|
Healthcare In Benin
Benin faces a number of population health challenges. Apart from modern medicine, traditional medicine plays a big role too. The Human Rights Measurement Initiative finds that Benin is fulfilling 59.2% of what it should be fulfilling for the right to health based on its level of income. When looking at the right to health with respect to children, Benin achieves 77.5% of what is expected based on its current income. In regards to the right to health amongst the adult population, the country achieves 81.5% of what is expected based on the nation's level of income. Benin falls into the "very bad" category when evaluating the right to reproductive health because the nation is fulfilling only 18.5% of what the nation is expected to achieve based on the resources (income) it has available. Water supply and sanitation According to the Joint Monitoring Program of the World Health Organization and UNICEF, three quarters of the Beninese population had access to an improved water sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benin
Benin ( , ; french: Bénin , ff, Benen), officially the Republic of Benin (french: République du Bénin), and formerly Dahomey, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the north-west, and Niger to the north-east. The majority of its population lives on the southern coastline of the Bight of Benin, part of the Gulf of Guinea in the northernmost tropical portion of the Atlantic Ocean. The capital is Porto-Novo, and the seat of government is in Cotonou, the most populous city and economic capital. Benin covers an area of and its population in was estimated to be approximately million. It is a tropical nation, dependent on agriculture, and is an exporter of palm oil and cotton. Some employment and income arise from subsistence farming. The official language of Benin is French, with indigenous languages such as Fon, Bariba, Yoruba and Dendi also spoken. The largest religious group in Benin is Sunni Islam (27 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porto-Novo
Porto-Novo (Portuguese: "New Port", , ; yo, Àjàṣẹ́, ), also known as Hogbonu and Ajashe, is the capital of Benin. The commune covers an area of and as of 2002 had a population of 223,552 people. Situated on an inlet of the Gulf of Guinea, in the southeastern portion of the country, the city was originally developed as a port for the transatlantic slave trade led by the Portuguese Empire. It is Benin's second-largest city, and although it is the official capital, where the national legislature sits, the larger city of Cotonou is the seat of government, where most of the government buildings are situated and government departments operate. Etymology The name ''Porto-Novo'' is of Portuguese origin, literally meaning "New Port". It remains untranslated in French, the national language of Benin. History Porto-Novo was once a tributary of the Yoruba kingdom of Oyo, which had offered it protection from the neighbouring Fon, who were expanding their influence and power in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COVID-19 Pandemic In Benin
The COVID-19 pandemic in Benin was a part of the ongoing worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 () caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (). The virus was confirmed to have reached Benin in March 2020. Background On 12 January 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) confirmed that a novel coronavirus was the cause of a respiratory illness in a cluster of people in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China, which was reported to the WHO on 31 December 2019. The case fatality ratio for COVID-19 has been much lower than SARS of 2003, but the transmission has been significantly greater, with a significant total death toll. Model-based simulations for Benin suggest that the 95% confidence interval for the time-varying reproduction number ''R t'' diminished to around 0.6 during the second half of 2021. Timeline March to June 2020 * On 16 March, the first COVID-19 case in the country was confirmed in Porto-Novo, the capital of Benin. Three days la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaria In Benin
Malaria in Benin is the leading cause of mortality among children under five years of age and morbidity among adults. Malaria accounts for 40 percent of outpatient consultations and 25 percent of all hospital admissions. Malaria places an enormous economic strain on Benin's development. The World Bank estimates that households in Benin spend approximately one quarter of their annual income on the prevention and treatment of malaria. Benin's long-term goal is to reduce the burden of malaria in order to improve national socio-economic development. Large-scale implementation of artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) and intermittent preventive treatment for pregnant women (IPTp) began in Benin in 2007 and has progressed rapidly. Rapid diagnostic tests, ACTs, and IPTp are being used in public health facilities nationwide and are being introduced into registered private clinics. More than 6 million long-lasting insecticide-treated nets have been distributed through mass and con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Female Genital Mutilation
Female genital mutilation (FGM), also known as female genital cutting, female genital mutilation/cutting (FGM/C) and female circumcision, is the ritual cutting or removal of some or all of the external female genitalia. The practice is found in some countries of Africa, Asia and the Middle East, and within communities abroad from countries in which FGM is common. UNICEF estimated, in 2016, that 200 million women in 30 countries—Indonesia, Iraq, Yemen, and 27 African countries including Egypt—had been subjected to one or more types of FGM. Typically carried out by a traditional circumciser using a blade, FGM is conducted from days after birth to puberty and beyond. In half of the countries for which national statistics are available, most girls are cut before the age of five. Procedures differ according to the country or ethnic group. They include removal of the clitoral hood (type 1-a) and clitoral glans (1-b); removal of the inner labia; and removal of the inner and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronavirus Disease 2019
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The disease quickly spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic. The symptoms of COVID‑19 are variable but often include fever, cough, headache, fatigue, breathing difficulties, loss of smell, and loss of taste. Symptoms may begin one to fourteen days after exposure to the virus. At least a third of people who are infected do not develop noticeable symptoms. Of those who develop symptoms noticeable enough to be classified as patients, most (81%) develop mild to moderate symptoms (up to mild pneumonia), while 14% develop severe symptoms (dyspnea, hypoxia, or more than 50% lung involvement on imaging), and 5% develop critical symptoms (respiratory failure, shock, or multiorgan dysfunction). Older people are at a higher risk of developing seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhoid Fever
Typhoid fever, also known as typhoid, is a disease caused by '' Salmonella'' serotype Typhi bacteria. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several days. This is commonly accompanied by weakness, abdominal pain, constipation, headaches, and mild vomiting. Some people develop a skin rash with rose colored spots. In severe cases, people may experience confusion. Without treatment, symptoms may last weeks or months. Diarrhea may be severe, but is uncommon. Other people may carry the bacterium without being affected, but they are still able to spread the disease. Typhoid fever is a type of enteric fever, along with paratyphoid fever. ''S. enterica'' Typhi is believed to infect and replicate only within humans. Typhoid is caused by the bacterium ''Salmonella enterica'' subsp. ''enterica'' serovar Typhi growing in the intestines, peyers patches, mesenteric lymph nodes, spleen, liver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin ten to fifteen days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria. Malaria is caused by single-celled microorganisms of the ''Plasmodium'' group. It is spread exclusively through bites of infected ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. The mosquito bite introduces the parasites from the mosquito's saliva into a person's blood. The parasites travel to the liver where they mature and reproduce. Five species of ''Plasmodium'' can infect and be spread by h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water-borne Diseases
Waterborne diseases are conditions (meaning adverse effects on human health, such as death, disability, illness or disorders) caused by pathogenic micro-organisms that are transmitted in water. These diseases can be spread while bathing, washing, drinking water, or by eating food exposed to contaminated water. They are a pressing issue in rural areas amongst developing countries all over the world. While diarrhea and vomiting are the most commonly reported symptoms of waterborne illness, other symptoms can include skin, ear, respiratory, or eye problems. Lack of clean water supply, sanitation and hygiene (WASH) are major causes for the spread of waterborne diseases in a community. Therefore, reliable access to clean drinking water and sanitation is the main method to prevent waterborne diseases. Microorganisms causing diseases that characteristically are waterborne prominently include protozoa and bacteria, many of which are intestinal parasites, or invade the tissues or circulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parakou
Parakou is the largest city in northern Benin, with an estimated population of around 206,667 people, and capital of the Borgou Department. Administratively the commune of Parakou makes up one of Benin's 77 communes. Since 2015, its mayor is Souradjou Adamou Karimou. History The city was founded in the 16th century by traders. Economy Parakou lies on the main north-south highway RNIE 2 and at the end of a railway to Cotonou. Markets This has made it an important market town, with major industries including cotton and textiles, peanut oil manufacture and brewing. The town grew initially from revenue generated from passing merchants that took goods from the region across the Sahara and the Mediterranean to Europe.Butler, Stuart (2019) ''Bradt Travel Guide - Benin'', pgs. 177-180 Parakou later became well known in the slave trade. Later traders concentrated on cotton and Parakou remains the hub of the Beninese cotton trade to this day, with considerable interest from Europe. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditional Medicine
Traditional medicine (also known as indigenous medicine or folk medicine) comprises medical aspects of traditional knowledge that developed over generations within the folk beliefs of various societies, including indigenous peoples, before the era of modern medicine. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines traditional medicine as "the sum total of the knowledge, skills, and practices based on the theories, beliefs, and experiences indigenous to different cultures, whether explicable or not, used in the maintenance of health as well as in the prevention, diagnosis, improvement or treatment of physical and mental illness". Traditional medicine is often contrasted with scientific medicine. In some Asian and African countries, up to 80% of the population relies on traditional medicine for their primary health care needs. When adopted outside its traditional culture, traditional medicine is often considered a form of alternative medicine. Practices known as traditional medicines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
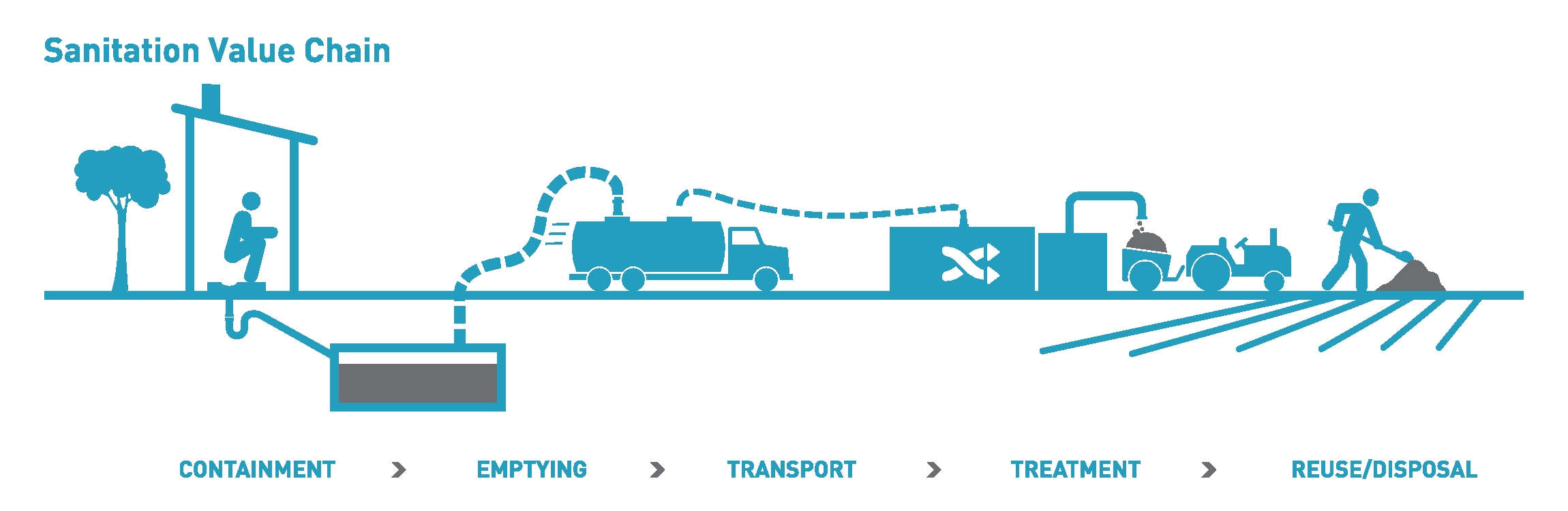
Improved Sanitation
Improved sanitation (related to but distinct from a " safely managed sanitation service") is a term used to categorize types of sanitation for monitoring purposes. It refers to the management of human feces at the household level. The term was coined by the Joint Monitoring Program (JMP) for Water Supply and Sanitation of UNICEF and WHO in 2002 to help monitor the progress towards Goal Number 7 of the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). The opposite of "improved sanitation" has been termed "unimproved sanitation" in the JMP definitions. The same terms are used to monitor progress towards Sustainable Development Goal 6 (Target 6.2, Indicator 6.2.1) from 2015 onwards.WHO and UNICEF (2017Progress on Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene: 2017 Update and SDG Baselines Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO) and the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), 2017 Here, they are a component of the definition for "safely managed sanitation service". The Joint Monitoring Program (JM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
_2.jpg)