|
Literary Archetypes
Archetypal literary criticism is a type of analytical theory that interprets a text by focusing on recurring myths and archetypes (from the Greek ''archē'', "beginning", and ''typos'', "imprint") in the narrative, symbols, images, and character types in literary works. As an acknowledged form of literary criticism, it dates back to 1934 when Classical scholar Maud Bodkin published '' Archetypal Patterns in Poetry''. Archetypal literary criticism's origins are rooted in two other academic disciplines, social anthropology and psychoanalysis; each contributed to literary criticism in separate ways. Archetypal criticism peaked in popularity in the 1940s and 1950s, largely due to the work of Canadian literary critic Northrop Frye (1912-1991). In the twenty-first century, archetypal literary criticism is no longer widely practiced; there have not been any major recent developments in the field (with the possible exception of biblical literary criticism), but it still has a place in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analytical Psychology
Analytical psychology (, sometimes translated as analytic psychology; also Jungian analysis) is a term referring to the psychological practices of Carl Jung. It was designed to distinguish it from Freud's psychoanalytic theories as their seven-year collaboration on psychoanalysis was drawing to an end between 1912 and 1913. The evolution of his science is contained in his monumental ''opus'', the '' Collected Works'', written over sixty years of his lifetime. The history of analytical psychology is intimately linked with the biography of Jung. At the start, it was known as the "Zurich school", whose chief figures were Eugen Bleuler, Franz Riklin, Alphonse Maeder and Jung, all centred in the Burghölzli hospital in Zurich. It was initially a theory concerning psychological complexes until Jung, upon breaking with Sigmund Freud, turned it into a generalised method of investigating archetypes and the unconscious, as well as into a specialised psychotherapy. Analytical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persephone
In ancient Greek mythology and Ancient Greek religion, religion, Persephone ( ; , classical pronunciation: ), also called Kore ( ; ) or Cora, is the daughter of Zeus and Demeter. She became the queen of the Greek underworld, underworld after her abduction by her uncle Hades, the king of the underworld, who would later take her into marriage. The myth of her abduction, her sojourn in the underworld, and her cyclical return to the surface represents her functions as the embodiment of spring and the personification of vegetation, especially grain crops, which disappear into the earth when sown, sprout from the earth in spring, and are harvested when fully grown. In Art in ancient Greece, Classical Greek art, Persephone is invariably portrayed robed, often carrying a wikt:sheaf, sheaf of grain. She may appear as a mystical divinity with a sceptre and a little box, but she was mostly represented in the process of being carried off by Hades. Persephone, as a vegetation deity, veg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comedy
Comedy is a genre of dramatic works intended to be humorous or amusing by inducing laughter, especially in theatre, film, stand-up comedy, television, radio, books, or any other entertainment medium. Origins Comedy originated in ancient Greece: in Athenian democracy, the public opinion of voters was influenced by political satire performed by comic poets in Ancient Greek theatre, theaters. The theatrical genre of Greek comedy can be described as a dramatic performance pitting two groups, ages, genders, or societies against each other in an amusing ''agon'' or conflict. Northrop Frye depicted these two opposing sides as a "Society of Youth" and a "Society of the Old". A revised view characterizes the essential agon of comedy as a struggle between a relatively powerless youth and the societal conventions posing obstacles to his hopes. In this struggle, the youth then becomes constrained by his lack of social authority, and is left with little choice but to resort to ruses which e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiotics
Semiotics ( ) is the systematic study of sign processes and the communication of meaning. In semiotics, a sign is defined as anything that communicates intentional and unintentional meaning or feelings to the sign's interpreter. Semiosis is any activity, conduct, or process that involves signs. Signs often are communicated by verbal language, but also by gestures, or by other forms of language, e.g. artistic ones (music, painting, sculpture, etc.). Contemporary semiotics is a branch of science that generally studies meaning-making (whether communicated or not) and various types of knowledge. Unlike linguistics, semiotics also studies non-linguistic sign systems. Semiotics includes the study of indication, designation, likeness, analogy, allegory, metonymy, metaphor, symbolism, signification, and communication. Semiotics is frequently seen as having important anthropological and sociological dimensions. Some semioticians regard every cultural phenomenon as being able to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structuralism
Structuralism is an intellectual current and methodological approach, primarily in the social sciences, that interprets elements of human culture by way of their relationship to a broader system. It works to uncover the structural patterns that underlie all the things that humans do, think, perceive, and feel. Alternatively, as summarized by philosopher Simon Blackburn, structuralism is: Blackburn, Simon, ed. 2008. "Structuralism." In '' Oxford Dictionary of Philosophy'' (2nd rev. ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. . p. 353."The belief that phenomena of human life are not intelligible except through their interrelations. These relations constitute a structure, and behind local variations in the surface phenomena there are constant laws of abstract structure." History and background The term ''structuralism'' is ambiguous, referring to different schools of thought in different contexts. As such, the movement in humanities and social sciences called structuralism r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Criticism
New Criticism was a Formalism (literature), formalist movement in literary theory that dominated American literary criticism in the middle decades of the 20th century. It emphasized close reading, particularly of poetry, to discover how a work of literature functioned as a self-contained, self-referential aesthetic object. The movement derived its name from John Crowe Ransom's 1941 book ''The New Criticism''. The works of University of Cambridge, Cambridge scholar I. A. Richards, especially his ''Practical Criticism'', ''The Principles of Literary Criticism'' and ''The Meaning of Meaning'', which offered what was claimed to be an empirical scientific approach, were important to the development of a New Critical methodology. Cleanth Brooks, John Crowe Ransom, W. K. Wimsatt, and Monroe Beardsley also made significant contributions to New Criticism. It was Wimsatt and Beardsley who introduced the ideas of Authorial intent, intentional fallacy and affective fallacy. Also very influenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomy Of Criticism
''Anatomy of Criticism: Four Essays'' (Princeton University Press, 1957) is a book by Canadian literary critic and theorist Northrop Frye that attempts to formulate an overall view of the scope, theory, principles, and techniques of literary criticism derived exclusively from literature. Frye consciously omits all specific and practical criticism, instead offering classically inspired theories of modes, symbols, myths and genres, in what he termed "an interconnected group of suggestions." The literary approach proposed by Frye in ''Anatomy'' was highly influential in the decades before deconstructivist criticism and other expressions of postmodernism came to prominence in American academia circa 1980s. Frye's four essays are sandwiched between a "Polemical Introduction" and a "Tentative Conclusion." The four essays are titled "Historical Criticism: Theory of Modes", "Ethical Criticism: Theory of Symbols", "Archetypal Criticism: A Theory of Myths", and "Rhetorical Criticism: Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
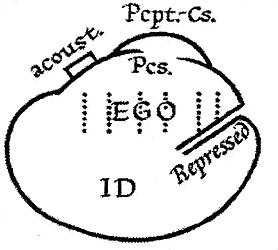
Ego, Super-ego, And Id
In psychoanalytic theory, the id, ego, and superego are three distinct, interacting agents in the psychic apparatus, outlined in Sigmund Freud's structural model of the psyche. The three agents are theoretical constructs that Freud employed to describe the basic structure of mental life as it was encountered in psychoanalytic practice. Freud himself used the German terms ''das Es'', ''Ich'', and ''Über-Ich'', which literally translate as "the it", "I", and "over-I". The Latin terms id, ego and superego were chosen by his original translators and have remained in use. The structural model was introduced in Freud's essay '' Beyond the Pleasure Principle'' (1920) and further refined and formalised in later essays such as ''The Ego and the Id'' (1923). Freud developed the model in response to the perceived ambiguity of the terms "conscious" and "unconscious" in his earlier ''topographical'' model. Broadly speaking, the id is the organism's unconscious array of uncoordinated ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Objective Psyche
In psychology, the collective unconsciousness () is a term coined by Carl Jung, which is the belief that the unconscious mind comprises the instincts of Jungian archetypes—innate symbols understood from birth in all humans. Jung considered the collective unconscious to underpin and surround the unconscious mind, distinguishing it from the personal unconscious of Freudian psychoanalysis. He believed that the concept of the collective unconscious helps to explain why similar themes occur in mythologies around the world. He argued that the collective unconscious had a profound influence on the lives of individuals, who lived out its symbols and clothed them in meaning through their experiences. The psychotherapeutic practice of analytical psychology revolves around examining the patient's relationship to the collective unconscious. Psychiatrist and Jungian analyst Lionel Corbett argues that the contemporary terms "autonomous psyche" or "objective psyche" are more commonly used toda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |