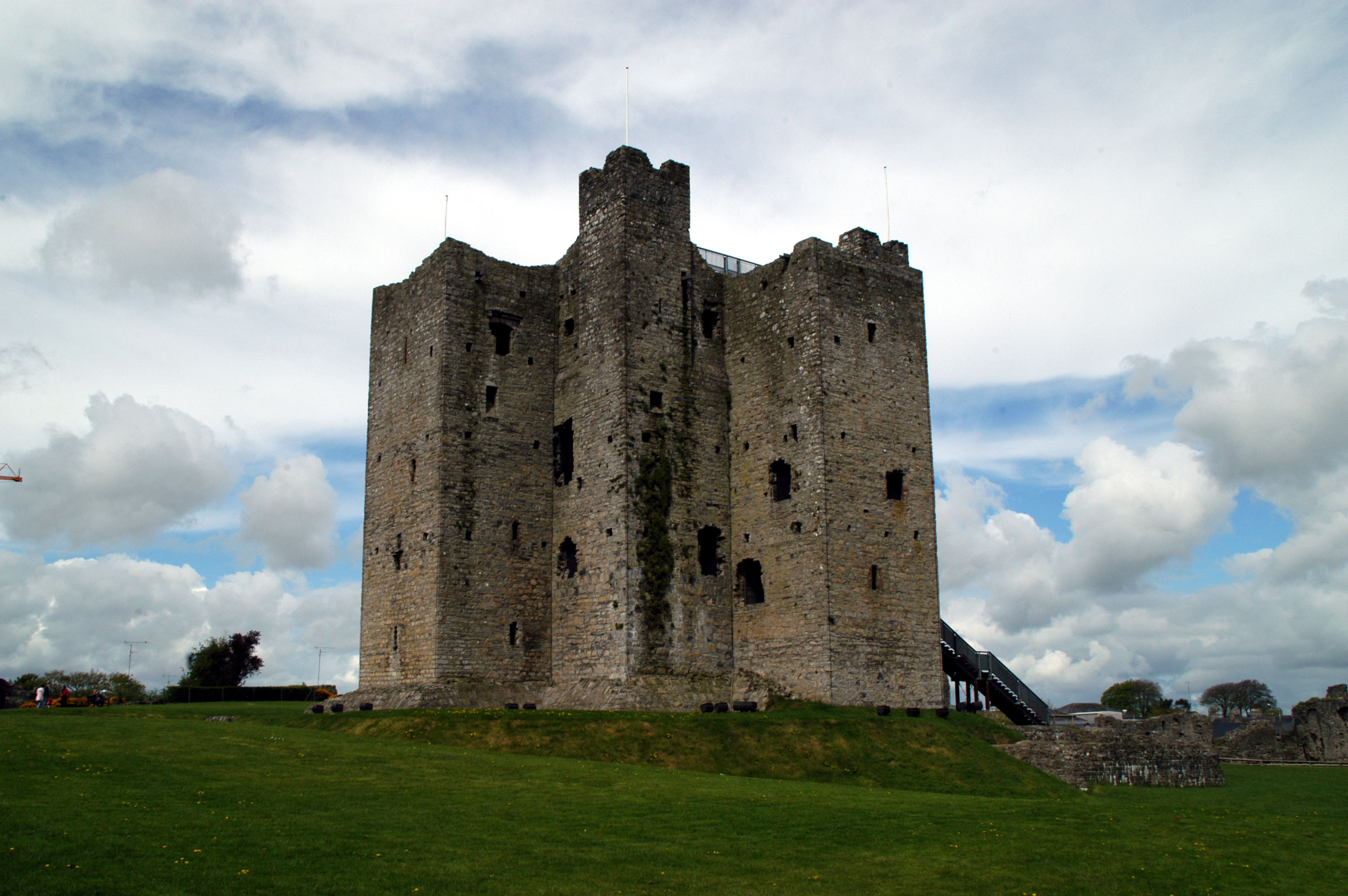
Barony Of Morgallion
Morgallion (, "plain of the Gailenga") is one of the baronies that comprise county Meath, Ireland. In 1172 King Henry II of England granted the Lordship of Meath to Hugh de Lacy to hold as King Murrough O Melaghlin held it. Once established de Lacy proceeded to divide up his newly acquired territory into feudal grants to his chief followers. He granted the territory of the Gaileanga-Mor sept (the lands of Magherigalon, later to be known as the Barony of Morgallion) to Gilbert de Angulo, who had arrived from Wales in 1171. The caput of the barony was at Nobber where de Angulo constructed a Motte A motte-and-bailey castle is a European fortification with a wooden or stone keep situated on a raised area of ground called a motte, accompanied by a walled courtyard, or bailey, surrounded by a protective ditch and palisade. Relatively easy to ... close to the site of an earlier ecclesiastical site. References Books [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lordship Of Ireland
The Lordship of Ireland ( ga, Tiarnas na hÉireann), sometimes referred to retroactively as Norman Ireland, was the part of Ireland ruled by the King of England (styled as "Lord of Ireland") and controlled by loyal Anglo-Norman lords between 1177 and 1542. The lordship was created following the Norman invasion of Ireland in 1169–1171. It was a papal fief, granted to the Plantagenet kings of England by the Holy See, via ''Laudabiliter''. As the Lord of Ireland was also the King of England, he was represented locally by a governor, variously known as the Justiciar, Lieutenant, Lord Lieutenant or Lord Deputy. The kings of England claimed lordship over the whole island, but in reality the king's rule only ever extended to parts of the island. The rest of the island – referred to subsequently as Gaelic Ireland – remained under the control of various Gaelic Irish kingdoms or chiefdoms, who were often at war with the Anglo-Normans. The area under English rule and law grew and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry II Of England
Henry II (5 March 1133 – 6 July 1189), also known as Henry Curtmantle (french: link=no, Court-manteau), Henry FitzEmpress, or Henry Plantagenet, was King of England from 1154 until his death in 1189, and as such, was the first Angevin king of England. King Louis VII of France made him Duke of Normandy in 1150. Henry became Count of Anjou and Maine upon the death of his father, Count Geoffrey V, in 1151. His marriage in 1152 to Eleanor of Aquitaine, former spouse of Louis VII, made him Duke of Aquitaine. He became Count of Nantes by treaty in 1158. Before he was 40, he controlled England; large parts of Wales; the eastern half of Ireland; and the western half of France, an area that was later called the Angevin Empire. At various times, Henry also partially controlled Scotland and the Duchy of Brittany. Henry became politically involved by the age of 14 in the efforts of his mother Matilda, daughter of Henry I of England, to claim the English throne, then occupied b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugh De Lacy, Lord Of Meath
Hugh de Lacy, Lord of Meath, 4th Baron Lacy (; before 1135 – 25 July 1186), was an Anglo-Norman landowner and royal office-holder. He had substantial land holdings in Herefordshire and Shropshire. Following his participation in the Norman Invasion of Ireland, he was granted, in 1172, the lands of the Kingdom of Meath by the Anglo-Norman King Henry II, but he had to gain control of them. The Lordship of Meath was then the most extensive liberty in Ireland. Early life Hugh de Lacy was the son of Gilbert de Lacy (died after 1163) of Ewyas Lacy, Weobley, and Ludlow. He is said to have had a dispute with Joscelin de Dinan as to certain lands in Herefordshire in 1154. He was in possession of his father's lands before 1163, and in 1165–66 held fifty-eight and three-quarters knights' fees, and had nine tenants without knight service. Career in Ireland In October 1171 Lacy went over with Henry II as part of an Anglo-Norman force to invade Ireland, and early in 1172 he was sent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lordship Of Meath
The Lordship of Meath was an extensive seigneurial Liberty (division), liberty in medieval History of Ireland (1169–1536), Ireland that was awarded to Hugh de Lacy, Lord of Meath, Hugh de Lacy by King Henry II of England by the service of fifty knights and with almost royal authority. The Lordship was roughly co-extensive with the Kingdoms of Ireland, medieval kingdom of Kingdom of Meath, Meath. At its greatest extent, it included all of the modern Counties of Ireland, counties of Fingal, County Meath, Meath (which takes its name from the kingdom), County Westmeath, Westmeath as well as parts of counties County Cavan, Cavan, County Kildare, Kildare, County Longford, Longford, County Louth, Louth and County Offaly, Offaly. The Lordship or Fee (feudal tenure), fiefdom was imbued with privileges enjoyed in no other Irish liberty, including the four royal pleas of arson, forestalling, rape, and treasure trove. Background Following the Norman invasion of Ireland, King Henry II visit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dundalk
Dundalk ( ; ga, Dún Dealgan ), meaning "the fort of Dealgan", is the county town (the administrative centre) of County Louth, Ireland. The town is on the Castletown River, which flows into Dundalk Bay on the east coast of Ireland. It is halfway between Dublin and Belfast, close to the border with Northern Ireland. It is the eighth largest urban area in Ireland, with a population of 39,004 as of the 2016 census. Having been inhabited since the Neolithic period, Dundalk was established as a Norman stronghold in the 12th century following the Norman invasion of Ireland, and became the northernmost outpost of The Pale in the Late Middle Ages. The town came to be nicknamed the "Gap of the North" where the northernmost point of the province of Leinster meets the province of Ulster. The modern street layout dates from the early 18th century and owes its form to James Hamilton (later 1st Earl of Clanbrassil). The legends of the mythical warrior hero Cú Chulainn are set in the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drogheda
Drogheda ( , ; , meaning "bridge at the ford") is an industrial and port town in County Louth on the east coast of Ireland, north of Dublin. It is located on the Dublin–Belfast corridor on the east coast of Ireland, mostly in County Louth but with the south fringes of the town in County Meath, north of Dublin. Drogheda has a population of approximately 41,000 inhabitants (2016), making it the List of settlements on the island of Ireland by population, eleventh largest settlement by population in all of Ireland, and the largest town in the Republic of Ireland by both population and area. It is the last bridging point on the River Boyne before it enters the Irish Sea. The UNESCO World Heritage Site of Newgrange is located west of the town. Drogheda was founded as two separately administered towns in two different territories: Drogheda-in-Kingdom of Meath, Meath (i.e. the Lordship of Meath, Lordship and Liberty of Meath, from which a charter was granted in 1194) and Drogheda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drumlins
A drumlin, from the Irish word ''droimnín'' ("littlest ridge"), first recorded in 1833, in the classical sense is an elongated hill in the shape of an inverted spoon or half-buried egg formed by glacial ice acting on underlying unconsolidated till or ground moraine. Assemblages of drumlins are referred to as fields or swarms; they can create a landscape which is often described as having a 'basket of eggs topography'. The low ground between two drumlins is known as a dungeon; dungeons have colder microclimates in winter from settling cold air. Morphology Drumlins occur in various shapes and sizes, including symmetrical (about the long axis), spindle, parabolic forms, and transverse asymmetrical forms. Generally, they are elongated, oval-shaped hills, with a long axis parallel to the orientation of ice flow and with an up-ice (stoss) face that is generally steeper than the down-ice (lee) face. Drumlins are typically 250 to 1,000 meters long and between 120 and 300 meters wide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |