|
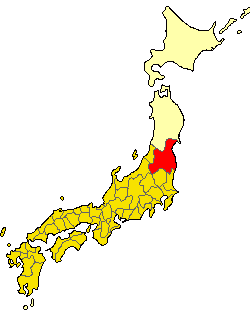
Kitakami, Iwate
is a Cities of Japan, city located in Iwate Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 92,311, and a population density of 210 persons per km2 in 37,085 households. The total area of the city is . The city is famous for the sakura that bloom in Tenshochi Park. Geography Kitakami is located in south-central Iwate Prefecture, in the Kitakami River valley, approximately 45 kilometers south of the prefectural capital of Morioka, and 490 kilometers north of Tokyo. The city is at the confluence of the Kitakami River and the Waga River and has an altitude ranging from 50 to 200 meters above sea level, rising to 400 meters in the east. Neighboring municipalities Iwate Prefecture *Hanamaki, Iwate, Hanamaki *Ōshū, Iwate, Ōshū *Nishiwaga, Iwate, Nishiwaga *Kanegasaki, Iwate, Kanegasaki Climate Kitakami has a humid subtropical climate, humid climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') characterized by mild summers and cold winters. The average annual temperature in Kitakami is 10.5&nbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cities Of Japan
A is a local administrative unit in Japan. Cities are ranked on the same level as and , with the difference that they are not a component of . Like other contemporary administrative units, they are defined by the Local Autonomy Law of 1947. City status Article 8 of the Local Autonomy Law sets the following conditions for a municipality to be designated as a city: *Population must generally be 50,000 or greater (原則として人口5万人以上) *At least 60% of households must be established in a central urban area (中心市街地の戸数が全戸数の6割以上) *At least 60% of households must be employed in commerce, industry or other urban occupations (商工業等の都市的業態に従事する世帯人口が全人口の6割以上) *Any other conditions set by prefectural ordinance must be satisfied (他に当該都道府県の条例で定める要件を満たしていること) The designation is approved by the prefectural governor and the Minister for Internal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kitakami River
The is the fourth largest river in Japan and the largest in the Tōhoku region. It is long and drains an area of . page 793 It flows through mostly rural areas of Iwate and Miyagi Prefectures. The source of the river is the Mount Nanashiruge in northern Iwate, from which it flows to the south between the Kitakami Mountains and the Ōu Mountains. The river is unusual in that it has two mouths, one flowing south into Ishinomaki Bay and the other flowing east into the Pacific Ocean, both in Ishinomaki City. The Kitakami river was an important transportation route during the Edo period and before the building of railways in the early Meiji period. Numerous dams have been constructed on the river and its tributaries from the Taishō and Shōwa periods for hydroelectric power generation, flood control and irrigation. However, another unusual feature is that there are no dams from its mouth to the Shijūshida Dam north of Morioka. This allows for a spectacular salmon run every fal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aterui
(died 21, AD 802 in Enryaku) was the most prominent chief of the Isawa (胆沢) band of Emishi in northern Japan. The Emishi were an indigenous people of North Japan, who were considered hirsute barbarians by the Yamato Japanese. Life Aterui was born in Isawa, Hitakami-no-kuni, what is now Mizusawa Ward of Ōshū City in southern Iwate Prefecture. Nothing is known of his life until the battle of Sufuse Village in 787. In 786, Ki no Asami Kosami was appointed by the Emperor Kanmu as the new General of Eastern Conquest and given a commission to conquer Aterui. In June 787, Kosami split his army in two and sent them north from Koromogawa on each side of the Kitakami River hoping to surprise Aterui at his home in Mizusawa. Burning houses and crops as they went they were surprised when Emishi cavalry swept down from the hills to the East and pushed them into the river. Over 1,000 armored infantry drowned in the river weighed down by their heavy armor. In September Kosami returned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emishi
The (also called Ebisu and Ezo), written with Chinese characters that literally mean "shrimp barbarians," constituted an ancient ethnic group of people who lived in parts of Honshū, especially in the Tōhoku region, referred to as in contemporary sources. The first mention of the Emishi in literature that can be corroborated with outside sources dates to the 5th century AD, in which they are referred to as (毛人 - "hairy people") in Chinese records. Some Emishi tribes resisted the rule of various Japanese Emperors during the Asuka, Nara and early Heian periods (7th–10th centuries AD). The origin of the Emishi is disputed. They are often thought to have descended from some tribes of the Jōmon people. Some historians believe that they were related to the Ainu people, but others disagree with this theory and see them as a completely distinct ethnicity.Aston, W.G., trans. Nihongi: Chronicles of Japan from the Earliest Times to AD 697. Tokyo: Charles E.Tuttle Co., 1972 (r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jōmon Period
The is the time in Japanese history, traditionally dated between 6,000–300 BCE, during which Japan was inhabited by a diverse hunter-gatherer and early agriculturalist population united through a common Jōmon culture, which reached a considerable degree of sedentism and cultural complexity. The name "cord-marked" was first applied by the American zoologist and orientalist Edward S. Morse, who discovered sherds of pottery in 1877 and subsequently translated it into Japanese as ''Jōmon''.Mason, 14 The pottery style characteristic of the first phases of Jōmon culture was decorated by impressing cords into the surface of wet clay and is generally accepted to be among the oldest in the world. The Jōmon period was rich in tools and jewelry made from bone, stone, shell and antler; pottery figurines and vessels; and lacquerware.Imamura, K. (1996) ''Prehistoric Japan: New Perspectives on Insular East Asia''. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press It is often compared to pre-C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutsu Province
was an old province of Japan in the area of Fukushima, Miyagi, Iwate and Aomori Prefectures and the municipalities of Kazuno and Kosaka in Akita Prefecture. Mutsu Province is also known as or . The term is often used to refer to the combined area of Mutsu and the neighboring province Dewa, which together make up the entire Tōhoku region. History Invasion by the Kinai government Mutsu, on northern Honshū, was one of the last provinces to be formed as land was taken from the indigenous Emishi, and became the largest as it expanded northward. The ancient regional capital of the Kinai government was Tagajō in present-day Miyagi Prefecture. * 709 ('' Wadō 2, 3rd month''), an uprising against governmental authority took place in Mutsu and in nearby Echigo Province. Troops were dispatched to subdue the revolt. * 712 (''Wadō 5''), Mutsu was separated from Dewa Province. Empress Genmei's ''Daijō-kan'' made cadastral changes in the provincial map of the Nara period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Meteorological Agency
The , abbreviated JMA, is an agency of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism. It is charged with gathering and providing results for the public in Japan that are obtained from data based on daily scientific observation and research into natural phenomena in the fields of meteorology, hydrology, seismology and volcanology, among other related scientific fields. Its headquarters is located in Minato, Tokyo. JMA is responsible for gathering and reporting weather data and forecasts for the general public, as well as providing aviation and marine weather. JMA other responsibilities include issuing warnings for volcanic eruptions, and the nationwide issuance of earthquake warnings of the Earthquake Early Warning (EEW) system. JMA is also designated one of the Regional Specialized Meteorological Centers of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO). It is responsible for forecasting, naming, and distributing warnings for tropical cyclones in the Northwestern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humid Subtropical Climate
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° and are located poleward from adjacent tropical climates. It is also known as warm temperate climate in some climate classifications. Under the Köppen climate classification, ''Cfa'' and ''Cwa'' climates are either described as humid subtropical climates or warm temperate climates. This climate features mean temperature in the coldest month between (or ) and and mean temperature in the warmest month or higher. However, while some climatologists have opted to describe this climate type as a "humid subtropical climate", Köppen himself never used this term. The humid subtropical climate classification was officially created under the Trewartha climate classification. In this classification, climates are termed humid subtropical when the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanegasaki, Iwate
is a Towns of Japan, town located in Iwate Prefecture, Japan. , the town had an estimated population of 15,580, and a population density of 87 persons per km² in 6,155 households. The total area of the town is . In June 2001, the 34.8 hectare old centre of town was protected as an Groups of Traditional Buildings, Important Preservation District by the national government for its traditional samurai residences. Geography Kanegasaki is located in the Tōhoku region of northern Japan at the confluence of the Kitakami River, Kitakami and Isawa River, Isawa rivers and is bordered to the north by Kitakami, Iwate, Kitakami-shi, to the east and south by Ōshū, Iwate, Ōshū-shi. In the mountains to the west, there is a large reservoir known as Sengaishi that is dammed and used for irrigating the rice paddies in the plain below. Kanegasaki is characterized by a variety of geographical features, including mountains and wide expanses of rice paddies to the west and a small merchant dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nishiwaga, Iwate
is a town in Iwate Prefecture, Japan. , the town had an estimated population of 5,468 in 2279 households, and a population density of 9 persons per km². The total area of the town is . The total area was . Geography Nishiwaga is located in the far southwestern corner of Iwate Prefecture, in the river valley of the Waga River, surrounded by the 1000-meter peaks of the Ōu Mountains on three sides. The area is noted for its extremely heavy snowfall in winter. The Yuda Dam is located in Nishiwaga and the Yuda Onsenkyō Prefectural Natural Park is located completely within its borders. Neighboring municipalities Iwate Prefecture *Hanamaki * Kitakami *Ōshū *Shizukuishi Akita Prefecture * Semboku * Daisen *Yokote * Misato * Higashinaruse Climate Nishiwaga has a humid continental climate (Köppen ''Dfa'') characterized by mild summers and cold winters with heavy snowfall. The average annual temperature in Nishiwaga is 8.9 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1561 mm with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ōshū, Iwate
is a city located in Iwate Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 114,620 and a population density of 120 persons per km² in 45,728 households. The total area of the city is . Ōshū is famous for its Maesawa Beef, numerous festivals, historic temples and shrines and Fujiwara no Sato, a theme park and movie lot based on the exploits of the Northern Fujiwaras in the 12th century. Many famous people claim Ōshū as their home, including Ichiro Ozawa, the long-time leader of the Democratic Party of Japan. Geography Ōshū is located in the south-central portion of Iwate Prefecture, bordered by the Akita Prefecture to the west. At 993.35 square kilometers, Ōshū is the second largest municipality in Iwate Prefecture in terms of land area. The city lies in a fertile plain straddling the Kitakami River and rises to the Ōu Mountains in the west and the Kitakami Mountains to the east. The city's highest point is Mt. Yakeishi-dake at 1,548 meters in the Ōu Moun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanamaki, Iwate
is a city in Iwate Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 94,691, and a population density of 100 persons per km², in 37,773 households. The total area of the city is . Hanamaki is famous as the birthplace of Kenji Miyazawa and for its hot spring resorts. Geography Hanamaki is located in central Iwate Prefecture, in the Kitakami River valley at the conflux of three rivers with the Kitakami River; the Sarugaishi-gawa from the east and the Se-gawa and Toyosawa-gawa from the west. In the west the city rises to the foothills of the Ōu Mountains with the highest peak being Mt. Matsukura at . To the east the city rises to the highest peak in the Kitakami Range, Mount Hayachine at . The largest reservoir is Lake Tase on the Sarugaishi River. Lake Hayachine on the Hienuki River is quite spectacular with steep mountains rising above it. Lake Toyosawa is in the western part of the city on the Toyosawa River. Parts of the city are within the borders of the Hayachi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |