|
Geonomateae
Geonomateae (also Geonomeae) is a palm tribe in the subfamily Arecoideae. It is an important Neotropical group due to its wide distribution across Central and South America, its diversity and abundance, and the use of a number of species by local human populations. The distribution of the tribe stretches from southeast Mexico down through Central America and into South America, notably Brazil and Bolivia, and species are also found in the Greater and Lesser Antilles. This tribe consists of a group of understory and sub-canopy palms that populate both tropical lowland and montane forests. While members of this group are relatively easy to collect, as they are not canopy palms or spiny palms, and are well represented in herbaria, the taxonomy and phylogeny of the species within the tribe are still uncertain. The resolution of the tribe has been disputed despite the fact that tribe's species are characterized by three morphological synapomorphies: the petals of pistillate flowers are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geonomateae
Geonomateae (also Geonomeae) is a palm tribe in the subfamily Arecoideae. It is an important Neotropical group due to its wide distribution across Central and South America, its diversity and abundance, and the use of a number of species by local human populations. The distribution of the tribe stretches from southeast Mexico down through Central America and into South America, notably Brazil and Bolivia, and species are also found in the Greater and Lesser Antilles. This tribe consists of a group of understory and sub-canopy palms that populate both tropical lowland and montane forests. While members of this group are relatively easy to collect, as they are not canopy palms or spiny palms, and are well represented in herbaria, the taxonomy and phylogeny of the species within the tribe are still uncertain. The resolution of the tribe has been disputed despite the fact that tribe's species are characterized by three morphological synapomorphies: the petals of pistillate flowers are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geonoma
''Geonoma'' is a genus of small to medium-sized palms native to the forest understorey of tropical Central and South America. This palm genus is one of the largest in the Neotropics. Its 64 species are distributed from Mexico and Haiti in the north to Paraguay in the south; two are found in the Lesser Antilles. Uses In South America, the leaves of species such as '' Geonoma deversa'', '' Geonoma orbignyana'', and '' Geonoma macrostachys'' are economically important for their use in thatching roofs. Taxonomy The genus is a member of the palm tribe Geonomateae (Arecaceae: Arecoideae), an important Neotropical group due to its wide distribution across Central and South America, its diversity and abundance, and the use of a number of species by local human populations. The distribution of the tribe Geonomeae stretches from southeast Mexico down through Central America and into South America, notably Brazil and Bolivia, and species are also found in the Greater and Lesser Antilles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Arecaceae Genera
This is a list of all the genus, genera in the botanical family Arecaceae, the palm family, based on Baker & Dransfield (2016), which is a revised listing of genera given in the 2008 edition of ''Genera Palmarum''. Taxonomy This is a list of all the genus, genera in the botanical family Arecaceae, the palm family, arranged by tribe (biology), tribes and subtribes within the family. ''Genera Palmarum'' (2008) lists 183 genera. ''Lanonia'', ''Saribus'', and the monotypic genera ''Jailoloa'', ''Wallaceodoxa'', ''Manjekia'', and ''Sabinaria'', which were described after 2008, have also been included below. ''Ceratolobus'', ''Daemonorops'', ''Pogonotium'', ''Wallichia'', ''Lytocaryum'', and the monotypic genera ''Retispatha'', ''Pritchardiopsis'', and ''Solfia'' have since been removed from ''Genera Palmarum'' (2008) as obsolete genera. This brings the total number of genera to 181 as of 2016. Subfamily Calamoideae *Tribe Eugeissoneae **''Eugeissona'' – Borneo, Malay Peninsula *Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pholidostachys
''Pholidostachys'' is a genus of palms found in Central America and northwestern South America (northwestern Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru , image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg , image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg , other_symbol = Great Seal of the State , other_symbol_type = Seal (emblem), National seal , national_motto = "Fi ...).Govaerts, R. & Dransfield, J. (2005). World Checklist of Palms: 1-223. The Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.Henderson, A. (2012). A revision of ''Pholidostachys'' (Arecaceae). Phytotaxa 43: 1-48. * '' Pholidostachys amazonensis'' A.J.Hend. - Peru * '' Pholidostachys dactyloides'' H.E.Moore. - Panama, Colombia, Ecuador * '' Pholidostachys kalbreyeri'' H.Wendl. ex Burret - Panama, Colombia * '' Pholidostachys occidentalis'' A.J.Hend. - Ecuador * '' Pholidostachys panamensis'' A.J.Hend. - Panama * '' Pholidostachys pulchra'' H.Wendl. ex Burret - Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Panama, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welfia
''Welfia'' is a genus of palms found in Central America (Panama, Costa Rica, Honduras, Nicaragua) and northwestern South America (Colombia, Ecuador, Peru). Only two species are currently recognized: ''Welfia regia'' and ''Welfia alfredii ''Welfia'' is a genus of Arecaceae, palms found in Central America (Panama, Costa Rica, Honduras, Nicaragua) and northwestern South America (Colombia, Ecuador, Peru). Only two species are currently recognized: ''Welfia regia'' and ''Welfia alfred ...''.Nelson Sutherland, C.H. (2008). Catálogo de las plantes vasculares de Honduras. Espermatofitas: 1-1576. SERNA/Guaymuras, Tegucigalpa, Honduras. References Geonomateae Flora of Central America Flora of South America Arecaceae genera {{palm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arecoideae
The Arecaceae is a family of perennial flowering plants in the monocot order Arecales. Their growth form can be climbers, shrubs, tree-like and stemless plants, all commonly known as palms. Those having a tree-like form are called palm trees. Currently, 181 genera with around 2,600 species are known, most of which are restricted to tropical and subtropical climates. Most palms are distinguished by their large, compound, evergreen leaves, known as fronds, arranged at the top of an unbranched stem. However, palms exhibit an enormous diversity in physical characteristics and inhabit nearly every type of habitat within their range, from rainforests to deserts. Palms are among the best known and most extensively cultivated plant families. They have been important to humans throughout much of history. Many common products and foods are derived from palms. In contemporary times, palms are also widely used in landscaping. In many historical cultures, because of their importance as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montane Forest
Montane ecosystems are found on the slopes of mountains. The alpine climate in these regions strongly affects the ecosystem because temperatures fall as elevation increases, causing the ecosystem to stratify. This stratification is a crucial factor in shaping plant community, biodiversity, metabolic processes and ecosystem dynamics for montane ecosystems. Dense montane forests are common at moderate elevations, due to moderate temperatures and high rainfall. At higher elevations, the climate is harsher, with lower temperatures and higher winds, preventing the growth of trees and causing the plant community to transition to montane grasslands, shrublands or alpine tundra. Due to the unique climate conditions of montane ecosystems, they contain increased numbers of endemic species. Montane ecosystems also exhibit variation in ecosystem services, which include carbon storage and water supply. Life zones As elevation increases, the climate becomes cooler, due to a decrease in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
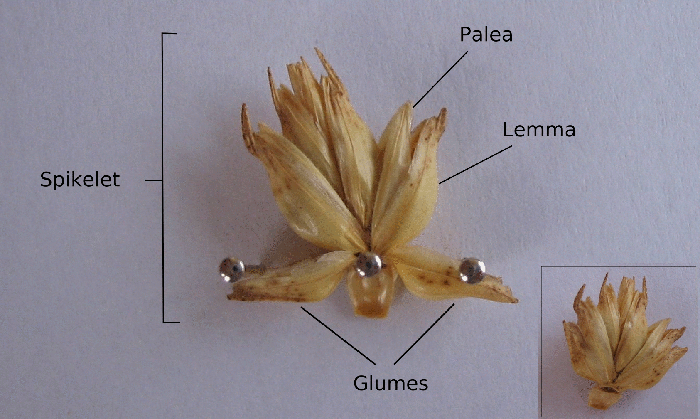
Rachilla (floral Axis)
A spikelet, in botany, describes the typical arrangement of the flowers of grasses, sedges and some other Monocots. Each spikelet has one or more florets. The spikelets are further grouped into panicles or spikes. The part of the spikelet that bears the florets is called the rachilla. In grasses In Poaceae, the grass family, a spikelet consists of two (or sometimes fewer) bracts at the base, called glumes, followed by one or more florets. A floret consists of the flower surrounded by two bracts, one external—the lemma—and one internal—the palea. The perianth is reduced to two scales, called lodicules, that expand and contract to spread the lemma and palea; these are generally interpreted to be modified sepals. The flowers are usually hermaphroditic—maize being an important exception—and mainly anemophilous or wind-pollinated, although insects occasionally play a role. Lemma Lemma is a phytomorphological term referring to a part of the spikelet. It is the lowermost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gynoecium
Gynoecium (; ) is most commonly used as a collective term for the parts of a flower that produce ovules and ultimately develop into the fruit and seeds. The gynoecium is the innermost whorl of a flower; it consists of (one or more) ''pistils'' and is typically surrounded by the pollen-producing reproductive organs, the stamens, collectively called the androecium. The gynoecium is often referred to as the "female" portion of the flower, although rather than directly producing female gametes (i.e. egg cells), the gynoecium produces megaspores, each of which develops into a female gametophyte which then produces egg cells. The term gynoecium is also used by botanists to refer to a cluster of archegonia and any associated modified leaves or stems present on a gametophyte shoot in mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. The corresponding terms for the male parts of those plants are clusters of antheridia within the androecium. Flowers that bear a gynoecium but no stamens are called ''pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synapomorphy
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form (or plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to have evolved in their most recent common ancestor. ) In cladistics, synapomorphy implies homology. Examples of apomorphy are the presence of erect gait, fur, the evolution of three middle ear bones, and mammary glands in mammals but not in other vertebrate animals such as amphibians or reptiles, which have retained their ancestral traits of a sprawling gait and lack of fur. Thus, these derived traits are also synapomorphies of mammals in general as they are not shared by other vertebrate animals. Etymology The word —coined by German entomologist Willi Hennig—is derived from the Ancient Greek words (''sún''), meaning "with, together"; (''apó''), meaning "away from"; and (''morphḗ''), meaning "shape, form". Clade analysis T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
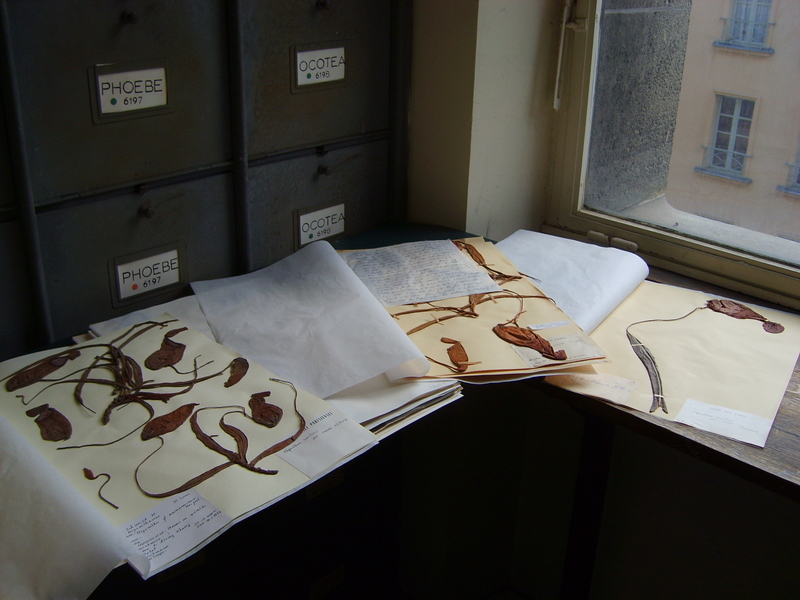
Herbarium
A herbarium (plural: herbaria) is a collection of preserved plant specimens and associated data used for scientific study. The specimens may be whole plants or plant parts; these will usually be in dried form mounted on a sheet of paper (called ''exsiccatum'', plur. ''exsiccata'') but, depending upon the material, may also be stored in boxes or kept in alcohol or other preservative. The specimens in a herbarium are often used as reference material in describing plant taxa; some specimens may be types. The same term is often used in mycology to describe an equivalent collection of preserved fungi, otherwise known as a fungarium. A xylarium is a herbarium specialising in specimens of wood. The term hortorium (as in the Liberty Hyde Bailey Hortorium) has occasionally been applied to a herbarium specialising in preserving material of horticultural origin. History The making of herbaria is an ancient phenomenon, at least six centuries old, although the techniques have changed l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geonoma Undata
''Geonoma undata'' is a species of medium-sized palm tree native to North and South America. It grows in the understory of tropical forests at high altitudes. This species has highly variable traits depending on its geographic location and several subspecies exist as a result. Taxonomy ''Geonoma undata'' is a neotropical species most closely related to ''G. lehmannii'', ''G. orbignyana'', ''G. talamancana'', and ''G. trigona''. In fact, ''G. undata'' is nearly indistinguishable from the species ''G. lehmannii'' and ''G. orbignyana''. The epithet name ''undata'' comes from the Latin term for "wavy" or "wave-like". Description This plant is a medium-sized, solitary palm that reaches a maximum height of 9-10 meters and has a trunk 10 cm wide in diameter at maturity. The leaves are approximately 2.5 m long and can be divided or undivided. If leaves are divided, they tend to be irregularly pinnate with the base of pinnate leaflets being diagonal to the stem rachis. The protecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |