|
Medusozoa Genera
Medusozoa is a clade in the phylum Cnidaria, and is often considered a subphylum. It includes the classes Hydrozoa, Scyphozoa, Staurozoa and Cubozoa, and possibly the parasitic Polypodiozoa. Medusozoans are distinguished by having a medusa stage in their often complex life cycle, a medusa typically being an umbrella-shaped body with stinging tentacles around the edge. With the exception of some Hydrozoa (and Polypodiozoa), all are called jellyfish in their free-swimming medusa phase. Evolution The phylum Cnidaria is widely accepted as being monophyletic and consisting of two clades, Anthozoa and Medusozoa. Anthozoa includes the classes Hexacorallia, the hard corals, and Octocorallia, the soft corals, as well as Ceriantharia, the tube-dwelling anemones. There is strong support for this group having been the first to branch off from the ancestral line. Medusozoa includes the classes Staurozoa, Cubozoa, Scyphozoa and Hydrozoa, but the relationships between these are unclear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrysaora Fuscescens
The Pacific sea nettle (''Chrysaora fuscescens''), or West Coast sea nettle, is a common Plankton, planktonic scyphozoan that lives in the eastern Pacific Ocean from Canada to Mexico. Sea nettles have a distinctive golden-brown bell with a reddish tint. The bell can grow to be larger than one meter (three feet) in diameter in the wild, though most are less than 50 cm across. The long, spiraling, white oral arms and the 24 undulating maroon tentacles may trail behind as far as 15 feet (4.6 m). For humans, its sting is often irritating, but rarely dangerous. ''Chrysaora fuscescens'' has proven to be very popular for display at public aquariums due to their bright colors and relatively easy maintenance. It is possible to establish polyps and culture ''Chrysaora'' in captivity. When provided appropriate aquarium conditions, the medusae do well under captive conditions. Taxonomy Johann Friedrich von Brandt described this species in 1835. The origin of the genus name ''Chrysaora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octocorallia
Octocorallia (also known as Alcyonaria) is a class of Anthozoa comprising around 3,000 species of water-based organisms formed of colonial polyps with 8-fold symmetry. It includes the blue coral, soft corals, sea pens, and gorgonians (sea fans and sea whips) within three orders: Alcyonacea, Helioporacea, and Pennatulacea. These organisms have an internal skeleton secreted by mesoglea and polyps with eight tentacles and eight mesentaries. As with all Cnidarians these organisms have a complex life cycle including a motile phase when they are considered plankton and later characteristic sessile phase. Octocorals have existed at least since the Ordovician period, as shown by Maurits Lindström's findings in the 1970s, however recent work has shown a possible Cambrian origin. Biology Octocorals resemble the stony corals in general appearance and in the size of their polyps, but lack the distinctive stony skeleton. Also unlike the stony corals, each polyp has only eight tentacle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haliclystus Stejnegeri 1
''Haliclystus'' is a genus of stalked jellyfish that contains 11 species and one nomen nudum (''Haliclystus sanjuanensis''). It is the largest genus in the order Stauromedusae. Members of this genus are found in the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Arctic, and Southern oceans. Two members of this genus, '' Haliclystus kerguelensis'' and ''Haliclystus antarcticus'', are found in the Southern hemisphere only. The remaining 9 members are found in the Northern hemisphere only.http://www.mapress.com/zootaxa/2010/f/zt02518p059.pdf Species in this genus have four longitudinal planes of symmetry. They have eight arms which are tipped with clusters of secondary tentacles. The number of these secondary tentacles is reported to vary across the different species. Species in this genus also have eight large pads known as anchors located between the arms. These vary in size and shape and currently play in important role in differentiating one species from another. Some, but not all, species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estonian Museum Of Natural History - Conularia
Estonian may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to Estonia, a country in the Baltic region in northern Europe * Estonians, people from Estonia, or of Estonian descent * Estonian language * Estonian cuisine * Estonian culture See also * * Estonia (other) * Languages of Estonia * List of Estonians This is a list of notable Estonians. Architects * Andres Alver (born 1953) *Dmitri Bruns (1929–2020) * Karl Burman (1882–1965) * Eugen Habermann (1884–1944) *Georg Hellat (1870–1943) *Otto Pius Hippius (1826–1883) * Erich Jacoby (1885� ... {{Disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actinostola 3
''Actinostola'' is a genus of sea anemones in the order Actiniaria. All members of this genus are deep-sea species, with some occurring at hydrothermal vents. Species The following species are recognised by the World Register of Marine Species The World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS) is a taxonomic database that aims to provide an authoritative and comprehensive list of names of marine organisms. Content The content of the registry is edited and maintained by scientific specialist ...: *'' Actinostola abyssorum'' (Danielssen, 1890) *'' Actinostola bulbosa'' (Carlgren, 1928) *'' Actinostola callosa'' (Verrill, 1882) *'' Actinostola capensis'' (Carlgren, 1928) *'' Actinostola carlgreni'' Wassilieff, 1908 *'' Actinostola chilensis'' McMurrich, 1904 *'' Actinostola crassicornis'' (Hertwig, 1882) *'' Actinostola faeculenta'' (McMurrich, 1893) *'' Actinostola georgiana'' Carlgren, 1927 *'' Actinostola groenlandica'' Carlgren, 1899 *'' Actinostola kerguelensis'' Carlgren, 1928 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comb Jelly
Ctenophora (; ctenophore ; ) comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and they are the largest animals to swim with the help of cilia. Depending on the species, adult ctenophores range from a few millimeters to in size. Only 100 to 150 species have been validated, and possibly another 25 have not been fully described and named. The textbook examples are cydippids with egg-shaped bodies and a pair of retractable tentacles fringed with tentilla ("little tentacles") that are covered with colloblasts, sticky cells that capture prey. Their bodies consist of a mass of jelly, with a layer two cells thick on the outside, and another lining the internal cavity. The phylum has a wide range of body forms, including the egg-shaped cydippids with retractable tentacles that capture prey, the flat generally combless pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ctenophora
Ctenophora (; ctenophore ; ) comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and they are the largest animals to swim with the help of cilia. Depending on the species, adult ctenophores range from a few millimeters to in size. Only 100 to 150 species have been validated, and possibly another 25 have not been fully described and named. The textbook examples are cydippids with egg-shaped bodies and a pair of retractable tentacles fringed with tentilla ("little tentacles") that are covered with colloblasts, sticky cells that capture prey. Their bodies consist of a mass of jelly, with a layer two cells thick on the outside, and another lining the internal cavity. The phylum has a wide range of body forms, including the egg-shaped cydippids with retractable tentacles that capture prey, the flat generally combless plat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animalia
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described—of which around 1 million are insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a bilaterally symmetric body plan. The Bilateria include the protostomes, containing animals such as nematodes, arthropods, flatworms, annelids and molluscs, and the deuterostomes, containing the echinode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptothecata
Leptothecata, or thecate hydroids, are an order of hydrozoans in the phylum Cnidaria. Their closest living relatives are the athecate hydroids, which are similar enough to have always been considered closely related, and the very apomorphic Siphonophorae, which were placed outside the "Hydroida". Given that there are no firm rules for synonymy for high-ranked taxa, alternative names like Leptomedusa, Thecaphora or Thecata, with or without the ending emended to "-ae", are also often used for Leptothecata. Leptothecata is surrounded by a chitinous outer layer as its exoskeleton, including gonophores, their reproductive organ. Leptothecata obtain radial symmetry, in which their gonads can be found in their radial canals. Their morphological characters normally have ranged from benthic to planktonic stages. Characters associated with benthic are the polyps and colony forms, while planktonic is medusae. Leptothecata has a vast and complex variation among all species within the hydrozo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
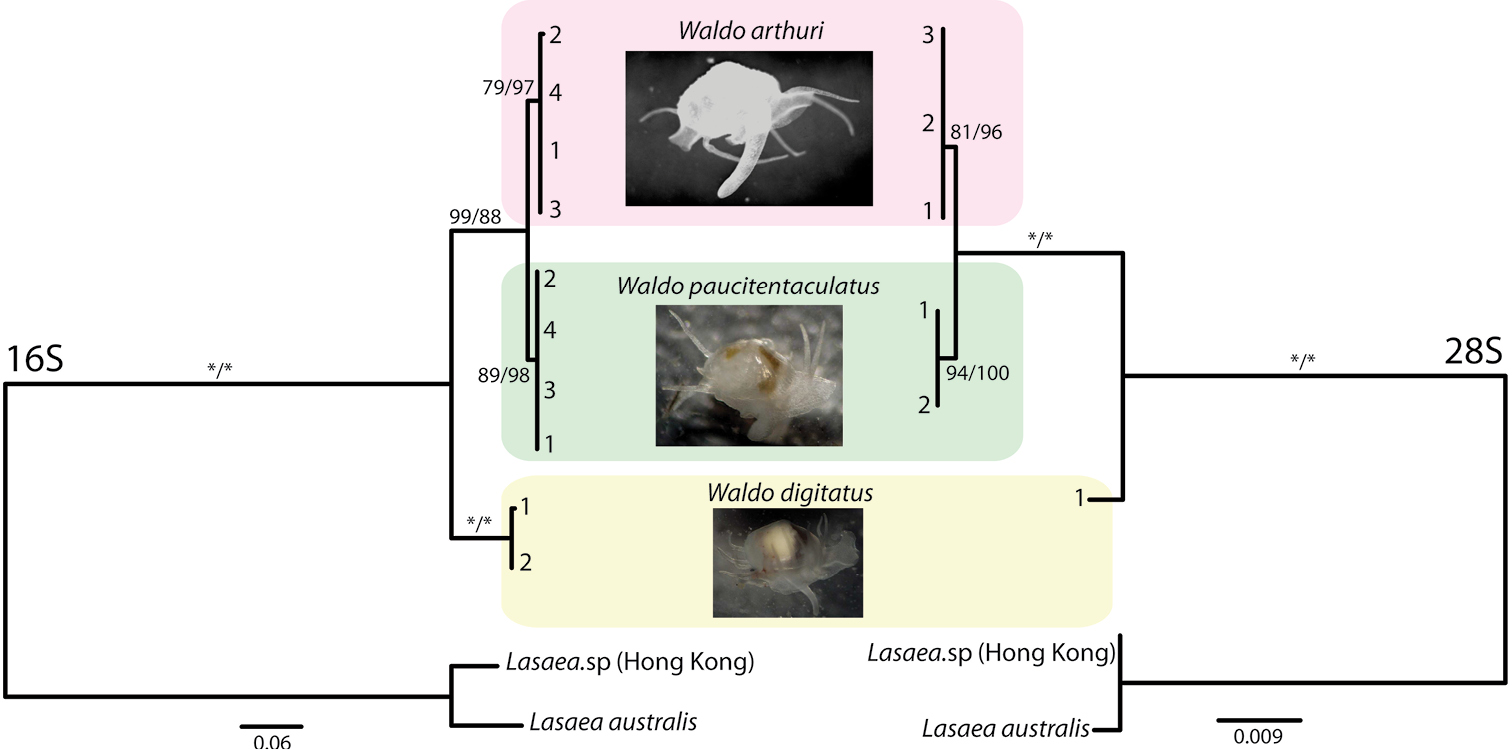
28S RDNA
28S ribosomal RNA is the structural ribosomal RNA (rRNA) for the LSU rRNA, large subunit (LSU) of eukaryotic cytoplasmic ribosomes, and thus one of the basic components of all eukaryotic cells. It has a size of 25S in plants and 28S in mammals, hence the alias of 25S–28S rRNA. Combined with 5.8S rRNA to the 5' side, it is the eukaryotic nuclear homologue of the 23S, prokaryotic 23S and MT-RNR2, mitochondrial 16S ribosomal RNAs. Use in phylogeny The genes coding for 28S rRNA are referred to as 28S rDNA. The comparison of the Nucleic acid sequence, sequences from these genes are sometimes used in molecular analysis to construct phylogenetic trees, for example in protists, Fungus, fungi, insects, arachnids, tardigrades, and vertebrates. Structure The 28S rRNA is typically 4000–5000 nt long. Some eukaryotes cleave 28S rRNA into two parts before assembling both into the ribosome, a phenomenon termed the "hidden break". Databases Several databases provide Sequence al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myxozoa
Myxozoa (etymology: Greek: μύξα ''myxa'' "slime" or "mucus" + thematic vowel o + ζῷον ''zoon'' "animal") is a subphylum of aquatic cnidarian animals – all obligate parasites. It contains the smallest animals ever known to have lived. Over 2,180 species have been described and some estimates have suggested at least 30,000 undiscovered species. Many have a two-host lifecycle, involving a fish and an annelid worm or a bryozoan. The average size of a myxosporean spore usually ranges from 10 μm to 20 μm, whereas that of a malacosporean (a subclade of the Myxozoa) spore can be up to 2 mm. Myxozoans can live in both freshwater and marine habitats. Myxozoans are highly derived cnidarians that have undergone dramatic evolution from a free swimming, self-sufficient jellyfish-like creature into their current form of obligate parasites composed of very few cells – sometimes only a single cell. As myxozoans evolved into microscopic parasites, they lost many g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18S RDNA
18S ribosomal RNA (abbreviated 18S rRNA) is a part of the ribosomal RNA. The S in 18S represents Svedberg units. 18S rRNA is an SSU rRNA, a component of the eukaryotic ribosomal small subunit ( 40S). 18S rRNA is the structural RNA for the small component of eukaryotic cytoplasmic ribosomes, and thus one of the basic components of all eukaryotic cells. 18S rRNA is the eukaryotic cytosolic homologue of 16S ribosomal RNA in prokaryotes and plastids. 18S rRNA is also a homologue of 12S ribosomal RNA in mitochondria. The genes coding for 18S rRNA are referred to as 18S rRNA genes. Sequence data from these genes is widely used in molecular analysis to reconstruct the evolutionary history of organisms, especially in vertebrates, as its slow evolutionary rate makes it suitable to reconstruct ancient divergences. Uses in phylogeny The small subunit (SSU) 18S rRNA gene is one of the most frequently used genes in phylogenetic studies and an important marker for random target polymera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |