|
John C. Frémont
John Charles Frémont or Fremont (January 21, 1813July 13, 1890) was an American explorer, military officer, and politician. He was a U.S. Senator from California and was the first Republican nominee for president of the United States in 1856 and founder of the California Republican Party when he was nominated. He lost the election to Democrat James Buchanan when Know Nothings split the vote. He was a native of Georgia but an opponent of slavery. In the 1840s, Frémont led five expeditions into the Western United States, the third of which included large-scale killing of indigenous peoples. During the Mexican–American War, he was a major in the U.S. Army and took control of California from the California Republic in 1846. Frémont was court-martialed and convicted of mutiny and insubordination after a conflict over who was the rightful military governor of California. His sentence was commuted and he was reinstated by President Polk, but Frémont resigned from the Army. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Governors Of Arizona
The governor of Arizona is the head of government of the U.S. state of Arizona. As the top elected official, the governor is the head of the executive branch of the Arizona state government and is charged with faithfully executing state laws. The governor has the power to either approve or veto bills passed by the Arizona State Legislature; to convene the legislature; and to grant pardons, except in cases of impeachment. The governor is also the commander-in-chief of the state's military forces. Twenty-three people have served as governor over 27 distinct terms. All of the repeat governors were in the state's earliest years, when George W. P. Hunt and Thomas Edward Campbell alternated as governor for 17 years and, after a two-year gap, Hunt served another term. One governor, Evan Mecham, was successfully impeached, and one, Fife Symington, resigned upon being convicted of a felony. The longest-serving governor was Hunt, who was elected seven times and served just under fourte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1864 United States Presidential Election
The 1864 United States presidential election was the 20th quadrennial presidential election. It was held on Tuesday, November 8, 1864. Near the end of the American Civil War, incumbent President Abraham Lincoln of the National Union Party easily defeated the Democratic nominee, former General George B. McClellan, by a wide margin of 212–21 in the electoral college, with 55% of the popular vote. For the election, the Republican Party and some Democrats created the National Union Party, especially to attract War Democrats. Despite some intra-party opposition from Salmon Chase and the Radical Republicans, Lincoln won his party's nomination at the 1864 National Union National Convention. Rather than re-nominate Vice President Hannibal Hamlin, the convention selected Andrew Johnson of Tennessee, a War Democrat, as Lincoln's running mate. John C. Frémont started to run as the nominee of the new Radical Democracy Party, which criticized Lincoln for being too moderate on the issu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
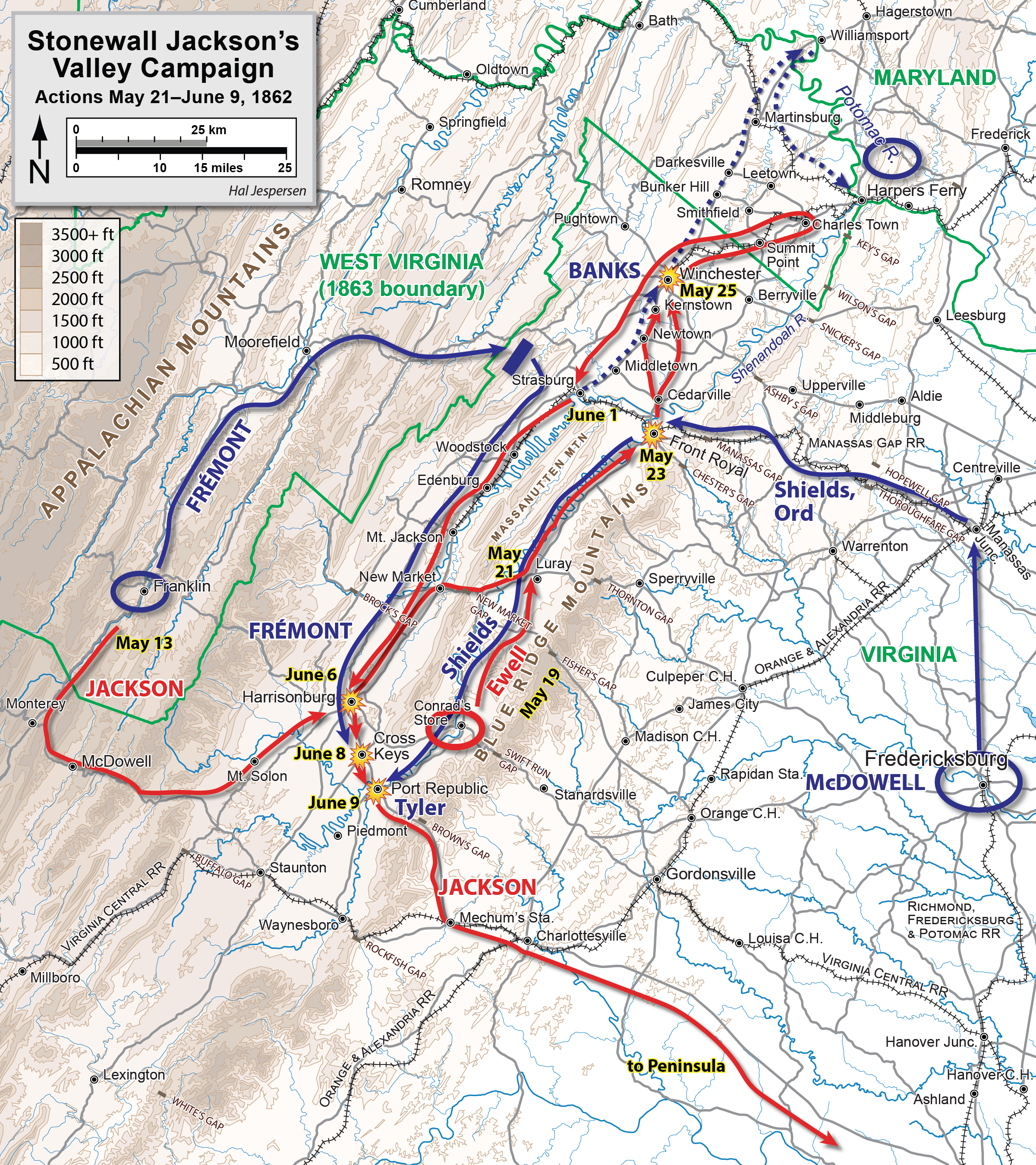
Battle Of Cross Keys
The Battle of Cross Keys was fought on June 8, 1862, in Rockingham County, Virginia, as part of Confederate Army Maj. Gen. Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson's campaign through the Shenandoah Valley during the American Civil War. Together, the battles of Cross Keys and Port Republic the following day were the decisive victories in Jackson's Valley Campaign, forcing the Union armies to retreat and leaving Jackson free to reinforce Gen. Robert E. Lee for the Seven Days Battles outside Richmond, Virginia. Background The hamlet of Port Republic, Virginia, lies on a neck of land between the North and South Rivers, which conjoin to form the South Fork Shenandoah River. On June 6–7, 1862, Jackson's army, numbering about 16,000, bivouacked north of Port Republic, Maj. Gen. Richard S. Ewell's division along the banks of Mill Creek near Goods Mill, and Brig. Gen. Charles S. Winder's division on the north bank of North River near the bridge. The 15th Alabama Infantry regiment was left t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Battle Of Springfield
Action at Springfield, also known as the Battle of First Springfield, was a battle of the American Civil War that took place on October 25, 1861, in Greene County, Missouri. It was the only Union victory in southwestern Missouri in 1861. Prelude Maj. Gen. John C. Frémont commanded the Union Department of the West, with headquarters in St. Louis. He formulated a plan to clear Confederate forces from the state, and then, if possible, carry the war into Arkansas and Louisiana. His force left St. Louis on October 7, 1861; it eventually numbered more than 20,000. He had 5,000 cavalry, which included Maj. Frank J. White's Prairie Scouts and Frémont's Body Guards under Maj. Charles Zagonyi. Maj. White became ill and turned his command over to Zagonyi. These two units scouted in front of the army. By December, the army had advanced into southwest Missouri. Opposing them was the main body of the pro-Confederate Missouri State Guard under Major General Sterling Price, at Springfield, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Wilson's Creek
The Battle of Wilson's Creek, also known as the Battle of Oak Hills, was the first major battle of the Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil War. It was fought on August 10, 1861, near Springfield, Missouri, Springfield, Missouri. Missouri was officially a neutral state, but its governor, Claiborne Fox Jackson, supported the South and secretly collaborated with Confederate States of America, Confederate troops. In August, Confederates under Brigadier General Benjamin McCulloch and Missouri State Guard troops under Maj. Gen. Sterling Price approached Brig. Gen. Nathaniel Lyon's Army of the West, camped at Springfield. On August 10, Lyon, in two columns commanded by himself and Col. Franz Sigel, attacked the Confederates on Wilsons Creek (Missouri), Wilson's Creek about southwest of Springfield. Confederate cavalry received the first blow and retreated from the high ground. Confederate infantry attacked the Union forces three times during the day but failed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states that had seceded. The central cause of the war was the dispute over whether slavery would be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prevented from doing so, which was widely believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction. Decades of political controversy over slavery were brought to a head by the victory in the 1860 U.S. presidential election of Abraham Lincoln, who opposed slavery's expansion into the west. An initial seven southern slave states responded to Lincoln's victory by seceding from the United States and, in 1861, forming the Confederacy. The Confederacy seized U.S. forts and other federal assets within their borders. Led by Confederate President Jefferson Davis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the 1845 American annexation of Texas, which Mexico still considered its territory. Mexico refused to recognize the Velasco treaty, because it was signed by President Antonio López de Santa Anna while he was captured by the Texan Army during the 1836 Texas Revolution. The Republic of Texas was ''de facto'' an independent country, but most of its Anglo-American citizens wanted to be annexed by the United States. Sectional politics over slavery in the United States were preventing annexation because Texas would have been admitted as a slave state, upsetting the balance of power between Northern free states and Southern slave states. In the 1844 United States presidential election, Democrat James K. Polk was elected on a platform of expand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major General (United States)
In the United States Armed Forces, a major general is a two-star general officer in the United States Army, Marine Corps, Air Force, and Space Force. A major general ranks above a brigadier general and below a lieutenant general. The pay grade of major general is O-8. It is equivalent to the rank of rear admiral in the other United States uniformed services which use naval ranks. It is abbreviated as MG in the Army, MajGen in the Marine Corps, and in the Air Force and Space Force. Major general is the highest permanent peacetime rank in the uniformed services as higher ranks are technically temporary and linked to specific positions, although virtually all officers promoted to those ranks are approved to retire at their highest earned rank. A major general typically commands division-sized units of 10,000 to 15,000 soldiers. The Civil Air Patrol also uses the rank of major general, which is its highest rank and is held only by its national commander. Statutory limits ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Army Major General Rank Insignia
Union commonly refers to: * Trade union, an organization of workers * Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets Union may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music * Union (band), an American rock group ** ''Union'' (Union album), 1998 * ''Union'' (Chara album), 2007 * ''Union'' (Toni Childs album), 1988 * ''Union'' (Cuff the Duke album), 2012 * ''Union'' (Paradoxical Frog album), 2011 * ''Union'', a 2001 album by Puya * ''Union'', a 2001 album by Rasa * ''Union'' (The Boxer Rebellion album), 2009 * ''Union'' (Yes album), 1991 * "Union" (Black Eyed Peas song), 2005 Other uses in arts and entertainment * ''Union'' (Star Wars), a Dark Horse comics limited series * Union, in the fictional Alliance–Union universe of C. J. Cherryh * '' Union (Horse with Two Discs)'', a bronze sculpture by Christopher Le Brun, 1999–2000 * The Union (Marvel Team), a Marvel Comics superhero team and comic series Education * Union Academy (other) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of The West
The Department of the West, later known as the Western Department, was a major command ( Department) of the United States Army during the 19th century. It oversaw the military affairs in the country west of the Mississippi River to the borders of California and Oregon. Organization The Department of the West was created in a reform of army organization nationwide on October 31, 1853, from a consolidation of the existing 6th Military District (headquartered at Jefferson Barracks, Missouri) and 7th Military District (Fort Smith, Arkansas) Departments. It reported directly to the headquarters of the Army in Washington, D.C. In the 1853 reorganization the Department of the Pacific was also created, from consolidation of the 10th (California) and 11th (Oregon) Departments. The Department of the West's headquarters continued at Jefferson Barracks in St. Louis, although it moved briefly to Fort Leavenworth, Kansas, during the Bleeding Kansas skirmishes. Civil War As the Southern states ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Battalion
The California Battalion (also called the first California Volunteer Militia and U.S. Mounted Rifles) was formed during the Mexican–American War (1846–1848) in present-day California, United States. It was led by U.S. Army Brevet Lieutenant Colonel John C. Fremont and composed of his cartographers, scouts and hunters and the California Volunteer Militia formed after the Bear Flag Revolt. The battalion's formation was officially authorized by Commodore Robert F. Stockton, commanding officer of the U.S. Navy Pacific Squadron. Formation Hostilities between U.S. and Mexican forces had been underway in Texas since April 1846 resulting in a formal declaration of war on 13 May 1846, by the U.S. Congress. On 17 May 1846, unofficial word reached the U.S. Navy fleet of four vessels at anchor in the harbor of Mazatlán, Mexico, and that hostilities had begun between Mexico and the United States. Commodore John D. Sloat, commander of the U.S. Navy's Pacific Squadron, dispatched his flag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Army
During the American Civil War, the Union Army, also known as the Federal Army and the Northern Army, referring to the United States Army, was the land force that fought to preserve the Union (American Civil War), Union of the collective U.S. state, states. It proved essential to the preservation of the United States as a working, viable republic. The Union Army was made up of the permanent Regular Army (United States), regular army of the United States, but further fortified, augmented, and strengthened by the many temporary units of dedicated United States Volunteers, volunteers, as well as including those who were drafted in to service as Conscription in the United States, conscripts. To this end, the Union Army fought and ultimately triumphed over the efforts of the Confederate States Army in the American Civil War. Over the course of the war, 2,128,948 men enlisted in the Union Army, including 178,895 United States Colored Troops, colored troops; 25% of the white men who s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |