|
Gothic War (376–382)
Between 376 and 382 the Gothic War against the Eastern Roman Empire, and in particular the Battle of Adrianople, is commonly seen as a major turning point in the history of the Roman Empire, the first of a series of events over the next century that would see the collapse of the Western Roman Empire, although its ultimate importance to the Empire's eventual fall is still debated. It was one of the many Gothic Wars with the Roman Empire. Background In the summer of 376, a massive number of Goths arrived on the Danube River, the border of the Roman Empire, requesting asylum from the Huns. There were two groups: the Thervings led by Fritigern and Alavivus and the Greuthungi led by Alatheus and Saphrax. Eunapius states their number as 200,000 including civilians but Peter Heather estimates that the Thervings may have had only 10,000 warriors and 50,000 people in total, with the Greuthungi about the same size. The Cambridge Ancient History places modern estimates at around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obelisk Of Theodosius
The Obelisk of Theodosius ( tr, Dikilitaş) is the Ancient Egyptian obelisk of Pharaoh Thutmose III re-erected in the Hippodrome of Constantinople (known today as ''At Meydanı'' or ''Sultanahmet Meydanı'', in the modern city of Istanbul, Turkey) by the Roman emperor Theodosius I in the 4th century AD. History The obelisk was first erected during the 18th dynasty by Pharaoh Thutmose III (1479–1425 BC) to the south of the seventh pylon of the great temple of Karnak. The Roman emperor Constantius II (337–361 AD) had it and another obelisk transported along the river Nile to Alexandria to commemorate his ''ventennalia'' or 20 years on the throne in 357. The other obelisk was erected on the '' spina'' of the Circus Maximus in Rome in the autumn of that year, and is now known as the Lateran Obelisk. The obelisk that would become the obelisk of Theodosius remained in Alexandria until 390; when Theodosius I (379–395 AD) had it transported to Constantinople and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ricomer
Flavius Richomeres or Ricomer (died 393) was a Frank who lived in the late 4th century. He took service in the Roman army and made a career as ''comes'', ''magister militum'', and ''consul''. He was an uncle of the general Arbogastes. He is possibly to be identified with the Richomeres who married Ascyla, whose son Theodemer later became king of the Franks. Life Around the years 377/378, Richomeres was ''comes domesticorum'' of Emperor Gratian and was transferred from Gaul to Thracia, where he was involved in the Gothic wars of Emperor Valens. At Adrianople, he tried to persuade Valens to wait on Gratian for support. When the Gothic leader Fritigern demanded hostages to secure peace from the Romans, he volunteered and departed the Roman camp to bring the other hostages safely to Fritigern, but before he arrived, some elements of the two armies got out of control and engaged, starting the famous Battle of Adrianople. Richomeres ended up at a battlefield in complete chaos, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Heather
Peter John Heather (born 8 June 1960) is a British historian of late antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Heather is Chair of the Medieval History Department and Professor of Medieval History at King's College London. He specialises in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the Goths, on which he for decades has been considered the world's leading authority. Biography Heather was born in Northern Ireland on 8 June 1960. He was educated at Maidstone Grammar School, and received his M.A. and D.Phil. from New College, Oxford. Among his teachers at Oxford were John Matthews and James Howard-Johnston. Heather subsequently lectured at Worcester College, Oxford, Yale University and University College London. In January 2008, Heather was appointed chair of the Medieval History Department and professor of medieval history at King's College London. Research As a historian, Heather specialises in late antiquity and the Early Middle Ages, especially the relationships between the Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eunapius
Eunapius ( el, Εὐνάπιος; fl. 4th–5th century AD) was a Greek sophist and historian of the 4th century AD. His principal surviving work is the ''Lives of Philosophers and Sophists'' ( grc-gre, Βίοι Φιλοσόφων καὶ Σοφιστῶν; la, Vitae sophistarum), a collection of the biographies of 23 philosophers and sophists. Life He was born at Sardis, AD 347. In his native city he studied under his relative, the sophist Chrysanthius, and while still a youth went to Athens, where he became a favourite pupil of Prohaeresius the rhetorician. He possessed considerable knowledge of medicine. In his later years he seems to have lived at Athens, teaching rhetoric. He was initiated into the Eleusinian Mysteries by the last Hierophant, Nestorius.Eunapius, ''Vit. Soph.'' 7.3.1; K. Clinton, ''Sacred Officials of the Eleusinian Mysteries'' (1974) p. 42ff. There is evidence that he was still living in the reign of the younger Theodosius. Writing Eunapius was the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alavivus
Alavivus (flourished in 4th century AD) was a Gothic co-king of a group of Thervingi together with Fritigern. Along with the latter he led the migration of the Thervingi from Dacia across the Danube into the Roman Empire in the late 4th century AD. Upon arrival in the Roman Empire, the Goths suffered from widespread famine, with some Gothic parents reportedly being forced to sell their children into slavery in return for rotten dog meat in order to avoid starvation. In 376, Valens' lieutenant Lupicinus invited Alavivus and Fritigern to a banquet to discuss provisions for their people, where Alavivus was assassinated. Fritigern on the other hand managed to escape, inciting a revolt which culminated with a decisive Gothic victory at the Battle of Adrianople The Battle of Adrianople (9 August 378), sometimes known as the Battle of Hadrianopolis, was fought between an Eastern Roman army led by the Eastern Roman Emperor Valens and Gothic rebels (largely Thervings as well as Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danube River
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , passing through or bordering Austria, Slovakia, Hungary, Croatia, Serbia, Romania, Bulgaria, Moldova, and Ukraine before draining into the Black Sea. Its drainage basin extends into nine more countries. List of cities and towns on Danube river, The largest cities on the river are Vienna, Budapest, Belgrade and Bratislava, all of which are the capitals of their respective countries; the Danube passes through four capital cities, more than any other river in the world. Five more capital cities lie in the Danube's basin: Bucharest, Sofia, Zagreb, Ljubljana and Sarajevo. The fourth-largest city in its basin is Munich, the capital of Bavaria, standing on the Isar River. The Danube is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest riv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. In his book '' Getica'' (c. 551), the historian Jordanes writes that the Goths originated in southern Scandinavia, but the accuracy of this account is unclear. A people called the '' Gutones''possibly early Gothsare documented living near the lower Vistula River in the 1st century, where they are associated with the archaeological Wielbark culture. From the 2nd century, the Wielbark culture expanded southwards towards the Black Sea in what has been associated with Gothic migration, and by the late 3rd century it contributed to the formation of the Chernyakhov culture. By the 4th century at the latest, several Gothic groups were distinguishable, among whom the Thervingi and Greuthungi were the most powerful. During this time, W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic Wars
The Gothic Wars were a long series of conflicts between the Goths and the Roman Empire between the years 249 and 554. The main wars are detailed below. Gothic War (249–253) (Goths under Cniva against the Roman Empire) The War was probably instigated after emperor Decius' predecessor Philip the Arab had refused to continue payments of annual subsidies to the tribes of the region initiated by Emperor Maximinus Thrax in 238 while they were starving. The Goths were led by King Cniva who had crossed the Danube in 249 or 250 with two armies. Cniva's main column of 70,000 unsuccessfully attacked Novae and were then defeated by Decius at the Battle of Nicopolis ad Istrum before moving on to Augusta Traiana pursued by Decius where at the Battle of Beroe they defeated him and looted the city. Decius was forced to withdraw his army north to Oescus leaving Cniva ample time to ravage Moesia and move on to Philippopolis (Thracia) (now Plovdiv in Bulgaria). Another army of about 20, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fall Of The Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vast territory was divided into several successor polities. The Roman Empire lost the strengths that had allowed it to exercise effective control over its Western provinces; modern historians posit factors including the effectiveness and numbers of the army, the health and numbers of the Roman population, the strength of the economy, the competence of the emperors, the internal struggles for power, the religious changes of the period, and the efficiency of the civil administration. Increasing pressure from invading barbarians outside Roman culture also contributed greatly to the collapse. Climatic changes and both endemic and epidemic disease drove many of these immediate factors. The reasons for the collapse are major subjects of the his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
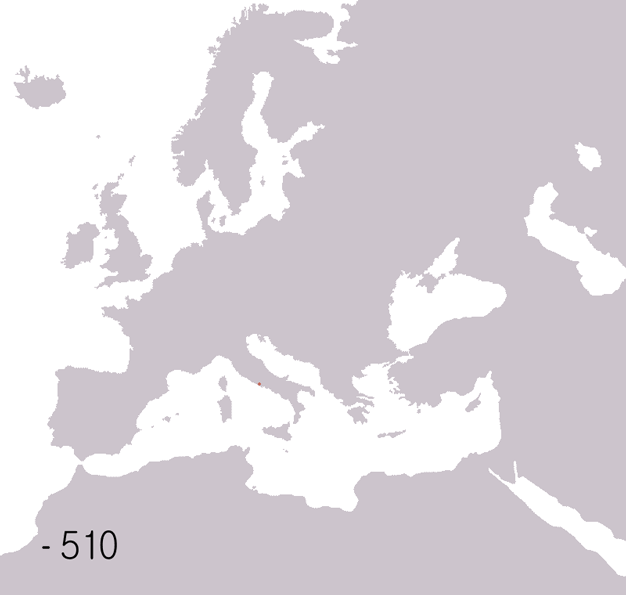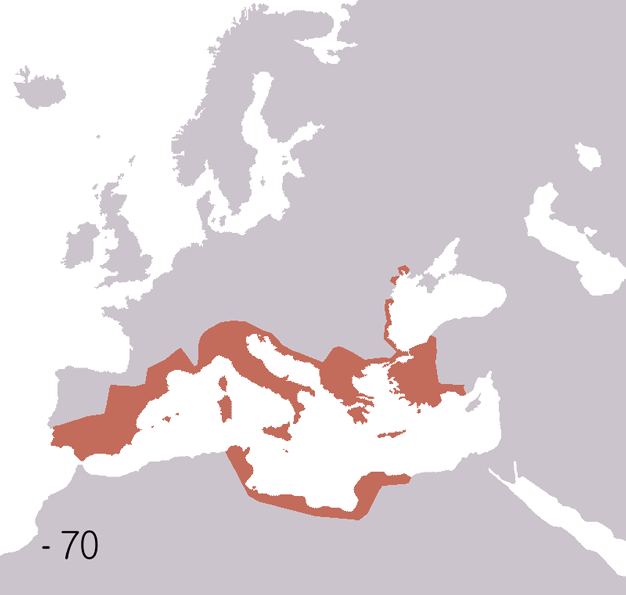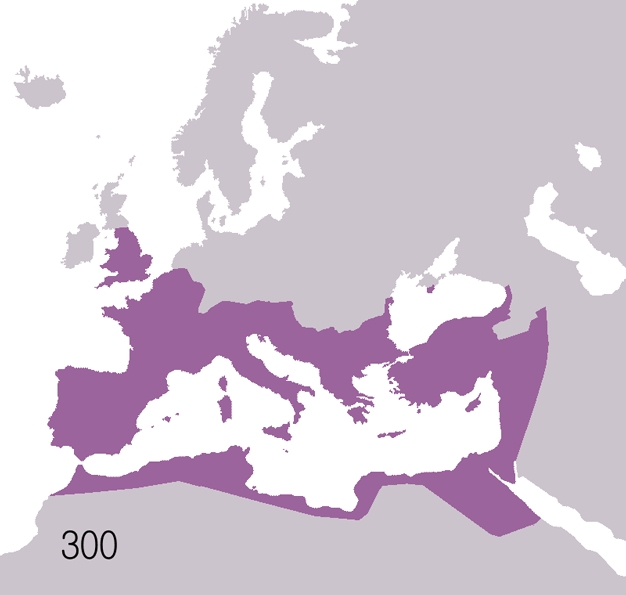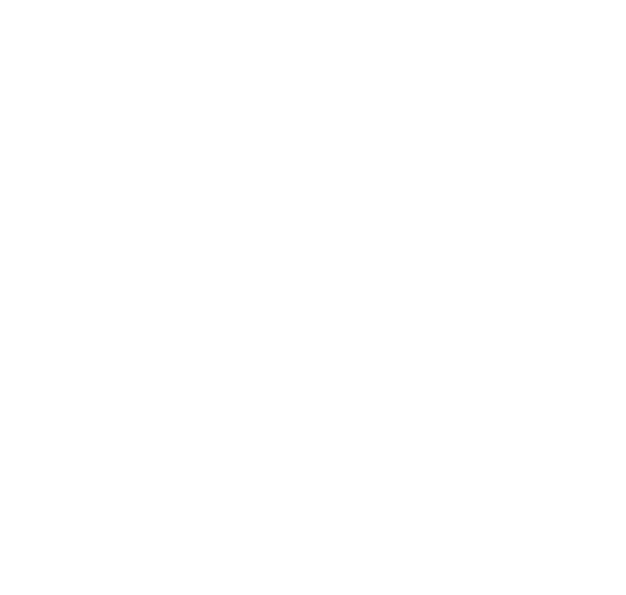
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a Principate with Italia as the metropole of its provinces and the city of Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. The city of Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until AD 476 when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople following the capture of the Western capital of Ravenna by the Germanic barbarians. The adoption of Christianity as the state church of the Roman Empire in AD 380 and the fall of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Adrianople
The Battle of Adrianople (9 August 378), sometimes known as the Battle of Hadrianopolis, was fought between an Eastern Roman army led by the Eastern Roman Emperor Valens and Gothic rebels (largely Thervings as well as Greutungs, non-Gothic Alans, and various local rebels) led by Fritigern. The battle took place in the vicinity of Adrianople, in the Roman province of Thracia (modern Edirne in European Turkey). It ended with an overwhelming victory for the Goths and the death of Emperor Valens.Zosimus, ''Historia Nova'', book 4. As part of the Gothic War (376–382), the battle is often considered the start of the events which led to the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century. A detailed contemporary account of the lead-up to the battle from the Roman perspective was written by Ammianus Marcellinus and forms the culminating point at the end of his history. Background In 376, the Goths, led by Alavivus and Fritigern, asked to be allowed to settle in the Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)