|
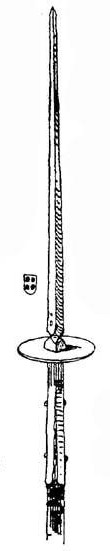
Medieval Weapons
The following is a list of Wikipedia articles of the types of weapons that were in use during the post-classical historical period (roughly between the mid 1st to mid 2nd millennia AD). Offensive weapons Melee weapons Trauma and cleaving weapons * Battle axe * Bec de corbin * Bludgeon * Club * Flail * Flanged mace * Horseman's pick * Mace * Morning star * Quarterstaff * Shestopyor, Pernach * War hammer Swords and hilt weapons Swords can have single or double bladed edges or even edgeless. The blade can be curved or straight. * Arming sword * Dagger * Estoc * Falchion * Katana * Knife * Longsword * Rapier * Sabre or Saber (Most sabers belong to the renaissance period, but some sabers can be found in the late medieval period) * Shortsword * Ulfberht (Frankish) Spears and polearms * Ahlspiess * Bardiche * Bec de Corbin * Bill * Glaive * Goedendag * Guisarme * Halberd * Lance * Lochaber axe * Lucerne hammer * Man catcher * Military fork * Partisan * Pike ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weapon
A weapon, arm or armament is any implement or device that can be used to deter, threaten, inflict physical damage, harm, or kill. Weapons are used to increase the efficacy and efficiency of activities such as hunting, crime, law enforcement, self-defense, warfare, or suicide. In broader context, weapons may be construed to include anything used to gain a tactical, strategic, material or mental advantage over an adversary or enemy target. While ordinary objects – sticks, rocks, bottles, chairs, vehicles – can be used as weapons, many objects are expressly designed for the purpose; these range from simple implements such as clubs, axes and swords, to complicated modern firearms, tanks, intercontinental ballistic missiles, biological weapons, and cyberweapons. Something that has been re-purposed, converted, or enhanced to become a weapon of war is termed weaponized, such as a weaponized virus or weaponized laser. History The use of weapons is a major driver of cult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dagger
A dagger is a fighting knife with a very sharp point and usually two sharp edges, typically designed or capable of being used as a thrusting or stabbing weapon.State v. Martin, 633 S.W.2d 80 (Mo. 1982): This is the dictionary or popular-use definition of a dagger, which has been used to describe everything from an ice pick to a folding knife with pointed blade as a 'dagger'. The Missouri Supreme Court used the popular definition of 'dagger' found in Webster's New Universal Dictionary ("a short weapon with a sharp point used for stabbing") to rule that an ordinary pointed knife with four-to-five inch blade constitutes a 'dagger' under the Missouri criminal code.California Penal Code 12020(a)(24):"dagger" means a ''knife or other instrument'' with or without a handguard that is ''capable of ready use as a stabbing weapon'' that may inflict great bodily injury or death. The State of California and other jurisdictions have seized upon the popular-use definition of a dagger to clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bill (weapon)
A bill is a class of agricultural implement used for trimming tree limbs, which was often repurposed for use as an infantry polearm. In English, the term 'Italian bill' is applied to the similar roncone or roncola, but the Italian version tended to have a long thrusting spike in addition to the cutting blade. The English distinguished among several varieties of bill, including the black, brown and forest bills, but the differences between them are currently not fully understood. Bills were adapted to military use through addition of various projecting blades. Other variants include the bill hook and bill-guisarme. Disambiguation The bill is similar in size, function and appearance to the halberd, and might be said to represent convergent evolution to fill a common niche: a pole-arm with a point to thrust with, a hook to drag with, and a spike/axe to cut with. The bill should not be conflated with a war-scythe, another pole-arm adapted from an agricultural implement, the scythe. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bardiche
A bardiche , berdiche, bardische, bardeche, or berdish is a type of polearm used from the 14th to 17th centuries in Europe. Ultimately a descendant of the medieval sparth or Danish axe, the bardiche proper appears around 1400, but there are numerous medieval manuscripts that depict very similar weapons beginning c. 1250. The bardiche differs from the halberd in having neither a hook at the back nor a spear point at the top. The use of bardiches started in early 14th century Austria and in Scandinavia in the late 15th century. In the 16th century the bardiche became a weapon associated with streltsy (Russian guardsmen armed with firearms). Description he broad-headed axewas succeeded by the ''berdiche'', a pole-axe, longer in shaft and having the narrow lower end of tall blade rounded inward and braced against the shaft. At first this lower end of the blade merely touched the wooden shaft; it then became fastened to it; next it embraced the shaft, developing for this purpose an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahlspiess
The ahlspiess (or awl pike) was a thrusting spear developed and used primarily in Germany and Austria from the 15th to 16th centuries. The ahlspiess consisted of a long thin spike of square cross section measuring up to about a metre (39 inches) in length, mounted on a round wooden shaft and sometimes secured with a pair of langets extending from the socket. The length of the shaft ranged from 1.6 to 1.8 m. (5 - 6 feet), and located at the base of the spike was a rondel guard (a circular metal plate) to protect the hands. Large numbers of these weapons have survived and are kept in the arsenal and museums of Vienna as well as the Metropolitan Museum of Art. Some ahlspiesse have thicker spikes which are round and much shorter than the usual form. These are seen in 14th century illustrations, suggesting that they may have been the precursors of the longer type which came later. These shorter forms are also known by the Italian term ''candeliere'', which refers to a round candlest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulfberht
The Ulfberht swords are a group of about 170 medieval swords found primarily in Northern Europe, dated to the 9th to 11th centuries, with blades inlaid with the inscription ''+VLFBERH+T or +VLFBERHT+''. The word "Ulfberht" is a Frankish personal name, possibly indicating the origin of the blades. Description The swords are at the transitional point between the Viking sword and the high medieval knightly sword. Most have blades of Oakeshott type X. They are also the starting point of the much more varied high medieval tradition of blade inscriptions. The reverse sides of the blades are inlaid with a geometric pattern, usually a braid pattern between vertical strokes. Numerous blades also bear this type of geometric pattern but no ''Vlfberht'' inscription. Ulfberht swords were made during a period when European swords were still predominantly pattern welded ("false Damascus"), but with larger blooms of steel gradually becoming available, so that higher quality swords made af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shortsword
The English language terminology used in the classification of swords is imprecise and has varied widely over time. There is no historical dictionary for the universal names, classification or terminology of swords; a sword was simply a double edged knife. Historical terms without a universal consensus of definition (i.e. "arming sword", "broadsword", "long sword", etc.) were used to label weapons of similar appearance but of different historical periods, regional cultures and fabrication technology. These terms were often described in relation to other unrelated weapons, without regard to their intended use and fighting style. In modern history, many of these terms have been given specific, often arbitrary meanings that are unrelated to any of their historical meanings. Terminology Some of these terms originate contemporaneously with the weapons which they describe. Others are modern or early modern terms used by antiquarians, curators, and modern-day sword enthusiasts for hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saber
A sabre ( French: �sabʁ or saber in American English) is a type of backsword with a curved blade associated with the light cavalry of the early modern and Napoleonic periods. Originally associated with Central European cavalry such as the hussars, the sabre became widespread in Western Europe during the Thirty Years' War. Lighter sabres also became popular with infantry of the early 17th century. In the 19th century, models with less curving blades became common and were also used by heavy cavalry. The military sabre was used as a duelling weapon in academic fencing in the 19th century, giving rise to a discipline of modern sabre fencing (introduced in the 1896 Summer Olympics) loosely based on the characteristics of the historical weapon in that it allows for cuts as well as thrusts. Etymology The English ''sabre'' is recorded from the 1670s, as a direct loan from French, where the ''sabre'' is an alteration of ''sable'', which was in turn loaned from German ''Säbel'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabre
A sabre ( French: �sabʁ or saber in American English) is a type of backsword with a curved blade associated with the light cavalry of the early modern and Napoleonic periods. Originally associated with Central European cavalry such as the hussars, the sabre became widespread in Western Europe during the Thirty Years' War. Lighter sabres also became popular with infantry of the early 17th century. In the 19th century, models with less curving blades became common and were also used by heavy cavalry. The military sabre was used as a duelling weapon in academic fencing in the 19th century, giving rise to a discipline of modern sabre fencing (introduced in the 1896 Summer Olympics) loosely based on the characteristics of the historical weapon in that it allows for cuts as well as thrusts. Etymology The English ''sabre'' is recorded from the 1670s, as a direct loan from French, where the ''sabre'' is an alteration of ''sable'', which was in turn loaned from German ''Säbel'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapier
A rapier () or is a type of sword with a slender and sharply-pointed two-edged blade that was popular in Western Europe, both for civilian use (dueling and self-defense) and as a military side arm, throughout the 16th and 17th centuries. Important sources for rapier fencing include the Italian Bolognese group, with early representatives such as Antonio Manciolino and Achille Marozzo publishing in the 1530s, and reaching the peak of its popularity with writers of the early 1600s (Salvator Fabris, Ridolfo Capo Ferro). In Spain, rapier fencing came to be known under the term of ("dexterity") in the second half of the 16th century, based on the theories of Jerónimo Sánchez de Carranza in his work ("The Philosophy of Arms and of their Dexterity and of Aggression and the Christian Defence"), published in 1569. The best known treatise of this tradition was published in French, by Girard Thibault, in 1630. The French small sword or court sword of the 18th century was a direct co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longsword
A longsword (also spelled as long sword or long-sword) is a type of European sword characterized as having a cruciform hilt with a grip for primarily two-handed use (around ), a straight double-edged blade of around , and weighing approximately . The "longsword" type exists in a morphological continuum with the medieval knightly sword and the Renaissance-era Zweihänder. It was prevalent during the late medieval and Renaissance periods (approximately 1350 to 1550), with early and late use reaching into the 12th and 17th centuries. Names English The longsword has many names in the English language, which, aside from variant spellings, include terms such as "bastard sword" and "hand-and-a-half sword." Of these, "bastard sword" is the oldest, its use being contemporaneous with the weapon's heyday. The French ' and the English "bastard sword" originate in the 15th or 16th century, originally in the general sense of "irregular sword, sword of uncertain origin", but by the mid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knife
A knife ( : knives; from Old Norse 'knife, dirk') is a tool or weapon with a cutting edge or blade, usually attached to a handle or hilt. One of the earliest tools used by humanity, knives appeared at least 2.5 million years ago, as evidenced by the Oldowan tools. Originally made of wood, bone, and stone (such as flint and obsidian), over the centuries, in step with improvements in both metallurgy and manufacturing, knife blades have been made from copper, bronze, iron, steel, ceramic, and titanium. Most modern knives have either fixed or folding blades; blade patterns and styles vary by maker and country of origin. Knives can serve various purposes. Hunters use a hunting knife, soldiers use the combat knife, scouts, campers, and hikers carry a pocket knife; there are kitchen knives for preparing foods (the chef's knife, the paring knife, bread knife, cleaver), table knives (butter knives and steak knives), weapons (daggers or switchblades), knives for throwing or juggling, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |