|
Managed File Transfer
Managed file transfer (MFT) is a technology that provides the secure transfer of data in an efficient and reliable manner. MFT software is marketed to companies as a more secure alternative to using insecure protocols like FTP (file transfer protocol) and HTTP to transfer files. By using an MFT solution, companies can avoid custom scripting and meet compliance requirements. Background From its inception, FTP has made moving large volumes of bulk data between any two entities — including file servers, applications, and trading partners — possible. However, FTP (and other communication protocols such as HTTP and SMTP) do not, on their own, provide a way to secure or manage file transfers. Regardless of the lack of security and management capabilities, many companies have continued to transport large batches of structured and unstructured data using these protocols. This practice is changing, however. According to Gartner Research, "Organizations of all sizes continue to inve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PeSIT
PeSIT (Protocol d’Echanges pour un Systeme Interbancaire de Telecompensation) is a File Transfer Protocol, file transfer protocol developed in 1986 by the French Interbank Teleclearing System Economic Interest GroupingGSIT. Designed by working groups of file transfer experts from large computing centers, it offers basic file transfer functionalities and advanced features for managing mass file transfers and organizing industrial-scale file transfer services. PeSIT connections occur between two named and identifiable partners. The initiator of a connection, acting as the PeSIT requester, negotiates with the PeSIT responder for sending or receiving a file, sending a message, or acknowledging a transfer. The negotiation for file transfer does not involve mentioning the file name or its location in the partners' file systems (File system, FS) but rather a virtual file identified by an identifier, "filename," which corresponds to local sets of definitions for accessing and reading a file ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secure Transmission
Secure may refer to: * Security, being protected against danger or loss(es) **Physical security, security measures that are designed to deny unauthorized access to facilities, equipment, and resources **Information security, defending information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, perusal, inspection, recording or destruction **Secure communication, when two entities are communicating and do not want a third party to listen in * Securitate (Romanian for "security"), the secret service of Communist Romania * Security (finance), e.g. secured loans **Secured transaction, a loan or a credit transaction in which the lender acquires a security interest in collateral owned by the borrower **Secured creditor, a creditor with the benefit of a security interest over some or all of the assets of the debtor * ''Secure'' (G5), a NatureServe conservation status similar to "Least Concern", indicating a species is not at risk of extinction * Sécure River The Séc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
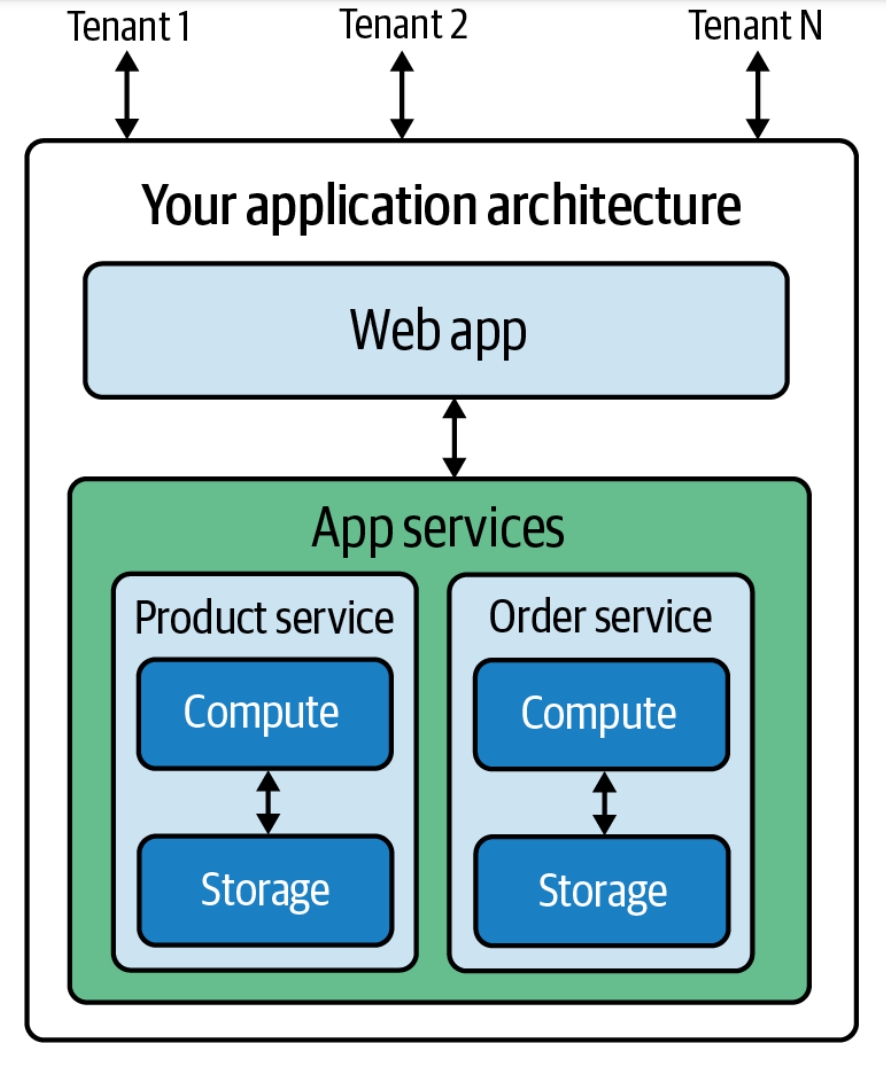
SaaS
Software as a service (SaaS ) is a cloud computing service model where the provider offers use of application software to a client and manages all needed physical and software resources. SaaS is usually accessed via a web application. Unlike other software delivery models, it separates "the possession and ownership of software from its use". SaaS use began around 2000, and by 2023 was the main form of software application deployment. Unlike most self-hosted software products, only one version of the software exists and only one operating system and configuration is supported. SaaS products typically run on rented infrastructure as a service (IaaS) or platform as a service (PaaS) systems including hardware and sometimes operating systems and middleware, to accommodate rapid increases in usage while providing instant and continuous availability to customers. SaaS customers have the abstraction of limitless computing resources, while economy of scale drives down the cost. SaaS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparison Of File Transfer Protocols
This article lists communication protocols that are designed for file transfer over a telecommunications network. Protocols for shared file systems—such as 9P and the Network File System—are beyond the scope of this article, as are file synchronization protocols. Protocols for packet-switched networks A packet-switched network transmits data that is divided into units called '' packets''. A packet comprises a header (which describes the packet) and a payload (the data). The Internet is a packet-switched network, and most of the protocols in this list are designed for its protocol stack, the IP protocol suite. They use one of two transport layer protocols: the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) or the User Datagram Protocol (UDP). In the tables below, the "Transport" column indicates which protocol(s) the transfer protocol uses at the transport layer. Some protocols designed to transmit data over UDP also use a TCP port for oversight. The " Server port" column ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secure File Transfer Program
is a command-line interface client program to transfer files using the SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP), which runs inside the encrypted Secure Shell connection. It provides an interactive interface similar to that of traditional command-line FTP clients. One common implementation of is part of the OpenSSH project. There are other command-line SFTP clients that use different names, such as lftp, PSFTP and PSCP (from PuTTY package) and WinSCP. See also * Comparison of SSH servers * Comparison of SSH clients An SSH client is a software program which uses the secure shell protocol to connect to a Server (computing), remote computer. This article compares a selection of notable clients. General Platform The operating systems or virtual machin ... References Command-line software SSH File Transfer Protocol clients {{security-software-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Application Programming Interface
An application programming interface (API) is a connection between computers or between computer programs. It is a type of software Interface (computing), interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how to build such a connection or interface is called an ''API specification''. A computer system that meets this standard is said to ''implement'' or ''expose'' an API. The term API may refer either to the specification or to the implementation. In contrast to a user interface, which connects a computer to a person, an application programming interface connects computers or pieces of software to each other. It is not intended to be used directly by a person (the end user) other than a computer programmer who is incorporating it into software. An API is often made up of different parts which act as tools or services that are available to the programmer. A program or a programmer that uses one of these parts is said to ''call'' that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Directory
Active Directory (AD) is a directory service developed by Microsoft for Windows domain networks. Windows Server operating systems include it as a set of processes and services. Originally, only centralized domain management used Active Directory. However, it ultimately became an umbrella title for various directory-based identity-related services. A domain controller is a server running the Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) role. It authenticates and authorizes all users and computers in a Windows domain-type network, assigning and enforcing security policies for all computers and installing or updating software. For example, when a user logs into a computer which is part of a Windows domain, Active Directory checks the submitted username and password and determines whether the user is a system administrator or a non-admin user. Furthermore, it allows the management and storage of information, provides authentication and authorization mechanisms, and establishes a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LDAP
The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP ) is an open, vendor-neutral, industry standard application protocol for accessing and maintaining distributed Directory service, directory information services over an Internet Protocol (IP) network. Directory services play an important role in developing intranet and Internet applications by allowing the sharing of information about users, systems, networks, services, and applications throughout the network. As examples, directory services may provide any organized set of records, often with a hierarchical structure, such as a corporate email directory. Similarly, a telephone directory is a list of subscribers with an address and a phone number. LDAP is specified in a series of Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) Standard Track publications known as Request for Comments (RFCs), using the description language ASN.1. The latest specification is Version 3, published aRFC 4511ref name="gracion Gracion.com. Retrieved on 2013-07-17. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Encryption
In cryptography, encryption (more specifically, encoding) is the process of transforming information in a way that, ideally, only authorized parties can decode. This process converts the original representation of the information, known as plaintext, into an alternative form known as ciphertext. Despite its goal, encryption does not itself prevent interference but denies the intelligible content to a would-be interceptor. For technical reasons, an encryption scheme usually uses a pseudo-random encryption key generated by an algorithm. It is possible to decrypt the message without possessing the key but, for a well-designed encryption scheme, considerable computational resources and skills are required. An authorized recipient can easily decrypt the message with the key provided by the originator to recipients but not to unauthorized users. Historically, various forms of encryption have been used to aid in cryptography. Early encryption techniques were often used in military m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HTTPS
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is an extension of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). It uses encryption for secure communication over a computer network, and is widely used on the Internet. In HTTPS, the communication protocol is encrypted using Transport Layer Security (TLS) or, formerly, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). The protocol is therefore also referred to as HTTP over TLS, or HTTP over SSL. The principal motivations for HTTPS are authentication of the accessed website and protection of the privacy and integrity of the exchanged data while it is in transit. It protects against man-in-the-middle attacks, and the bidirectional block cipher encryption of communications between a client and server protects the communications against eavesdropping and tampering. The authentication aspect of HTTPS requires a trusted third party to sign server-side digital certificates. This was historically an expensive operation, which meant fully authenticated HTTPS conn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secure Copy
Secure copy protocol (SCP) is a means of securely transferring computer files between a local host and a remote server (computing), host or between two remote hosts. It is based on the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol. "SCP" commonly refers to both the Secure Copy Protocol and the program itself. According to OpenSSH developers in April 2019, SCP is outdated, inflexible and not readily fixed; they recommend the use of more modern protocols like SSH File Transfer Protocol, SFTP and rsync for file transfer. As of OpenSSH version 9.0, scp client therefore uses SFTP for file transfers by default instead of the legacy SCP/RCP protocol. Secure Copy Protocol The SCP is a network protocol, based on the BSD rcp (Unix), RCP protocol, which supports file transfers between hosts on a network. SCP uses Secure Shell (SSH) for data transfer and uses the same mechanisms for authentication, thereby ensuring the Information security#Authenticity, authenticity and confidentiality of the data in trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SSH File Transfer Protocol
In computing, the SSH File Transfer Protocol, also known as Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP), is a network protocol that provides file access, file transfer, and file management over any reliable data stream. It was designed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) as an extension of the Secure Shell protocol (SSH) version 2.0 to provide secure file transfer capabilities, and is seen as a replacement of File Transfer Protocol (FTP) due to superior security. The IETF Internet Draft states that, even though this protocol is described in the context of the SSH-2 protocol, it could be used in a number of different applications, such as secure file transfer over Transport Layer Security (TLS) and transfer of management information in VPN applications. This protocol assumes that it is run over a secure channel, such as SSH, that the server has already authenticated the client, and that the identity of the client user is available to the protocol. Capabilities Compar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |