|
History Of Edinburgh
While the area around modern-day Edinburgh has been inhabited for thousands of years, the history of Edinburgh as a definite settlement can be traced to the early Middle Ages when a hillfort was established in the area, most likely on the Castle Rock. From the seventh to the tenth centuries it was part of the Anglian Kingdom of Northumbria, becoming thereafter a royal residence of the Scottish kings. The town that developed next to the stronghold was established by royal charter in the early 12th century, and by the middle of the 14th century was being described as the capital of Scotland. The area known as the New Town was added from the second half of the 18th century onwards. Edinburgh was Scotland's largest city until Glasgow outgrew it in the first two decades of the 19th century. Following Scottish devolution in the very late 20th century, Scotland's Parliament was established in Edinburgh. Origins The earliest known human habitation in the Edinburgh area is from Cramo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
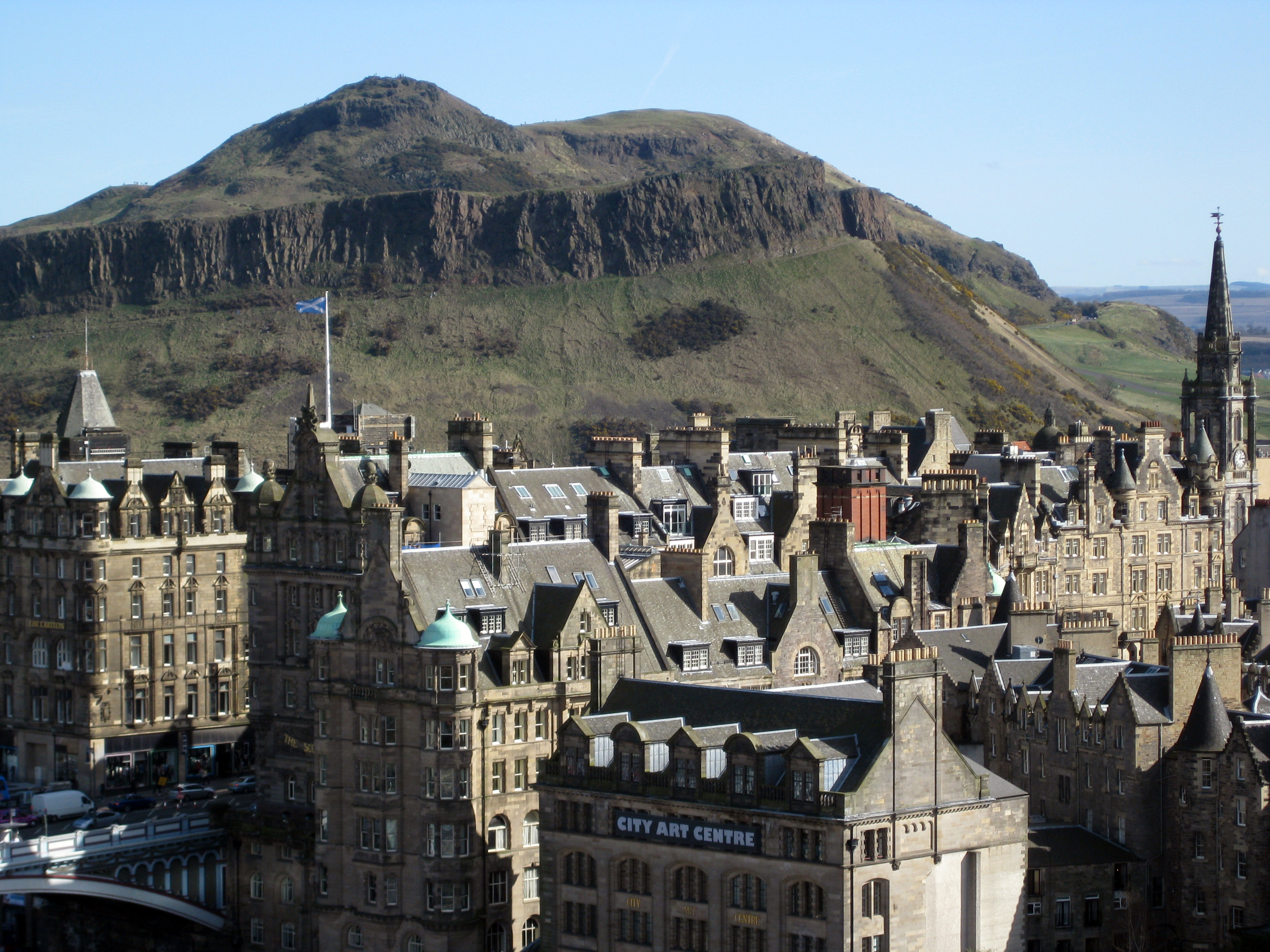
Arthurs Seat Edinburgh
Arthurs may refer to: People ;Surnames: * Charles Arthurs (1881–1932), English footballer * Dante Arthurs (born 1984), convicted murderer * Declan Arthurs (1965 – 1987), IRA member * Faye Arthurs, New York City Ballet dancer * George Arthurs (1875-1944), British songwriter and lyricist * Harry Arthurs (born 1935), Canadian lawyer, academic, and academic administrator * Jack Arthurs (1922-2020), American businessman and politician * James Arthurs (1866 – 1937), Canadian senator * John Arthurs (born 1947), retired American basketball player * Paul Arthurs (born 1965), member of the defunct British band Oasis * Wayne Arthurs (tennis) (born 1971), Australian tennis player * Wayne Arthurs (politician) member of the Legislative Assembly of Ontario Places * Arthur's Hill, Newcastle upon Tyne, England * Arthur's Pass (mountain pass), mountain pass in the Southern Alps of the South Island of New Zealand * Arthur's Pass, village in the Southern Alps of the South Island of New Ze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentland Hills
The Pentland Hills are a range of hills southwest of Edinburgh, Scotland. The range is around in length, and runs southwest from Edinburgh towards Biggar and the upper Clydesdale. Etymology The name is first recorded for the farm of Pentland ( 1050, 1200) and probably derives from Brythonic ''pen llan'', head or top end of the church or enclosure. In the late 15th to mid-16th centuries, land transfers refer to Pentlandmure and Pentland – documents that also list adjacent parcels of land with such still-recognisable names as Loganehous, Hilend, Boghall and Mortounhall. 'Muir', in Pentlandmure, describes common grazings where the farm's livestock would be pastured in summer; and gradually the name was linked more specifically with the slopes of the nearby hills (perhaps Allermuir, Woodhouselee or Castlelaw). The name is completely unrelated to the name of the Pentland Firth in the north of Scotland. Timothy Pont mapped the area in the 1590s, and his work appeared in the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh Castle
Edinburgh Castle is a historic castle in Edinburgh, Edinburgh, Scotland. It stands on Castle Rock (Edinburgh), Castle Rock, which has been occupied by humans since at least the Iron Age, although the nature of the early settlement is unclear. There has been a royal castle on the rock since at least the reign of David I of Scotland, David I in the 12th century, and the site continued to be a royal residence until 1633. From the 15th century, the castle's residential role declined, and by the 17th century it was principally used as military barracks with a large garrison. Its importance as a part of Scotland's national heritage was recognised increasingly from the early 19th century onwards, and various restoration programmes have been carried out over the past century and a half. As one of the most important strongholds in the Kingdom of Scotland, Edinburgh Castle was involved in many historical conflicts from the Wars of Scottish Independence in the 14th century to the Jacobite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Din Eidyn
Eidyn was the region around modern Edinburgh in Britain's sub-Roman and early medieval periods, approximately the 5th–7th centuries. It centred on the stronghold of Din Eidyn, thought to have been at Castle Rock, now the site of Edinburgh Castle, and apparently included much of the area below the Firth of Forth. It was the most important district of the Brittonic kingdom of Gododdin, and a significant power in the Hen Ogledd, or Old North, the Brittonic-speaking area of what is now southern Scotland and northern England. The site of Din Eidyn has been nearly continuously occupied since the Bronze Age, serving as a stronghold of the Votadini during the Roman era and later the principal centre of their successors, the Gododdin kingdom. Eidyn's importance to the Hen Ogledd is reflected in the medieval poem '' Y Gododdin'', which concerns a war band that gathered there for a raid around AD 600. After years of decline, Eidyn was conquered by the Angles in 638. Eidyn left a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gododdin
The Gododdin () were a Brittonic people of north-eastern Britannia, the area known as the Hen Ogledd or Old North (modern south-east Scotland and north-east England), in the sub-Roman period. Descendants of the Votadini, they are best known as the subject of the 6th-century Welsh poem '' Y Gododdin'', which memorialises the Battle of Catraeth and is attributed to Aneirin. The name ''Gododdin'' is the Modern Welsh form, but the name appeared in Old Welsh as ''Guotodin'' and derived from the tribal name ''Votadini'' recorded in Classical sources, such as in Greek texts from the Roman period. Kingdom It is not known exactly how far the kingdom of the Gododdin extended, possibly from the Stirling area to the kingdom of ''Bryneich'' (Bernicia), and including what are now the Lothian and Borders regions of eastern Scotland. It was bounded to the west by the Brittonic Kingdom of Strathclyde, and to the north by the Picts. Those living around Clackmannanshire were known a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
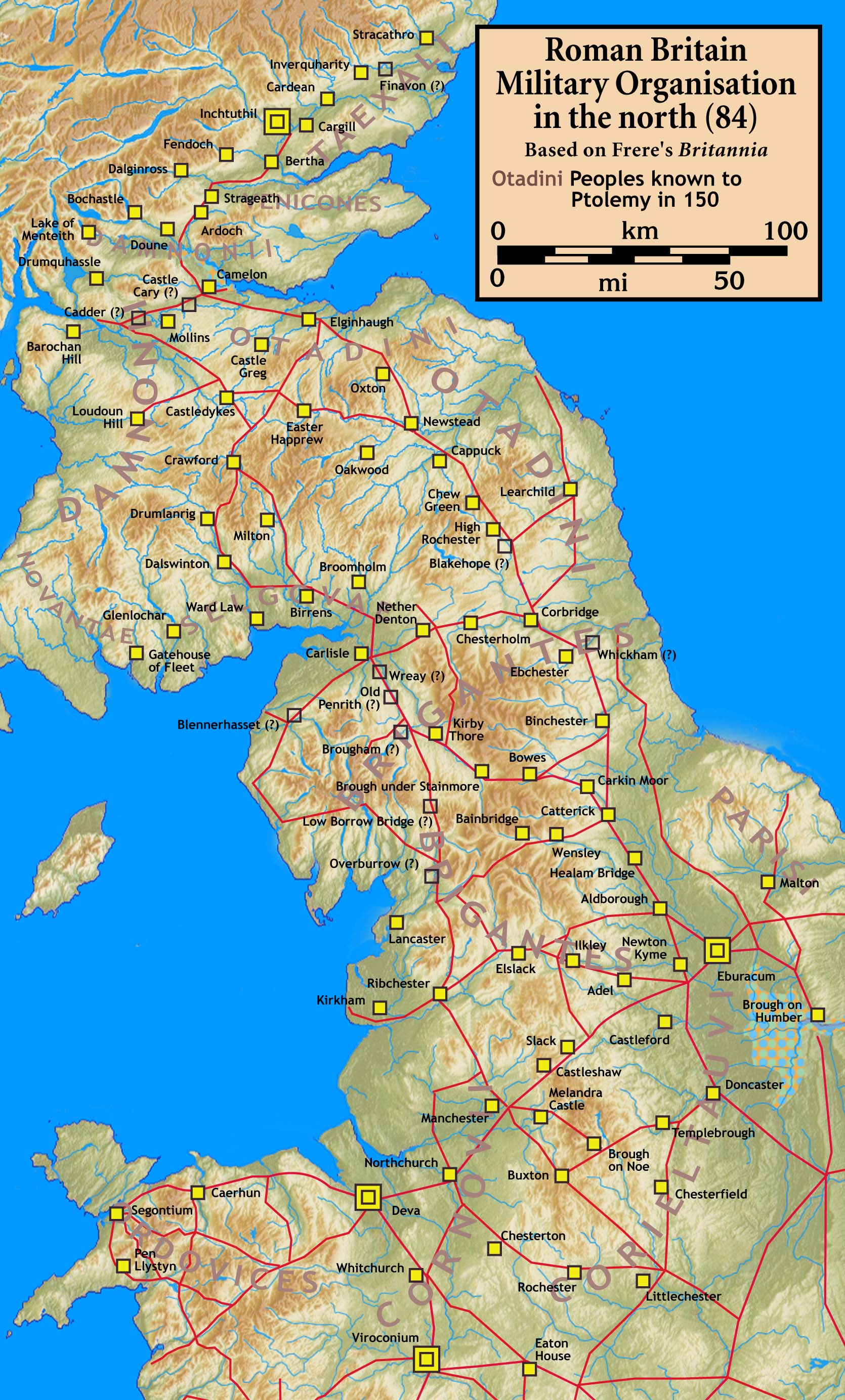
Dere Street
Dere Street or Deere Street is a modern designation of a Roman road which ran north from Eboracum (York), crossing the Stanegate at Corbridge ( Hadrian's Wall was crossed at the Portgate, just to the north) and continuing beyond into what is now Scotland, later at least as far as the Antonine Wall. Portions of its route are still followed by modern roads, including the A1 (south of the River Tees), the B6275 road through Piercebridge, where Dere Street crosses the River Tees, and the A68 north of Corbridge in Northumberland. Name The Roman name for the route is lost. Its English name corresponds with the post-Roman Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Deira, through which the first part of its route lies. That kingdom possibly took its name from the Yorkshire River Derwent. The term "street" derives from its Old English sense (from la, via strata), which referred to any paved road and had no particular association with urban thoroughfares. Portions of the road in Scotland we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Roads In Britannia
Roman roads in Britannia were initially designed for military use, created by the Roman Army during the nearly four centuries (AD 43–410) that Britannia was a province of the Roman Empire. It is estimated that about of paved trunk roads (surfaced roads running between two towns or cities) were constructed and maintained throughout the province. Most of the known network was complete by 180. The primary function of the network was to allow rapid movement of troops and military supplies, but it subsequently provided vital infrastructure for commerce, trade and the transportation of goods. A considerable number of Roman roads remained in daily use as core trunk roads for centuries after the end of Roman rule in Britain in 410. Some routes are now part of the UK's national road network. Others have been lost or are of archeological and historical interest only. After the Romans departed, systematic construction of paved highways in the United Kingdom did not resume unt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eboracum
Eboracum () was a fort and later a city in the Roman province of Britannia. In its prime it was the largest town in northern Britain and a provincial capital. The site remained occupied after the decline of the Western Roman Empire and ultimately developed into the present-day city York, occupying the same site in North Yorkshire, England. Two Roman emperors died in Eboracum: Septimius Severus in 211 AD, and Constantius Chlorus in 306 AD. Etymology The first known recorded mention of Eboracum by name is dated , and is an address containing the genitive form of the settlement's name, ''Eburaci'', on a wooden stylus tablet from the Roman fortress of Vindolanda in what is now the modern Northumberland. During the Roman period, the name was written both ''Eboracum'' and ''Eburacum'' (in nominative form). The name ''Eboracum'' comes from the Common Brittonic ''*Eburākon'', which means "Taxus baccata, yew tree place". The word for "yew" was ''*ebura'' in Proto-Celtic (cf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
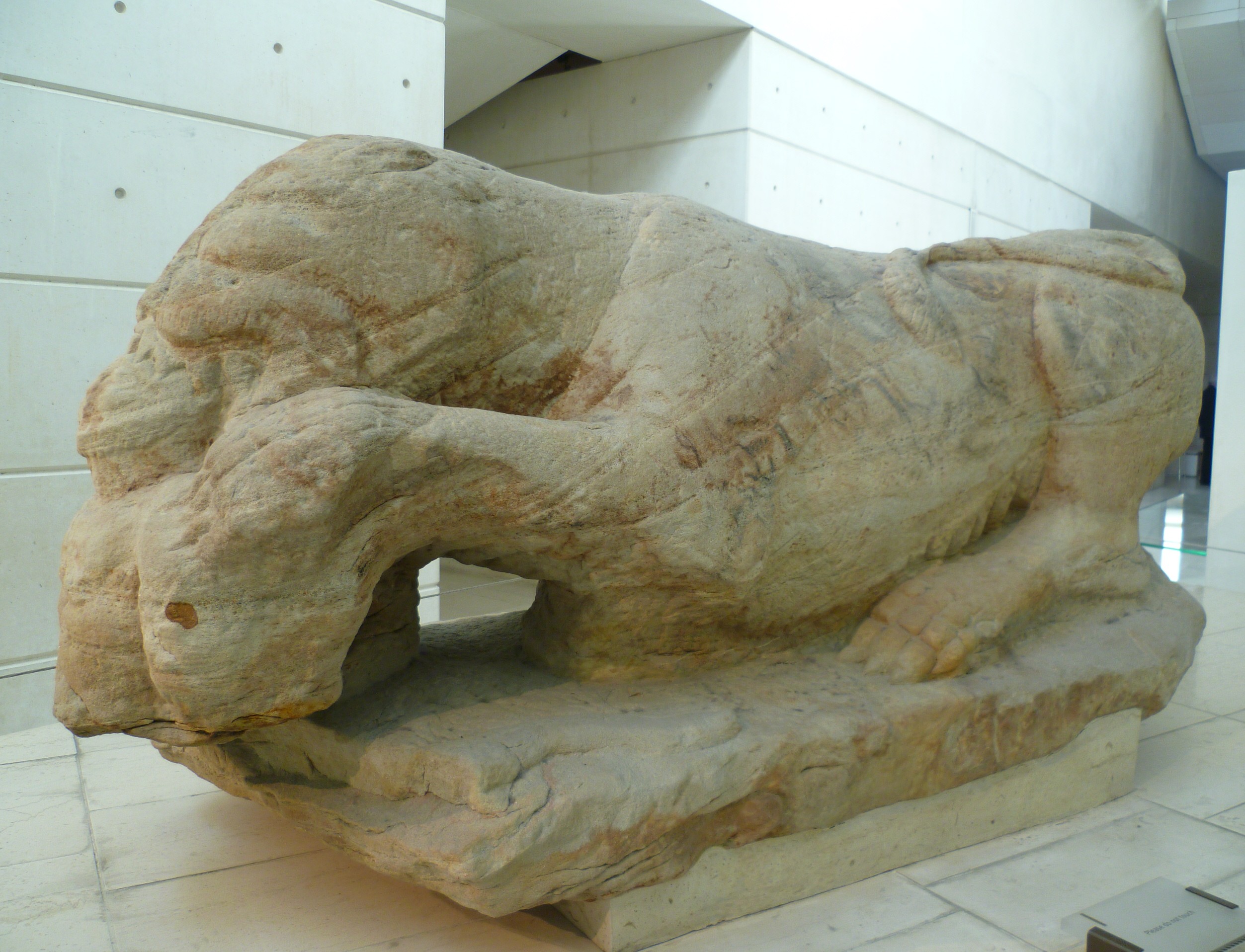
Cramond Roman Fort
Cramond Roman Fort is a Roman-Era archaeological site at Cramond, Edinburgh, Scotland. The settlement may be the "Rumabo" listed in the 7th-century ''Ravenna Cosmography''. The fort was established around 140 AD and occupied until around 170 AD, with a further period of occupation from around 208 to 214 AD. Among the many archaeological finds, one of the most famous is a sculpture known as the Cramond Lioness. History The fort at Cramond was located on the River Almond at the point where it flows into the Forth. In Roman times, there was probably a natural harbour here. One suggested interpretation is that Cramond formed a chain of Lothian forts along with Carriden and Inveresk. The fort was established around 140 AD during the building of the Antonine Wall, and remained in use until around 170 AD when the Romans retreated south to Hadrian's Wall. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Votadini
The Votadini, also known as the ''Uotadini'', ''Wotādīni'', ''Votādīni'', or ''Otadini'' were a Brittonic people of the Iron Age in Great Britain. Their territory was in what is now south-east Scotland and north-east England, extending from the Firth of Forth and around modern Stirling to the River Tyne, including at its peak what are now the Falkirk, Lothian and Borders regions and Northumberland. This area was briefly part of the Roman province of ''Britannia''. The earliest known capital of the Votadini appears to have been the Traprain Law hill fort in East Lothian, until that was abandoned in the early 5th century. They afterwards moved to Din Eidyn (Edinburgh). The name is recorded as ''Votadini'' in classical sources, and as ''Otodini'' on old maps of ancient Roman Britain. Their descendants were the early medieval kingdom known in Old Welsh as '' Guotodin'', and in later Welsh as ''Gododdin'' . One of the oldest known pieces of British literature is a poem ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Britons (historical)
The Britons ( *''Pritanī'', la, Britanni), also known as Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons, were people of Celtic language and culture who inhabited Great Britain from at least the British Iron Age and into the Middle Ages, at which point they diverged into the Welsh, Cornish and Bretons (among others). They spoke the Common Brittonic language, the ancestor of the modern Brittonic languages. The earliest written evidence for the Britons is from Greco-Roman writers and dates to the Iron Age.Koch, pp. 291–292. Celtic Britain was made up of many tribes and kingdoms, associated with various hillforts. The Britons followed an Ancient Celtic religion overseen by druids. Some of the southern tribes had strong links with mainland Europe, especially Gaul and Belgica, and minted their own coins. The Roman Empire conquered most of Britain in the 1st century, creating the province of Britannia. The Romans invaded northern Britain, but the Britons and Caledonians in the north rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a Principate with Italia as the metropole of its provinces and the city of Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. The city of Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until AD 476 when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople following the capture of the Western capital of Ravenna by the Germanic barbarians. The adoption of Christianity as the state church of the Roman Empire in AD 380 and the fall of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)