|
Lakes Of Lithuania
There are about 6,000 lakes in Lithuania, covering 950 km², or 1.5% of the territory of Lithuania. The lakes are not evenly distributed; most are situated in the Baltic Highlands, which begin near the border with Poland on the southeast and extend northward along the border with Belarus to Latvia. About 1,200 are supported only by groundwater and neither receive nor distribute any surface water. However, many of the other lakes are interconnected by complex passages and rivulets. These lake systems are major tourist attractions in Aukštaitija National Park and are popular with kayakers. The lakes in and near the Molėtai district municipality are a weekend destination for many residents of Vilnius, who have built summer houses and villas in the area. Lake origins The great majority of Lithuania's lakes formed after the Wisconsin glaciation, Wisconsin glacier retreated. The oldest date from about 13,000 years before the present. The varieties of glacial lakes include: * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand and silt can be carried in suspension in river water and on reaching the sea bed deposited by sedimentation; if buried, they may eventually become sandstone and siltstone (sedimentary rocks) through lithification. Sediments are most often transported by water (fluvial processes), but also wind (aeolian processes) and glaciers. Beach sands and river channel deposits are examples of fluvial transport and deposition, though sediment also often settles out of slow-moving or standing water in lakes and oceans. Desert sand dunes and loess are examples of aeolian transport and deposition. Glacial moraine deposits and till are ice-transported sediments. Classification Sediment can be classified based on its grain size, grain shape, and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
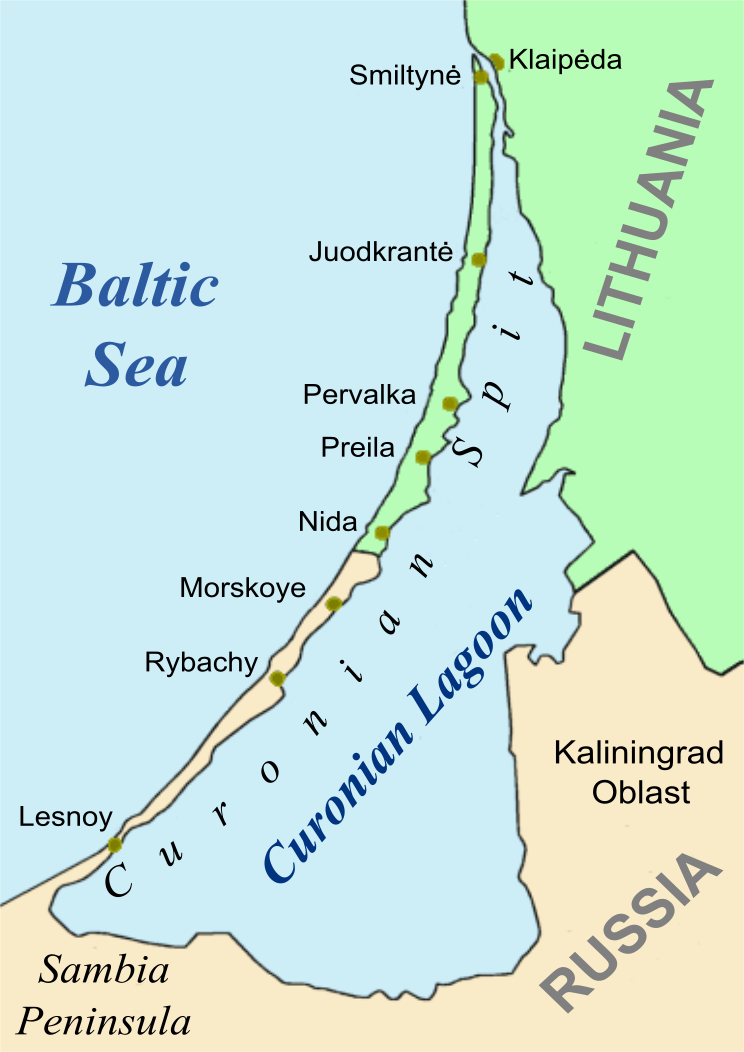
Curonian Lagoon
The Curonian Lagoon (or Bay, Gulf; russian: Куршский залив, lt, Kuršių marios, pl, Zalew Kuroński, german: Kurisches Haff, lv, Kuršu joma) is a freshwater lagoon separated from the Baltic Sea by the Curonian Spit. Its surface area is . The Neman River ( lt, Nemunas) supplies about 90% of its inflows; its watershed consists of about 100,450 square kilometres in Lithuania and Russia's Kaliningrad Oblast. Human history In the 13th century, the area around the lagoon was part of the ancestral lands of the Curonians and Old Prussians. Later it bordered the historical region of Lithuania Minor. At the northern end of the Spit, the Klaipėda Strait connects the lagoon to the Baltic Sea, and the place was chosen by the Teutonic Knights in 1252 to found ''Memelburg'' castle and the city of Memel — officially called Klaipėda in 1923–39, when the Memel Territory was separated from Germany, and again after 1945, when it became part of the Lithuanian SSR. As the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krokų Lanka
Krokų Lanka is the only lake of marine origin in Lithuania and the largest lake in the Šilutė District Municipality. It is located in the Nemunas Delta Regional Park on the Baltic Sea shore near Nemunas Delta and Ventė Cape. It covers a territory of 788 ha. Aukštumala bog, covering 3018 ha and used for peat production since 1882, is located just north of the lake and Mingė village is located on the western bank. In the south a narrow strip of water connects the lake with Atmata, a branch of the Neman River. Krokų Lanka was created when alluvial deposits from the Neman River separated a part of the Curonian Lagoon. The lake is very shallow, with greatest depth of only 2.5 meters, and overgrown with water plants. It is poised to eventually turn into a bog but now it is a paradise for a variety of water birds, including Eurasian bittern (''Botaurus stellaris''), greylag goose (''Anser anser''), Montagu's harrier (''Circus pygargus''), black-tailed godwit (''Limosa limosa''), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hectares
The hectare (; SI symbol: ha) is a non-SI metric unit of area equal to a square with 100-metre sides (1 hm2), or 10,000 m2, and is primarily used in the measurement of land. There are 100 hectares in one square kilometre. An acre is about and one hectare contains about . In 1795, when the metric system was introduced, the ''are'' was defined as 100 square metres, or one square decametre, and the hectare ("hecto-" + "are") was thus 100 ''ares'' or km2 (10,000 square metres). When the metric system was further rationalised in 1960, resulting in the International System of Units (), the ''are'' was not included as a recognised unit. The hectare, however, remains as a non-SI unit accepted for use with the SI and whose use is "expected to continue indefinitely". Though the dekare/decare daa (1,000 m2) and are (100 m2) are not officially "accepted for use", they are still used in some contexts. Description The hectare (), although not a unit of SI, is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biržai District Municipality
Biržai (, known also by several alternative names) is a town in northern Lithuania. Biržai is famous for its reconstructed Biržai Castle manor, and the whole region is renowned for its many traditional-recipe beer breweries. Names The name of the town is of Lithuanian origin and is spelled in different forms in other languages: Birsen (German), Birże (Polish), Birzhai (Биржай, Russian - pre-1917 Биржи), and בירז/Birz or Birzh (Yiddish) and simplified to Birzai in English. History The town's first written mention dates to 1455. The construction of Biržai Castle began in 1586, and the town was granted Magdeburg Rights in 1589. In 1575, as preparation for the castle's construction, a dam was built on the Agluona and Apaščia Rivers at their confluence, and the artificial Lake Širvėna, covering about , was created. It is the oldest surviving artificial lake in Lithuania. The town's history is closely associated with the Radziwiłł family (Lithuanian: Radv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinkhole
A sinkhole is a depression or hole in the ground caused by some form of collapse of the surface layer. The term is sometimes used to refer to doline, enclosed depressions that are locally also known as ''vrtače'' and shakeholes, and to openings where surface water enters into underground passages known as ''ponor'', swallow hole or swallet. A ''cenote'' is a type of sinkhole that exposes groundwater underneath. A ''sink'' or ''stream sink'' are more general terms for sites that drain surface water, possibly by infiltration into sediment or crumbled rock. Most sinkholes are caused by karst processes – the chemical dissolution of carbonate rocks, collapse or suffosion processes. Sinkholes are usually circular and vary in size from tens to hundreds of meters both in diameter and depth, and vary in form from soil-lined bowls to bedrock-edged chasms. Sinkholes may form gradually or suddenly, and are found worldwide. Formation Natural processes Sinkholes may capture surf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neman River
The Neman, Nioman, Nemunas or MemelTo bankside nations of the present: Lithuanian: be, Нёман, , ; russian: Неман, ''Neman''; past: ger, Memel (where touching Prussia only, otherwise Nieman); lv, Nemuna; et, Neemen; pl, Niemen; ; uk, Німан, ''Niman'' is a river in Europe that rises in central Belarus and flows through Lithuania then forms the northern border of Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia's western exclave, which specifically follows its southern channel. It drains into the Curonian Lagoon, narrowly connected to the Baltic Sea. It flows about , so is considered a major Eastern European river. It flows generally west to Grodno within of the Polish border, north to Kaunas, then westward again to the sea. The largest river in Lithuania, and the third-largest in Belarus, it is navigable for most of its length. It starts from two small headwaters merging about southwest of the town of Uzda – about southwest of capital city Minsk. Only , an eastward mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxbow Lake
An oxbow lake is a U-shaped lake or pool that forms when a wide meander of a river is cut off, creating a free-standing body of water. In South Texas, oxbows left by the Rio Grande are called '' resacas''. In Australia, oxbow lakes are called billabongs. The word "oxbow" can also refer to a U-shaped bend in a river or stream, whether or not it is cut off from the main stream. Geology An oxbow lake forms when a meandering river erodes through the neck of one of its meanders. This takes place because meanders tend to grow and become more curved over time. The river then follows a shorter course that bypasses the meander. The entrances to the abandoned meander eventually silt up, forming an oxbow lake. Because oxbow lakes are stillwater lakes, with no current flowing through them, the entire lake gradually silts up, becoming a bog or swamp and then evaporating completely. When a river reaches a low-lying plain, often in its final course to the sea or a lake, it meanders wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Drūkšiai
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a Depression (geology), basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the World Ocean, ocean, although, like the much larger oceans, they do form part of the Earth's water cycle. Lakes are distinct from lagoons, which are generally coastal parts of the ocean. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which also lie on land, though there are no official or scientific definitions. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams, which usually flow in a channel on land. Most lakes are fed and drained by rivers and streams. Natural lakes are generally found in mountainous areas, rift zones, and areas with ongoing glacier, glaciation. Other lakes are found in endorheic basins or along the courses of mature rivers, where a river channel has widened into a basin. Some parts of the world have many lakes formed by the chaotic dra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peat
Peat (), also known as turf (), is an accumulation of partially decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, moors, or muskegs. The peatland ecosystem covers and is the most efficient carbon sink on the planet, because peatland plants capture carbon dioxide (CO2) naturally released from the peat, maintaining an equilibrium. In natural peatlands, the "annual rate of biomass production is greater than the rate of decomposition", but it takes "thousands of years for peatlands to develop the deposits of , which is the average depth of the boreal orthernpeatlands", which store around 415 gigatonnes (Gt) of carbon (about 46 times 2019 global CO2 emissions). Globally, peat stores up to 550 Gt of carbon, 42% of all soil carbon, which exceeds the carbon stored in all other vegetation types, including the world's forests, although it covers just 3% of the land's surface. ''Sphagnum'' moss, also called peat moss, is one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetlands
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The primary factor that distinguishes wetlands from terrestrial land forms or Body of water, water bodies is the characteristic vegetation of aquatic plants, adapted to the unique anoxic hydric soils. Wetlands are considered among the most biologically diverse of all ecosystems, serving as home to a wide range of plant and animal species. Methods for assessing wetland functions, wetland ecological health, and general wetland condition have been developed for many regions of the world. These methods have contributed to wetland conservation partly by raising public awareness of the functions some wetlands provide. Wetlands occur naturally on every continent. The water in wetlands is either freshwater, brackish or saltwater. The main wetland ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)



.jpg)
