|
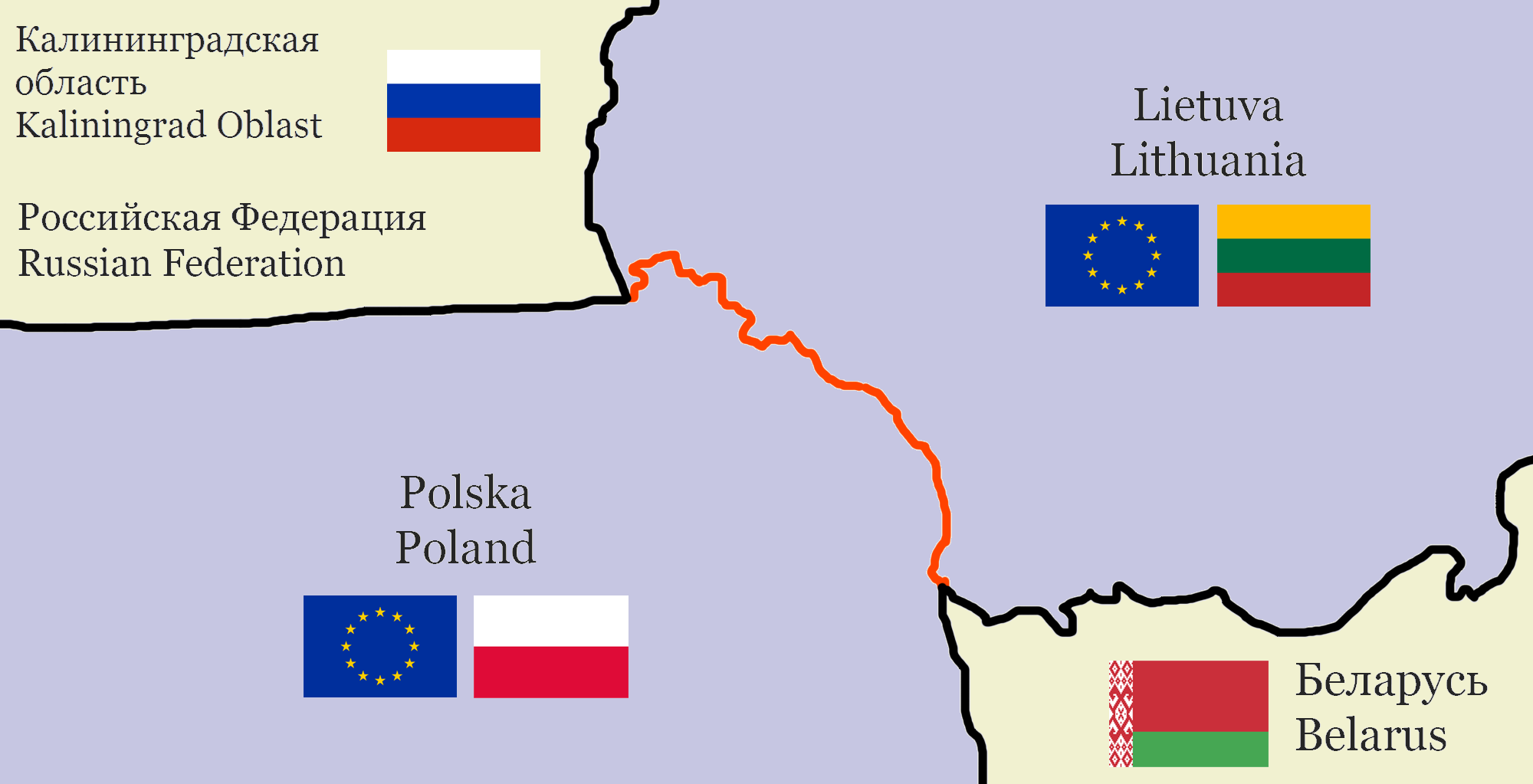
Lithuania–Poland Border
The Lithuania–Poland border is the state border between the Republic of Lithuania and the Republic of Poland. The length of the border is .. Page gives Polish PWN Encyklopedia as reference. It runs from the Lithuania–Poland–Russia tripoint southeast to the Belarus–Lithuania–Poland tripoint. It is an internal border of the European Union and the Schengen Zone. It is the only land border that one of the Baltic states (which are members of the EU and NATO) shares with a country that is not a member of the Commonwealth of Independent States. History In medieval times, the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania had a vast and often changing border.Stephen R. Burant and Voytek Zubek, ''Eastern Europe's Old Memories and New Realities: Resurrecting the Polish–Lithuanian Union'', East European Politics and Societies 1993; 7; 370online/ref> From the Union of Lublin (1569) to the Partitions of Poland, there was no Polish-Lithuanian border, as both countries wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suwałki Agreement
The Suwałki Agreement, Treaty of Suvalkai, or Suwalki Treaty ( pl, Umowa suwalska, lt, Suvalkų sutartis) was an agreement signed in the town of Suwałki between Poland and Lithuania on October 7, 1920. It was registered in the '' League of Nations Treaty Series'' on January 19, 1922. Both countries had re-established their independence in the aftermath of World War I and did not have well-defined borders. They waged the Polish–Lithuanian War over territorial disputes in the Suwałki and Vilnius Regions. At the end of September 1920, Polish forces defeated the Soviets at the Battle of the Niemen River, thus militarily securing the Suwałki Region and opening the possibility of an assault on the city of Vilnius (Wilno). Polish Chief of State, Józef Piłsudski, had planned to take over the city since mid-September in a false flag operation known as Żeligowski's Mutiny. Under pressure from the League of Nations, Poland agreed to negotiate, hoping to buy time and divert atte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congress Poland
Congress Poland, Congress Kingdom of Poland, or Russian Poland, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland, was a polity created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna as a semi-autonomous Polish state, a successor to Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. It was established when the French ceded a part of Polish territory to the Russian Empire following France's defeat in the Napoleonic Wars. In 1915, during World War I, it was replaced by the German-controlled nominal Regency Kingdom until Poland regained independence in 1918. Following the partitions of Poland at the end of the 18th century, Poland ceased to exist as an independent nation for 123 years. The territory, with its native population, was split between the Habsburg monarchy, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Russian Empire. After 1804, an equivalent to Congress Poland within the Austrian Empire was the Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria, also commonly referred to as "Austrian Poland". The area incorporated into Prussia and subse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragoon Ride 150323-A-WZ553-127
Dragoons were originally a class of mounted infantry, who used horses for mobility, but dismounted to fight on foot. From the early 17th century onward, dragoons were increasingly also employed as conventional cavalry and trained for combat with swords and firearms from horseback. While their use goes back to the late 16th century, dragoon regiments were established in most European armies during the 17th and early 18th centuries; they provided greater mobility than regular infantry but were far less expensive than cavalry. The name reputedly derives from a type of firearm, called a ''dragon'', which was a handgun version of a blunderbuss, carried by dragoons of the French Army. The title has been retained in modern times by a number of armoured or ceremonial mounted regiments. Origins and name The establishment of dragoons evolved from the practice of sometimes transporting infantry by horse when speed of movement was needed. In 1552, Alexander Farnese, Duke of Parma mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schengen Area
The Schengen Area ( , ) is an area comprising 27 European countries that have officially abolished all passport and all other types of border control at their mutual borders. Being an element within the wider area of freedom, security and justice policy of the EU, it mostly functions as a single jurisdiction under visa policies in the European Union, a common visa policy for international travel purposes. The area is named after the 1985 Schengen Agreement and the 1990 Schengen Convention, both signed in Schengen, Luxembourg. Of the 27 EU member states of the European Union, member states, 23 participate in the Schengen Area. Of the five EU members that are not part of the Schengen Area, three—Bulgaria and the European Union, Bulgaria, Cyprus and the European Union, Cyprus and Romania and the European Union, Romania—are legally obligated to join the area in the future; Croatia has been approved to join on January 1, 2023; Ireland and the European Union, Ireland maintains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Act Of The Re-Establishment Of The State Of Lithuania
The Act of the Re-Establishment of the State of Lithuania or Act of March 11 ( lt, Aktas dėl Lietuvos nepriklausomos valstybės atstatymo) was an independence declaration by Lithuania adopted on March 11, 1990, signed by all members of the Supreme Council of the Republic of Lithuania led by Sąjūdis. The act emphasized restoration and legal continuity of the interwar-period Lithuania, which was occupied by the Soviet Union and lost independence in June 1940. It was the first Soviet republic of the 15 Soviet republics to declare independence from the Soviet Union. The other 14 Soviet republics would later declare their independence. These events (being part of the broader process dubbed the "parade of sovereignties") would lead to the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. Background Loss of independence After the partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in the 18th century, Lithuania was part of the Russian Empire. In the aftermath of the Russian Revolution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occupation Of The Baltic States
The Baltic states of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania were invaded and occupied in June 1940 by the Soviet Union, under the leadership of Stalin and auspices of the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact that had been signed between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union in August 1939, immediately before the outbreak of World War II. The three countries were then annexed into the Soviet Union (formally as " constituent republics") in August 1940. The United States and most other Western countries never recognised this incorporation, considering it illegal. On 22 June 1941, Nazi Germany attacked the Soviet Union and within weeks occupied the Baltic territories. In July 1941, the Third Reich incorporated the Baltic territory into its ''Reichskommissariat Ostland''. As a result of the Red Army's Baltic Offensive of 1944, the Soviet Union recaptured most of the Baltic states and trapped the remaining German forces in the Courland pocket until their formal surrender in May 1945. Latvian plenipotentiar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aftermath Of World War II
The aftermath of World War II was the beginning of a new era started in late 1945 (when World War II ended) for all countries involved, defined by the decline of all colonial empires and simultaneous rise of two superpowers; the Soviet Union (USSR) and the United States (US). Once Allies during World War II, the US and the USSR became competitors on the world stage and engaged in the Cold War, so called because it never resulted in overt, declared total war between the two powers but was instead characterized by espionage, political subversion and proxy wars. Western Europe and Asia were rebuilt through the American Marshall Plan, whereas Central and Eastern Europe fell under the Soviet sphere of influence and eventually behind an "Iron Curtain". Europe was divided into a US-led Western Bloc and a USSR-led Eastern Bloc. Internationally, alliances with the two blocs gradually shifted, with some nations trying to stay out of the Cold War through the Non-Aligned Movement. The war als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suwałki Region
Suwałki Region ( pl, Suwalszczyzna ; lt, Suvalkų kraštas, Suvalkija, russian: cувалкщина, german: Sudauen) is a small region around the city of Suwałki (known in Lithuanian as ''Suvalkai'') in northeastern Poland near the border with Lithuania. It encompasses the powiats of Augustów, Suwałki, and Sejny, and roughly corresponds to the southern part of the former Suwałki Governorate. The region was disputed between Poland and Lithuania after their re-emergence as independent states following World War I. This dispute along with the Vilnius question was the cause of the Polish-Lithuanian War and the Sejny Uprising. The area has been subsequently part of Poland until today, with the exception of the German and Soviet occupation during World War II. The Suwałki Region remains as the center of the Lithuanian minority in Poland. History The Neolithic era ushered in the first settled agricultural communities in the area of present-day Poland, whose founders had migra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demarcation Line
{{Refimprove, date=January 2008 A political demarcation line is a geopolitical border, often agreed upon as part of an armistice or ceasefire. Africa * Moroccan Wall, delimiting the Moroccan-controlled part of Western Sahara from the Sahrawi-controlled part Americas * The Line of Demarcation was one specific line drawn along a meridian in the Atlantic Ocean as part of the Treaty of Tordesillas in 1494 to divide new lands claimed by Portugal from those of Spain. This line was drawn in 1493 after Christopher Columbus returned from his maiden voyage to the Americas. * The Mason–Dixon line (or "Mason and Dixon's Line") is a demarcation line between four U.S. states, forming part of the borders of Pennsylvania, Maryland, Delaware, and West Virginia (then part of Virginia). It was surveyed between 1763 and 1767 by Charles Mason and Jeremiah Dixon in the resolution of a border dispute between British colonies in Colonial America. Asia Middle East * The Blue Line is a bor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish–Lithuanian War
The Polish–Lithuanian War (in Polish historiography, Polish–Lithuanian Conflict) was an undeclared war between newly-independent Lithuania and Poland following World War I, which happened mainly, but not only, in the Vilnius and Suwałki regions. The war is viewed differently by the respective sides. According to Lithuanian historians, it was part of the Lithuanian Wars of Independence and lasted from May 1919 to 29 November 1920. Polish historians deem the Polish-Lithuanian war as occurring only in September–October 1920. From the spring of 1920, the conflict also became part of the wider Polish–Soviet War and was largely shaped by its progress. It was subject to international mediation at the Conference of Ambassadors and the League of Nations. In the aftermath of World War I, the military and political situation in the region was chaotic, as multiple countries, notably Lithuania, Poland, and Soviet Russia, vied with each other over control of these areas. The Polish-Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 1918 and 1939. The state was established on 6 November 1918, before the end of the First World War. The Second Republic ceased to exist in 1939, when Invasion of Poland, Poland was invaded by Nazi Germany, the Soviet Union and the Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovak Republic, marking the beginning of the European theatre of World War II, European theatre of the Second World War. In 1938, the Second Republic was the sixth largest country in Europe. According to the Polish census of 1921, 1921 census, the number of inhabitants was 27.2 million. By 1939, just before the outbreak of World War II, this had grown to an estimated 35.1 million. Almost a third of the population came from minority groups: 13.9% Ruthenians; 10% Ashkenazi Jews; 3.1% Belarusians; 2.3% Germans and 3.4% Czechs and Lithuanians. At the same time, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vilna Governorate
The Vilna Governorate (1795–1915; also known as Lithuania-Vilnius Governorate from 1801 until 1840; russian: Виленская губерния, ''Vilenskaya guberniya'', lt, Vilniaus gubernija, pl, gubernia wileńska) or Government of Vilnius was a governorate (') of the Russian Empire created after the Third Partition of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1795. It was part of the Lithuanian General Governorate, which was called the Vilnius General Governorate after 1830, and was attached to the Northwestern Krai. The seat was in Vilnius (Vilna in Russian), where the Governors General resided. History The first governorates, Vilnius Governorate (consisting of eleven uyezds or districts) and Slonim Governorate, were established after the third partition of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. Just a year later, on December 12, 1796, by order of Tsar Paul I they were merged into one governorate, called the Lithuanian Governorate, with its capital in Vilnius. By orde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |