|
Geology Of Ukraine
The geology of Ukraine is the regional study of rocks, minerals, tectonics, natural resources and groundwater in Ukraine. The oldest rocks in the region are part of the Ukrainian Shield and formed more than 2.5 billion years ago in the Archean eon of the Precambrian. Extensive tectonic evolution and numerous orogeny mountain-building events fractured the Crust (geology), crust into numerous block, Horst (geology), horsts, grabens and Depression (geology), depressions. Ukraine was intermittently flooded as the crust downwarped during much of the Paleozoic, Mesozoic and early Cenozoic, before the formation of the Alps and Carpathian Mountains defined much of its current topography and tectonics. Ukraine was impacted by the Quaternary glaciation, Pleistocene glaciations within the last several hundred thousand years. The country has numerous metal deposits as well as minerals, building stone and high-quality industrial sands. Stratigraphy, tectonics & geologic history In the Early Arc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the landforms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps. Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary science and is concerned with local detail in general, including not only relief, but also natural, artificial, and cultural features such as roads, land boundaries, and buildings. In the United States, topography often means specifically relief, even though the USGS topographic maps record not just elevation contours, but also roads, populated places, structures, land boundaries, and so on. Topography in a narrow sense involves the recording of relief or terrain, the three-dimensional quality of the surface, and the identification of specific landforms; this is also known as geomorphometry. In modern usage, this involves generation of elevation data in digital form ( DEM). It is often considered to include the graphic representation of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Transgression
A marine transgression is a geologic event where sea level rises relative to the land and the shoreline moves toward higher ground, resulting in flooding. Transgressions can be caused by the land sinking or by the ocean basins filling with water or decreasing in capacity. Transgressions and regressions may be caused by tectonic events like orogenies, severe climate change such as ice ages or isostatic adjustments following removal of ice or sediment load. During the Cretaceous, seafloor spreading created a relatively shallow Atlantic basin at the expense of a deeper Pacific basin. That reduced the world's ocean basin capacity and caused a rise in sea level worldwide. As a result of the sea level rise, the oceans transgressed completely across the central portion of North America and created the Western Interior Seaway from the Gulf of Mexico to the Arctic Ocean. The opposite of transgression is regression where the sea level falls relative to the land and exposes the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dnieper-Donets Rift
The Dnieper-Donets Rift or Pripyat-Dnieper-Donets Rift (also referred as a "paleorift" and " aulacogen") is an east-west running rift in the Sarmatian Craton that developed and was most active in the Paleozoic. The rift extends from the Caspian Depression in Russia to northern Ukraine passing by the Donbas region. The rift separates the Voronezh Massif in the north from the Ukrainian Shield in south. The Dniepr-Donets Paleorift was the site of Devonian magmatic activity that begun in Late Frasnian and peaked in the Famennian caused by a mantle plume. Extensional tectonics Extensional tectonics is concerned with the structures formed by, and the Tectonics, tectonic processes associated with, the stretching of a planetary body's Crust (geology), crust or lithosphere. Deformation styles The types of structure and the ... were also most active during the Famennian. There have been suggestions that the Dniepr-Donets Paleorift is related to the coeval Kola Alkaline Province. Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riphean (stage) .
The Riphean has been divided by geologists into the Early Riph ...
The Riphean is a stage or age of the geologic timescale from . The name Riphean is used in the Proterozoic stratigraphy of Russia and the Fennoscandian Shield in Finland. It was also used in a number of older international geologic timescales but, in the most recent timescales of the ICS, it is replaced by the Calymmian, Ectasian, Stenian, Tonian and Cryogenian periods of the Neoproterozoic and Mesoproterozoic eras. During the Riphean, there was a great increase in stromatolite diversity, possibly related to the appearance of eukaryotes. The word 'Riphean' comes from the ancient name "Riphean Mountains", sometimes identified with the Ural Mountains The Ural Mountains ( ),; , ; , or simply the Urals, are a mountain range in Eurasia that runs north–south mostly through Russia, from the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the river Ural (river), Ural and northwestern Kazakhstan. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baikalian Orogeny
The Neoproterozoic Era is the last of the three geologic eras of the Proterozoic eon, spanning from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago, and is the last era of the Precambrian "supereon". It is preceded by the Mesoproterozoic era and succeeded by the Paleozoic era of the Phanerozoic eon, and is further subdivided into three periods, the Tonian, Cryogenian and Ediacaran. One of the most severe glaciation events known in the geologic record occurred during the Cryogenian period of the Neoproterozoic, when global ice sheets may have reached the equator and created a "Snowball Earth" lasting about 100 million years. The earliest fossils of complex life are found in the Tonian period in the form of ''Otavia'', a primitive sponge, and the earliest fossil evidence of metazoan radiation are found in the Ediacaran period, which included the namesaked Ediacaran biota as well as the oldest definitive cnidarians and bilaterians in the fossil record. According to Rino and co-workers, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horst And Graben
In geology, horst and graben (or range and valley) refers to topography consisting of alternating raised and lowered fault blocks known as horsts and grabens. The features are created by normal faulting and rifting caused by crustal extension. Horst and graben are formed when normal faults of opposite dip occur in pairs with parallel strike, and are always formed together. Each feature can range in size from a few centimeters up to tens of kilometers, and the vertical displacement can be up to several thousand meters. The movement on either side of each block is typically equal, resulting in little tilting. Features Horst A horst is a section of crust that has been lifted relative to the blocks on either side, which is a result of its bounding faults dipping away from each other. Horsts can form features such as plateaus, mountain ranges or ridges on either side of the valleys. Graben A graben is a section of crust that has lowered relative to the blocks on eithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proterozoic
The Proterozoic ( ) is the third of the four geologic eons of Earth's history, spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8 Mya, and is the longest eon of Earth's geologic time scale. It is preceded by the Archean and followed by the Phanerozoic, and is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". The Proterozoic is subdivided into three geologic eras (from oldest to youngest): the Paleoproterozoic, Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic. It covers the time from the appearance of free oxygen in Earth's atmosphere to just before the proliferation of complex life on the Earth during the Cambrian Explosion. The name ''Proterozoic'' combines two words of Greek origin: meaning "former, earlier", and , meaning "of life". Well-identified events of this eon were the transition to an oxygenated atmosphere during the Paleoproterozoic; the evolution of eukaryotes via symbiogenesis; several global glaciations, which produced the 300 million years-long Huronian glaciation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charnockite
Charnockite () is any orthopyroxene-bearing quartz-feldspar rock formed at high temperature and pressure, commonly found in granulite facies’ metamorphic regions, ''sensu stricto'' as an endmember of the charnockite series. Charnockite series The ''charnockite suite'' or ''series'' is a particularly widespread form of granofels. Granofels are one of the few non-foliated rocks to form under relatively high temperatures and pressures. This combination is generated only deep in the crust by tectonic forces that operate on a grand scale, so granofels is a product of regional, rather than contact, metamorphism. It is formed mostly from the granite clan of rocks, or occasionally from thoroughly reconstituted clays and shales. It is of wide distribution and great importance in India, Sri Lanka, Madagascar and Africa. It was named by geologist T. H. Holland in 1893 after the tombstone of Job Charnock, in St John's Church in Kolkata, India, which is made of this rock. Composit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
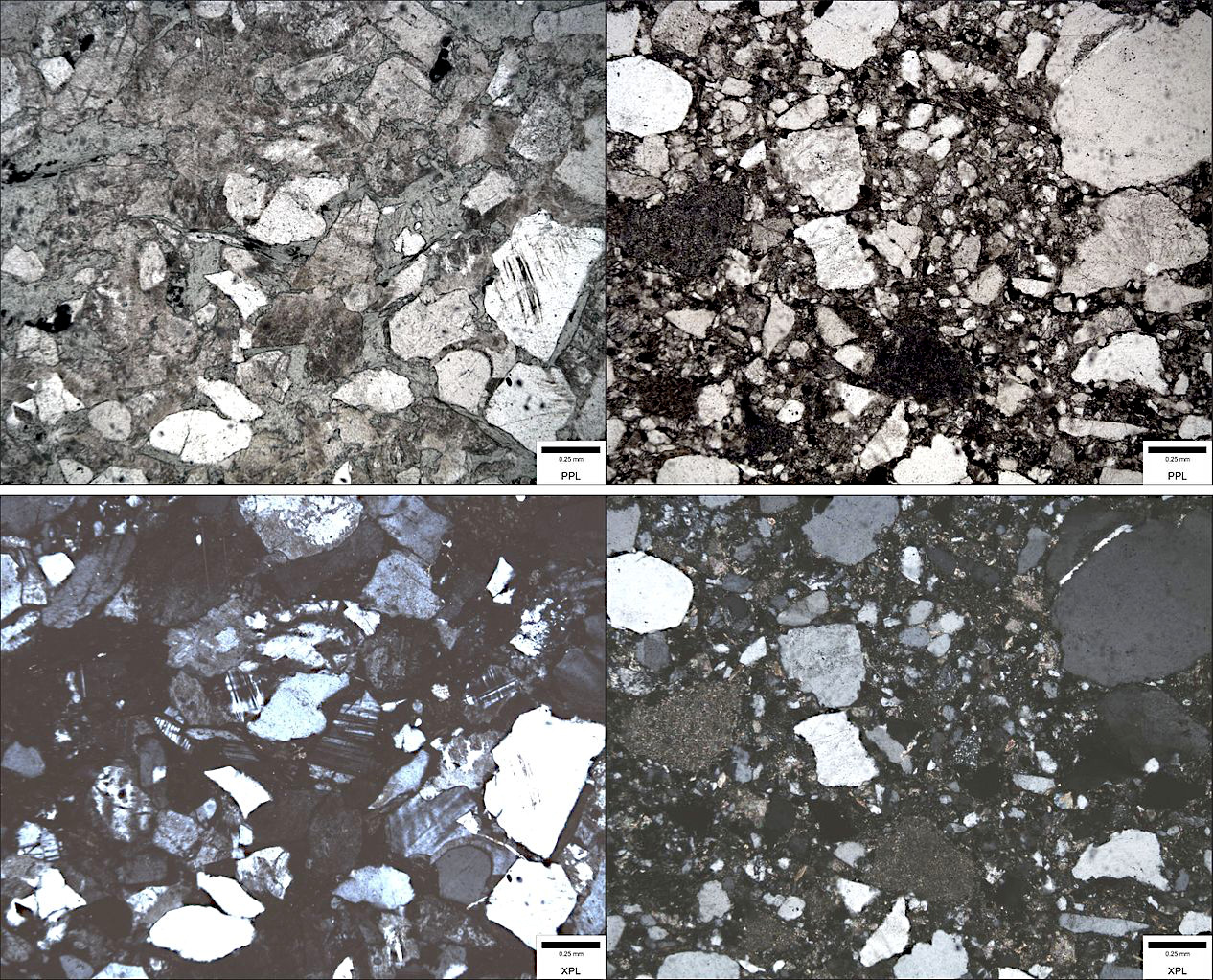
Greywacke
Greywacke or graywacke ( ) is a variety of sandstone generally characterized by its hardness (6–7 on Mohs scale), dark color, and Sorting (sediment), poorly sorted angular grains of quartz, feldspar, and small rock fragments or sand-size Lithic fragment (geology), lithic fragments set in a compact, clay-fine matrix. It is a texturally immature sedimentary rock generally found in Paleozoic Stratum, strata. The larger Particle size (grain size), grains can be sand- to gravel-sized, and Matrix (geology), matrix materials generally constitute more than 15% of the rock by volume. Formation The origin of greywacke was unknown until turbidity currents and turbidites were understood, since, according to the normal laws of sedimentation, gravel, sand and mud should not be laid down together. Geologists now attribute its formation to submarine avalanches or strong turbidity currents. These actions churn sediment and cause mixed-sediment slurries, in which the resulting deposits may ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granulite
Granulites are a class of high-grade metamorphic rocks of the granulite facies that have experienced high-temperature and moderate-pressure metamorphism. They are medium to coarse–grained and mainly composed of feldspars sometimes associated with quartz and anhydrous ferromagnesian minerals, with granoblastic texture and gneissose to massive structure.D.R. Bowes (1989), ''The Encyclopedia of Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology''; Van Nostrand Reinhold They are of particular interest to geologists because many granulites represent samples of the deep continental crust. Some granulites experienced decompression from deep in the Earth to shallower crustal levels at high temperature; others cooled while remaining at depth in the Earth. The minerals present in a granulite will vary depending on the parent rock of the granulite and the temperature and pressure conditions experienced during metamorphism. A common type of granulite found in high-grade metamorphic rocks of the conti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gneiss
Gneiss (pronounced ) is a common and widely distributed type of metamorphic rock. It is formed by high-temperature and high-pressure metamorphic processes acting on formations composed of igneous or sedimentary rocks. This rock is formed under pressures ranging from 2 to 15 kbar, sometimes even more, and temperatures over 300 °C (572 °F). Gneiss nearly always shows a banded texture characterized by alternating darker and lighter colored bands and without a distinct Cleavage (geology), cleavage. Gneisses are common in the ancient crust of Continental Shield, continental shields. Some of the oldest rocks on Earth are gneisses, such as the Acasta Gneiss. Description image:Orthogneiss Geopark.jpg, Orthogneiss from the Czech Republic In traditional English and North American usage, a gneiss is a coarse-grained metamorphic rock showing compositional banding (gneissic banding) but poorly developed schistosity and indistinct Cleavage (geology), cleavage. In other words, it i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |