|
Languages Of Estonia
The official language of Estonia is Estonian language, Estonian, a Uralic languages, Uralic language of the Finnic languages, Finnic branch, which is related to Finnish language, Finnish. It is unrelated to the bordering Russian language, Russian and Latvian language, Latvian languages, both of which are Indo-European languages, Indo-European (more specifically East Slavic languages, East Slavic and Baltic languages, Baltic, respectively). Minority languages Võro Võro language, Võro is a language from the Finnic languages, Finnic branch of the Uralic languages. It used to be considered a dialect of the South Estonian, South Estonian dialect group of the Estonian language, but nowadays it has its own literary standard and is in search of official recognition as an indigenous regional language of Estonia. Seto dialect Seto dialect, Seto is a language from the Finnic languages, Finnic branch of the Uralic languages. It is sometimes identified as a dialect of either South Es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estonian Language
Estonian ( ) is a Finnic language and the official language of Estonia. It is written in the Latin script and is the first language of the majority of the country's population; it is also an official language of the European Union. Estonian is spoken natively by about 1.1 million people: 922,000 people in Estonia and 160,000 elsewhere. Classification By Convention (norm), conventions of historical linguistics, Estonian is classified as a part of the Finnic languages, Finnic (a.k.a. Baltic Finnic) branch of the Uralic languages, Uralic (a.k.a. Uralian, or Finno-Ugric languages, Finno-Ugric) language family. Other Finnic languages include Finnish language, Finnish and several endangered languages spoken around the Baltic Sea and in northwestern Russia. Estonian is typically subclassified as a Southern Finnic language, and it is the second-most-spoken language among all the Finnic languages. Alongside Finnish, Hungarian language, Hungarian and Maltese language, Maltese, Estonian is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uralic Languages
The Uralic languages ( ), sometimes called the Uralian languages ( ), are spoken predominantly in Europe and North Asia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian, Finnish, and Estonian. Other languages with speakers above 100,000 are Erzya, Moksha, Mari, Udmurt and Komi spoken in the European parts of the Russian Federation. Still smaller minority languages are Sámi languages of the northern Fennoscandia; other members of the Finnic languages, ranging from Livonian in northern Latvia to Karelian in northwesternmost Russia; the Samoyedic languages and the others of members of the Ugric languages, Mansi and Khanty spoken in Western Siberia. The name ''Uralic'' derives from the family's purported "original homeland" (''Urheimat'') hypothesized to have been somewhere in the vicinity of the Ural Mountains, and was first proposed by Julius Klaproth in ''Asia Polyglotta'' (1823). Finno-Ugric is sometimes used as a synonym for Uralic but more accu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Võros
Võros ( Võro: ''võrokõsõq,'' pronounced , , ) are the indigenous inhabitants of historical Võromaa (''Vana Võromaa''), a region in Southeastern Estonia (Võru and Põlva Counties with parts extending into Valga and Tartu Counties). The term is particularly used by proponents of a regional identity. About 70,000 people live in historical Võromaa and many more identify as Võros although they live outside the territory, mostly in Tartu and Tallinn. See also * Võru County Võru County ( or ''Võrumaa''; ) is a county in southern Estonia. It is bordered by Valga and Põlva counties, Latvia's Alūksne and Ape municipalities, and Russia's Pskov Oblast (making it the only Estonian county to border two countries) ... (Võrumaa, Võromaa) * Võro language * Võro Institute * '' Uma Leht'' External linksInformation about Võros in Eurominority References *Ehala, Martin & Niglas, Katrin (2007): Empirical evaluation of a mathematical model of ethnolinguistic v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, officially the Orthodox Catholic Church, and also called the Greek Orthodox Church or simply the Orthodox Church, is List of Christian denominations by number of members, one of the three major doctrinal and jurisdictional groups of Christianity, with approximately 230 million baptised members. It operates as a Communion (Christian), communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its Bishop (Orthodox Church), bishops via local Holy Synod, synods. The church has no central doctrinal or governmental authority analogous to the pope of the Catholic Church. Nevertheless, the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople is recognised by them as ''primus inter pares'' (), a title held by the patriarch of Rome prior to 1054. As one of the oldest surviving religious institutions in the world, the Eastern Orthodox Church has played an especially prominent role in the history and culture of Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeastern Europe. Since 2018, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Setomaa
Setomaa (; , ) is a region south of Lake Peipus and traditionally inhabited by the Setos, Seto people. The Seto dialect is a variety of South Estonian language, South Estonian. The historic range of Setomaa is located in the territories of present-day Estonia and Russia. Estonian Setomaa presently consists of lands in Võru County located in southeastern Estonia and bordering Russia. Petseri (Russian: Pechory) has been the historic and cultural centre for the Setos. Current subdivision Estonian Setomaa consists of: *In Võrumaa county: **Setomaa Parish (municipality) The Russian part consists of Pechorsky District, part of Pskov Oblast. Between 1918 and 1944, the area was part of Estonia, administered as Petseri County. After Estonia regained its independence from the Soviet Union in 1991, there was a dispute between Estonia and Russia over the possession of this territory until Estonia dropped its territorial claims to these areas in 1995. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders of Russia, land borders with fourteen countries. Russia is the List of European countries by population, most populous country in Europe and the List of countries and dependencies by population, ninth-most populous country in the world. It is a Urbanization by sovereign state, highly urbanised country, with sixteen of its urban areas having more than 1 million inhabitants. Moscow, the List of metropolitan areas in Europe, most populous metropolitan area in Europe, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, while Saint Petersburg is its second-largest city and Society and culture in Saint Petersburg, cultural centre. Human settlement on the territory of modern Russia dates back to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Setos
Setos (, , , ) are an indigenous Finnic peoples and linguistic minority that have historically lived in the borderlands between modern day Estonia and Russia. Setos have historically spoken the Seto language and been Orthodox Christians.Kalkun, A., Kupari, H., & Vuola, E. (2018). ''Coping with Loss of Homeland through Orthodox Christian Processions: Contemporary Practices among Setos, Karelians, and Skolt Sámi in Estonia and Finland''. ''Practical matters'', ''11''. http://practicalmattersjournal.org/2018/06/11/coping-with-loss-of-homeland-2/ The Seto language (like Estonian and Finnish) belongs to the Finnic group of the Uralic language family. Since the early 2000s, the Setos have sought greater recognition, rather than having their language considered a dialect of Estonian. Eastern Orthodox Christianity, with influences from local folk religions is widely practiced by the Seto peoples. The ancestral homes of many Setos can be found to the south of Lake Peipus, in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tartu Language
The Tartu dialect (Estonian: ') is a dialect of South Estonian spoken in Estonia, near the city of Tartu. It bears similarities to Mulgi dialect, Mulgi, particularly the Tarvastu and Helme varieties. It has historically, along with northern Võro language, Võro, been the basis for the South Estonian literary language. Usage In the 2011 Estonian census, 4109 people were reported to be speaking the Tartu language, and in the 17310 people were reported to have spoken the language. It reached its peak in the 17th century and declined until the 2000s. Its speaker numbers have been increasing ever since, but the majority of speakers are aging, and there is a lack of media in Tartu. Revival movements for Tartu have not been as strong as those for the Seto dialect, Seto, Mulgi dialect, Mulgi and Võro language, Võro languages. Literature Jakob Hurt's collection "Eesti mõtteloo" contains his sermons in the Rõngu dialect of Tartu. In modern literature, Mats Traat was the main u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regional Language
* A regional language is a language spoken in a region of a sovereign state, whether it be a small area, a federated state or province or some wider area. Internationally, for the purposes of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages, "''regional or minority languages''" ''means languages that are:'' #''traditionally used within a given territory of a State by nationals of that State who form a group numerically smaller than the rest of the State's population and'' #''different from the official language(s) of that State'' Recognition of regional or minority languages must not be confused with recognition as an official language. Relationship with official languages In some cases, a regional language may be closely related to the state's main language or official language. For example: *The Frisian languages spoken in the Netherlands and Germany, which belong to the Germanic family. *The Gutnish language, a regional language spoken in Gotland and related to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
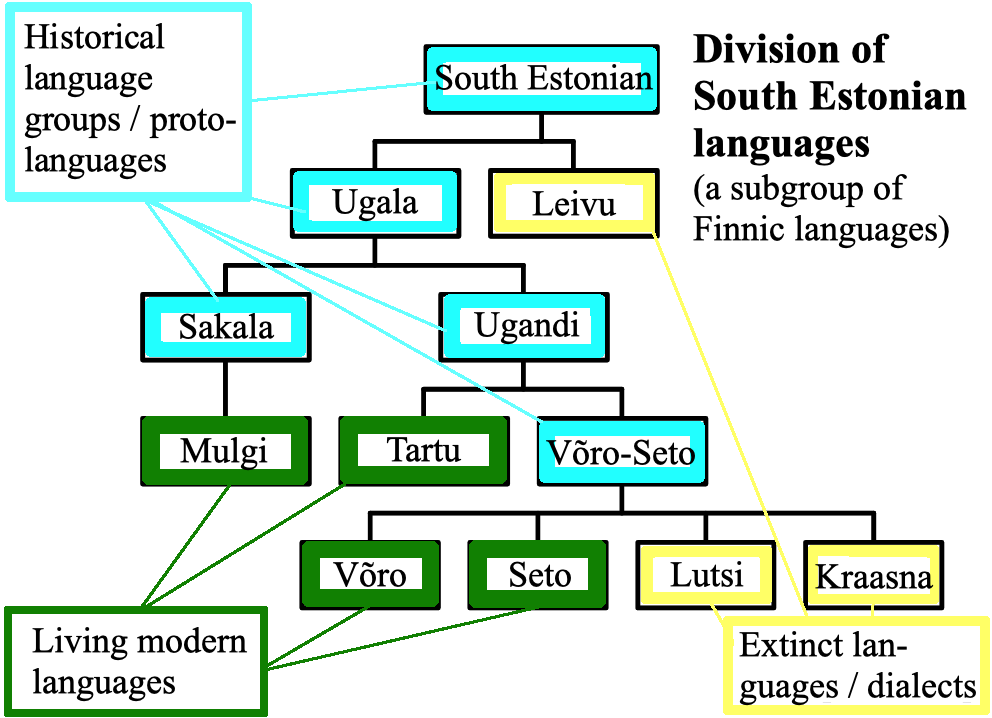
South Estonian
South Estonian, or Võro-Seto, is a Finnic language spoken in south-eastern Estonia, encompassing the Tartu, Mulgi, Võro and Seto dialects. Diachronically speaking, Estonian and South Estonian are in separate branches of the Finnic languages, with Estonian being more closely related to Finnish than it is to South Estonian. Note that reconstructed *č and *c stand for affricates , . Modern Standard Estonian has evolved on the basis of the dialects of Northern Estonian. However, from the 17th to the 19th centuries in Southern Estonia, literature was published in a standardized form of Southern Tartu and Northern Võro. That usage was called Tartu or literary South Estonian. The written standard was used in the schools, churches and courts of the Võro and Tartu linguistic area but not in the Seto and Mulgi areas. After Estonia gained independence in 1918, the standardized Estonian language policies were implemented further throughout the country. The government officials ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Languages
The Baltic languages are a branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family spoken natively or as a second language by a population of about 6.5–7.0 million people''"Lietuviai Pasaulyje"'' (PDF) (in Lithuanian). Lietuvos statistikos departamentas. Retrieved 5 May 2015. mainly in areas extending east and southeast of the Baltic Sea in Europe. Together with the Slavic languages, they form the Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European family. Scholars usually regard them as a single Subgrouping, subgroup divided into two branches: West Baltic languages, West Baltic (containing only extinct languages) and East Baltic languages, East Baltic (containing at least two Modern language, living languages, Lithuanian language, Lithuanian, Latvian l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Slavic Languages
The East Slavic languages constitute one of three regional subgroups of the Slavic languages, distinct from the West Slavic languages, West and South Slavic languages. East Slavic languages are currently spoken natively throughout Eastern Europe, and eastwards to Siberia and the Russian Far East. In part due to the large historical influence of the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union, the Russian language, Russian language is also spoken as a lingua franca in many regions of the Caucasus and Central Asia. Of the three Slavic branches, East Slavic is the most spoken, with the number of native speakers larger than the Western and Southern branches combined. The common consensus is that Belarusian language, Belarusian, Russian language, Russian and Ukrainian language, Ukrainian are the extant East Slavic languages. Some linguists also consider Rusyn language, Rusyn a separate language, although it is sometimes considered a dialect of Ukrainian. The modern East Slavic languages desce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |