|
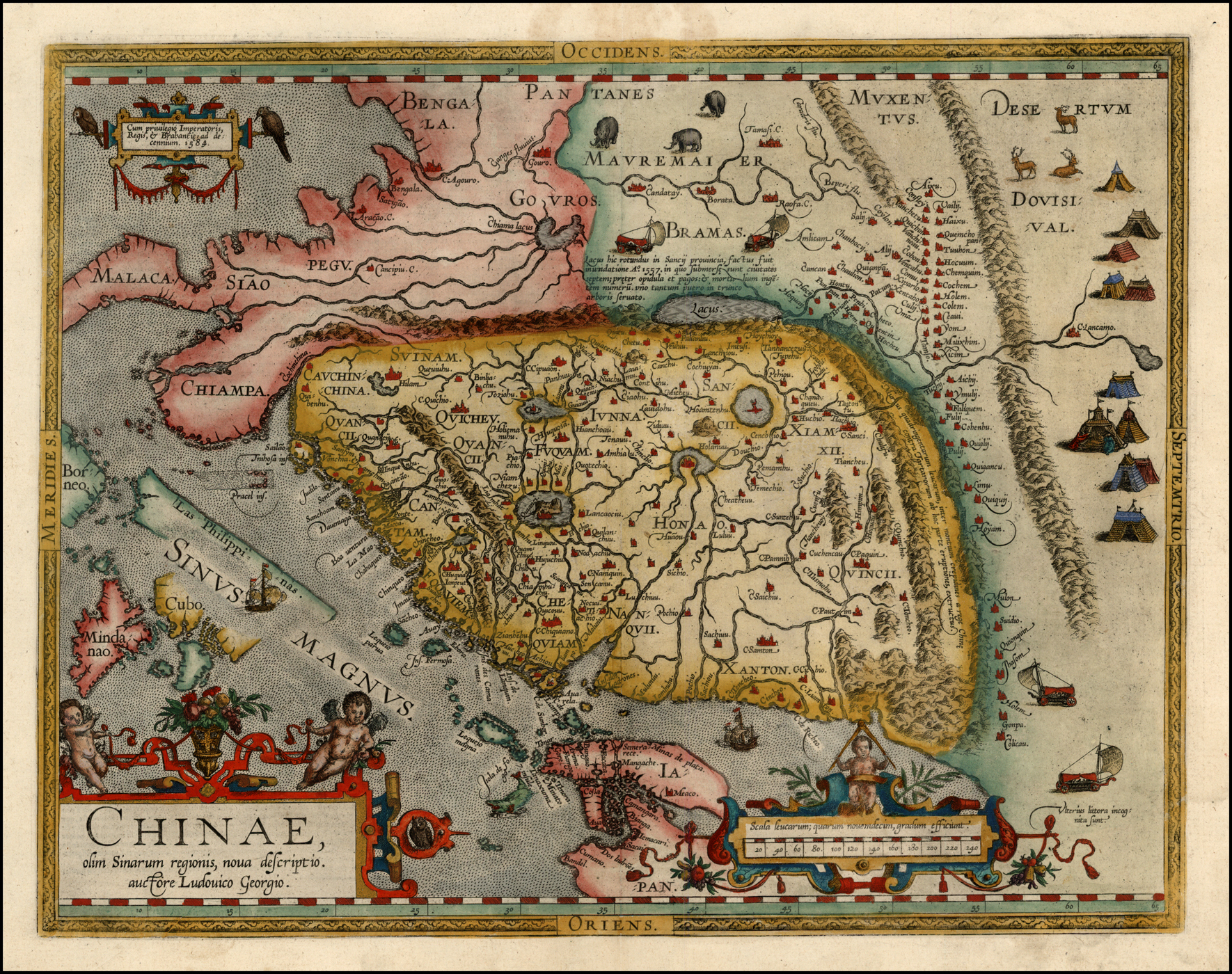
History Of Beijing
The city of Beijing has a long and rich history that dates back over 3,000 years. Prior to the unification of China by the Qin Shi Huang, First Emperor in 221 BC, Beijing had been for centuries the capital of the ancient states of Ji (state), Ji and Yan (state), Yan. It was a provincial center in the earliest unified empires of China, Qin dynasty, Qin and Han dynasty, Han. The northern border of ancient China ran close to the present city of Beijing, and northern nomadic tribes frequently broke in from across the border. Thus, the area that was to become Beijing emerged as an important strategic and a local political centre. During the first millennia of History of China#Imperial China, imperial rule, Beijing was a provincial city in North China, northern China. Its stature grew in the 10th to the 13th centuries when the nomadic Khitan people, Khitan and forest-dwelling Jurchen people, Jurchen peoples from beyond the Great Wall expanded southward and made the city a capital of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Names Of Beijing
"Beijing" is from pinyin ''Běijīng,'' which is romanized from , the Chinese name for this city. The pinyin system of transliteration was approved by the Chinese government in 1958, but little used until 1979. It was gradually adopted by various news organizations, governments, and international agencies over the next decade. Etymology The Chinese characters ("north") and ("capital") together mean the "Northern Capital". The name was first used during the reign of the Ming dynasty's Yongle Emperor, who made his northern fief a second capital, along with Nanjing (, the "Southern Capital"), in 1403 after successfully dethroning his nephew during the Jingnan Campaign. The name was restored in 1949 at the founding of the People's Republic of China. Peking Portugal was the first European country to contact China in modern times. In Portuguese, the city is called ''Pequim.'' This name appeared in the letters of Francis Xavier in 1552. It transferred to English as "Pekin" and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jin Dynasty (265–420)
Jin is a toneless pinyin romanization of various Chinese names and words. These have also been romanized as Kin and Chin (Wade–Giles). "Jin" also occurs in Japanese and Korean. It may refer to: States Jìn 晉 * Jin (Chinese state) (晉國), major state of the Zhou dynasty, existing from the 11th century BC to 376 BC * Jin dynasty (266–420) (晉朝), also known as Liang Jin and Sima Jin * Jin (Later Tang precursor) (晉國; 907–923), Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period * Later Jin (Five Dynasties) (後晉; 936–947), Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period Jīn 金 * Jin dynasty (1115–1234) (金朝), also known as the Jurchen Jin * Later Jin (1616–1636) (後金; 1616–1636), precursor of the Qing dynasty Others * Jin (Korean state) (辰國), precursor of the Jinhan Confederation * Balhae (698–713), originally known as Jin (震) Places * Jin Prefecture (Shanxi) (晉州), a former Chinese prefecture centered on present-day Linfen, Shanxi * Jin Prefecture (Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Dynasties
The Northern and Southern dynasties () was a period of political division in the history of China that lasted from 420 to 589, following the tumultuous era of the Sixteen Kingdoms and the Jin dynasty (266–420)#Eastern Jin, Eastern Jin dynasty. It is sometimes considered as the latter part of a longer period known as the Six Dynasties (220–589). Albeit an age of civil war and political chaos, it was also a time of flourishing arts and culture, advancement in technology, and the spread of Mahayana, Mahayana Buddhism and Taoism, Daoism. The period saw large-scale migration of the Han Chinese, Han people to the lands south of the Yangtze. The period came to an end with the unification of all of China proper by Emperor Wen of Sui, Emperor Wen of the Sui dynasty. During this period, the process of sinicization accelerated among the non-Han ethnicities in the north and among the indigenous peoples in the south. This process was also accompanied by the increasing popularity of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Later Yan
Yan, known in historiography as the Later Yan (; 384 – 407 or 409) was a dynastic state of China ruled by the Xianbei people, located in modern-day northeast China, during the era of Sixteen Kingdoms. All rulers of the Later Yan declared themselves "emperors". Rulers of the Later Yan See also *Battle of Canhebei * Wu Hu *List of past Chinese ethnic groups *Xianbei The Xianbei (; ) were a Proto-Mongolic ancient nomadic people that once resided in the eastern Eurasian steppes in what is today Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeastern China. They originated from the Donghu people who splintered into the ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Yan History of Mongolia 384 establishments 409 disestablishments Dynasties in Chinese history Former countries in Chinese history 4th-century establishments in China ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Qin
The Former Qin, also called Fu Qin (苻秦), (351–394) was a dynastic state of the Sixteen Kingdoms in Chinese history ruled by the Di ethnicity. Founded by Fu Jian (posthumously Emperor Jingming) who originally served under the Later Zhao dynasty, it completed the unification of northern China in 376. Its capital was Xi'an up to the death of the Emperor Xuanzhao in 385. Despite its name, the Former Qin was much later and less powerful than the Qin dynasty which had ruled all of China proper during the 3rd century BC. The adjectival prefix "former" is used to distinguish it from the "Later Qin dynasty" (384-417). In 383, the severe defeat of the Former Qin by the Jin dynasty at the Battle of Fei River encouraged uprisings, splitting Former Qin territory into two noncontiguous pieces after the death of Fu Jian. One fragment, at present-day Taiyuan, Shanxi was soon overwhelmed in 386 by the Xianbei under the Later Yan and the Dingling. The other struggled in greatly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Yan
The Former Yan (; 337–370) was a dynastic state ruled by the Xianbei during the era of Sixteen Kingdoms in China. Initially, Murong Huang and his son Murong Jun claimed the Jin dynasty-created title "Prince of Yan," but subsequently, in 352, after seizing most of the former Later Zhao territory, Murong Jun would declare himself emperor, and after that point, the rulers of the Former Yan declared themselves "emperors". History During the winter of 342, the Xianbei of Former Yan, ruled by the Murong clan, attacked and destroyed Goguryeo's capital, Hwando, capturing 50,000 Goguryeo men and women to use as slave labor in addition to taking the queen mother and queen prisoner, and forced King Gogukwon to flee for a while. The Xianbei also devastated Buyeo in 346, accelerating Buyeo migration to the Korean peninsula. Their capital was Yan (Beijing) in 350, then Yecheng in 357, and finally Luoyang in 364. File:MurongPainting.jpg, Painting depicting a Xianbei Murong archer in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Jin
Eastern may refer to: Transportation *China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai * Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways *Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 1926 to 1991 *Eastern Air Lines (2015), an American airline that began operations in 2015 *Eastern Airlines, LLC, previously Dynamic International Airways, a U.S. airline founded in 2010 *Eastern Airways, an English/British regional airline *Eastern Provincial Airways, a defunct Canadian airline that operated from 1949 to 1986 *Eastern Railway (other), various railroads * Eastern Avenue (other), various roads *Eastern Parkway (other), various parkways *Eastern Freeway, Melbourne, Australia *Eastern Freeway Mumbai, Mumbai, India *, a cargo liner in service 1946-65 Education *Eastern University (other) * Eastern College (other) Other uses * Eastern Broadcasting Limited, former name of Maritime Broadcasting System, Canad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shi Le
Shi Le (274–17 August 333), courtesy name Shilong, formally Emperor Ming of (Later) Zhao, was the founding emperor of the Jie-led Later Zhao dynasty of China. At a young age he was sold as a slave by Jin officials, but he later helped start a rebellion and eventually became a powerful general for the Xiongnu-led Han Zhao dynasty, conquering most of northern China in Han Zhao's name but holding the territory under his own control. In 319, after a dispute with the Han Zhao emperor Liu Yao, he broke away from Han Zhao and formed his own state, Later Zhao, and in 329 he captured Liu Yao and conquered Han Zhao, adding western China to his empire as well. Shi Le was known as a brilliant general, but was criticized by historians for excessive cruelty during his campaigns. He also put too much power in the hands of his ambitious and even more ferocious nephew Shi Hu who, after Shi Le's death, seized power from Shi Le's son Shi Hong. Early life Shi Le was born in 274—but was no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Later Zhao
The Later Zhao (; 319–351) was a dynasty of the Sixteen Kingdoms in northern China. It was founded by the Shi family of the Jie ethnicity. The Jie were most likely a Yeniseian people and spoke next to Chinese one of the Yeniseian languages.Vovin, Alexander. "Did the Xiongnu speak a Yeniseian language?". Central Asiatic Journal 44/1 (2000), pp. 87–104. The Later Zhao was the second in territorial size to the Former Qin dynasty that once unified northern China under Fu Jiān. When Later Zhao was founded by former Han general Shi Le, the capital was at Xiangguo (襄國, in modern Xingtai, Hebei), but in 335 Shi Hu moved the capital to Yecheng (鄴城, in modern Handan, Hebei), where it would remain for the rest of the state's history (except for Shi Zhi's brief attempt to revive the state at Xiangguo). Rulers of the Later Zhao Rulers family tree See also *Jie (ethnic group) * Wei–Jie war *List of past Chinese ethnic groups * Wu Hu * Buddhism in China *''Memoirs of Emine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yanqing County
Yanqing District (), formerly known as Yanqing County before 2015, is a district of the municipality of Beijing located northwest of the city proper of Beijing. The district consists of 3 subdistricts, 11 towns and 4 townships, and borders the Beijing districts of Huairou to the east and Changping to the south as well as the Hebei counties of Huailai to the west and Chicheng to the north. The district hosted the Expo 2019, and hosted alpine skiing, bobsled, luge and skeleton during the 2022 Winter Olympics. History In the Tang dynasty, Guichuan County, named after the Gui River, was established and belonged to the Gui Prefecture in Hebei, with a defensive military city. Eventually in 1952, it was reassigned to the Zhangjiakou Special Zone :zh:张家口专区">zh.html" ;"title=":zh:张家口专区.html" ;"title="nowiki/>:zh:张家口专区">zh">:zh:张家口专区.html" ;"title="nowiki/>:zh:张家口专区">zhin Hebei Province, and in 1958, it was transferred to Beijing. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanggu Commandery
Shanggu Commandery ( zh, 上谷郡) was a commandery in imperial China from the Warring States period to Tang dynasty. It was located in present-day Hebei and Beijing. The commandery was established by the state of Yan for the defense against the Xiongnu. In Western Han dynasty, it administered 15 counties, including Juyang (沮陽), Quanshang (泉上), Pan (潘), Jundu (軍都), Juyong (居庸), Goumao (雊瞀), Yiyu (夷輿), Ning (寧), Changping (昌平), Guangning (廣寧), Zhuolu (涿鹿), Qieju (且居), Ru (茹), Nüqi (女祈) and Xialuo (下落). Guangyang Commandery was merged into Shanggu in Emperor Guangwu of Han's reign, but was restored in 96 AD, and two former Shanggu counties – Jundu and Changping – was transferred there. Later during Eastern Han, only 8 counties remained, namely Juyang, Pan, Ning, Guangning, Juyong, Goumao, Zhuolu and Xialuo. The total number of households was 36,008 in 2 AD, while the population was 117,762. In 140 AD, the population was 51, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huairou District
Huairou District () is situated in northern Beijing about from the city center (about a 1½ to 2 hour drive). History In 1995 during the United Nation's 4th World's Women Conference in Beijing, the Civil Society community was forced to meet in the Huairou district, an hour from the official proceedings, leading to a great deal of discontent, as many of the non-governmental actors present felt marginalized. In a tent at the Civil Society Village established especially for poor, grassroots women at the conference (organized by GROOTS International), the Huairou Commission, a registered non-governmental organization with a global secretariat in Brooklyn, NY, was established to ensure that grassroots women would have a voice at subsequent UN conferences and in other development processes. Also in 1995, film industry began to develop in Yangsong, a town in the southeast of Huairou. China Film Group Corporation built its studio in Huairou in 2005. In 2014, another international confe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |