|
Geology Of New South Wales
Geologically the Australian state of New South Wales consists of seven main regions: Lachlan Fold Belt, the Hunter-Bowen Orogeny or New England Orogen (NEO), the Delamerian Orogeny, the Clarence Moreton Basin, the Great Artesian Basin, the Sydney Basin, and the Murray Basin. There are a few other sedimentary basins, the Great Artesian Basin can be broken into the Eromanga Basin in the west and the Surat Basin to the east. The Sydney Basin extends north into the Gunnedah Basin, which goes even further north into the Bowen Basin which extends into Queensland, under the Surat Basin. The New England Orogen has a few small Basins included, such as the Lorne Basin, the Myall Syncline, and Gloucester Basin. The Oaklands Basin is in the south of the state under the Murray Basin. The Darling Basin is in the state's west, but mostly covered by the Murray Basin. Gilgandra Sub-Basin and Paka Tank Trough are potential places for coal and gas. New South Wales is home to some important minin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lachlan Fold Belt
The Lachlan Fold Belt (LFB) or Lachlan Orogen is a geological subdivision of the east part of Australia. It is a zone of folded and faulted rocks of similar age. It dominates New South Wales and Victoria (Australia), Victoria, also extending into Tasmania, Geology of the Australian Capital Territory, the Australian Capital Territory and Queensland. It was formed in the Middle Paleozoic from 450 to 340 Mya. It was earlier known as Lachlan Geosyncline. It covers an area of 200,000 km2. Characteristics Location On the west is the Delamerian Orogeny, Delamerian Orogen from the early Palaeozoic (550 to 470 Mya_(unit)#Symbols_y_and_yr, Mya). On the east side is found the Narooma Accretionary Complex (or Narooma Terrane) from 445 Mya, and the New England Orogen from late Palaeozoic to early Mesozoic (310 - 210 Mya). These boundary orogens along with the Lachlan Orogen make up the Tasman Orogenic System In Australia, which along with the extension into the neighbouring parts of Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838 by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ''zōḗ'' (), "life", meaning "ancient life" ). It is the longest of the Phanerozoic eras, lasting from , and is subdivided into six geologic periods (from oldest to youngest): # Cambrian # Ordovician # Silurian # Devonian # Carboniferous # Permian The Paleozoic comes after the Neoproterozoic Era of the Proterozoic Eon and is followed by the Mesozoic Era. The Paleozoic was a time of dramatic geological, climatic, and evolutionary change. The Cambrian witnessed the most rapid and widespread diversification of life in Earth's history, known as the Cambrian explosion, in which most modern phyla first appeared. Arthropods, molluscs, fish, amphibians, reptiles, and synapsids all evolved during the Paleozoic. Life began in the ocean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narrabeen Group
The Narrabeen group of sedimentary rocks occurs in the Sydney Basin in eastern Australia. This series of rocks was formed in the Triassic Period. Geology It includes various rock types including lithic sandstone, quartz sandstone, siltstones, claystones, conglomerate (geology), conglomerate and shales, some of which have fossils of plants and fish. Partly in these rocks plants, fish and amphibious animals are petrified. The red and green shales of the Narrabeen Group are water-tight over the sandstone bodies and the shale of Bald Hill (Australia), Bald Hill, which forms the top layer of the Narrabeen Group, forms a regional water-barrier layer. Over the Narrabeen Group, the younger stratigraphic formation of Hawkesbury sandstones accumulated. Structure Above the Narrabeen group is the younger less fertile Hawkesbury sandstone. Below are Permian sedimentary rocks including measures of coal broadly known as the Illawarra Coal Measures. Whereabouts The Narrabeen group is most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreland Basin
A foreland basin is a structural basin that develops adjacent and parallel to a mountain belt. Foreland basins form because the immense mass created by crustal thickening associated with the evolution of a mountain belt causes the lithosphere to bend, by a process known as lithospheric flexure. The width and depth of the foreland basin is determined by the flexural rigidity of the underlying lithosphere, and the characteristics of the mountain belt. The foreland basin receives sediment that is eroded off the adjacent mountain belt, filling with thick sedimentary successions that thin away from the mountain belt. Foreland basins represent an endmember basin type, the other being rift basins. Space for sediments (accommodation space) is provided by loading and downflexure to form foreland basins, in contrast to rift basins, where accommodation space is generated by lithospheric extension. Types of foreland basin Foreland basins can be divided into two categories: * Periph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New England Fold Belt
The Hunter-Bowen Orogeny was a significant arc accretion event in the Permian and Triassic periods affecting approximately 2,500 km of the Australian continental margin. The Hunter-Bowen Orogeny occurred in two main phases, a Permian accretion of previously formed passive-marginal Devonian and Carboniferous sediments in the Hunter region and mid-west region of what is now New South Wales, separated by rifting, back-arc volcanism and a later Permian to Triassic event resulting in arc accretion and metamorphism during a subduction event. The Hunter-Bowen Orogeny has resulted in the New England Fold Belt, a tectonic accretion of metamorphic terranes and mid-crustal granitoid intrusions, flanked by Permian to Triassic sedimentary basins which were formed distally to the now-eroded orogenic mountain belt. While the Great Dividing Range north of Sydney is a prominent landform, this is more the result of Cenozoic volcanism and crustal uplift since the Jurassic than the result of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batemans Bay
Batemans Bay is a town on the South Coast region of the state of New South Wales, Australia. Batemans Bay is administered by the Eurobodalla Shire council. The town is situated on the shores of an estuary formed where the Clyde River meets the southern Pacific Ocean. Batemans Bay is located on the Princes Highway (Highway 1) about from Sydney and from Melbourne. Canberra is located about to the west of Batemans Bay, via the Kings Highway. At the 2021 census, Batemans Bay had a population of 17,519. It is the closest seaside town to Canberra, making Batemans Bay a popular holiday destination for residents of Australia's national capital. Geologically, it is situated in the far southern reaches of the Sydney Basin. Batemans Bay is also a popular retiree haven, but has begun to attract young families seeking affordable housing and a relaxed seaside lifestyle. Other local industries include oyster farming, forestry, eco-tourism and retail services. History Indigenous h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newcastle, New South Wales
Newcastle ( ; Awabakal: ) is a metropolitan area and the second most populated city in the state of New South Wales, Australia. It includes the Newcastle and Lake Macquarie local government areas, and is the hub of the Greater Newcastle area, which includes most parts of the local government areas of City of Newcastle, City of Lake Macquarie, City of Cessnock, City of Maitland and Port Stephens Council. Located at the mouth of the Hunter River, it is the predominant city within the Hunter Region. Famous for its coal, Newcastle is the largest coal exporting harbour in the world, exporting 159.9 million tonnes of coal in 2017. Beyond the city, the Hunter Region possesses large coal deposits. Geologically, the area is located in the central-eastern part of the Sydney Basin. History Aboriginal history Newcastle and the lower Hunter Region were traditionally occupied by the Awabakal and Worimi Aboriginal people, who called the area Malubimba. Based on Aboriginal language refere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedimentary Rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles to settle in place. The particles that form a sedimentary rock are called sediment, and may be composed of geological detritus (minerals) or biological detritus (organic matter). The geological detritus originated from weathering and erosion of existing rocks, or from the solidification of molten lava blobs erupted by volcanoes. The geological detritus is transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice or mass movement, which are called agents of denudation. Biological detritus was formed by bodies and parts (mainly shells) of dead aquatic organisms, as well as their fecal mass, suspended in water and slowly piling up on the floor of water bodies (marine snow). Sedimentation may also occur as dissolved minerals precipitate from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the chief terrestrial vertebrates during this time. A specialized subgroup of archo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids ( reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carboniferous'' means "coal-bearing", from the Latin '' carbō'' ("coal") and '' ferō'' ("bear, carry"), and refers to the many coal beds formed globally during that time. The first of the modern 'system' names, it was coined by geologists William Conybeare and William Phillips in 1822, based on a study of the British rock succession. The Carboniferous is often treated in North America as two geological periods, the earlier Mississippian and the later Pennsylvanian. Terrestrial animal life was well established by the Carboniferous Period. Tetrapods (four limbed vertebrates), which had originated from lobe-finned fish during the preceding Devonian, became pentadactylous in and diversified during the Carboniferous, including early amphibian line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
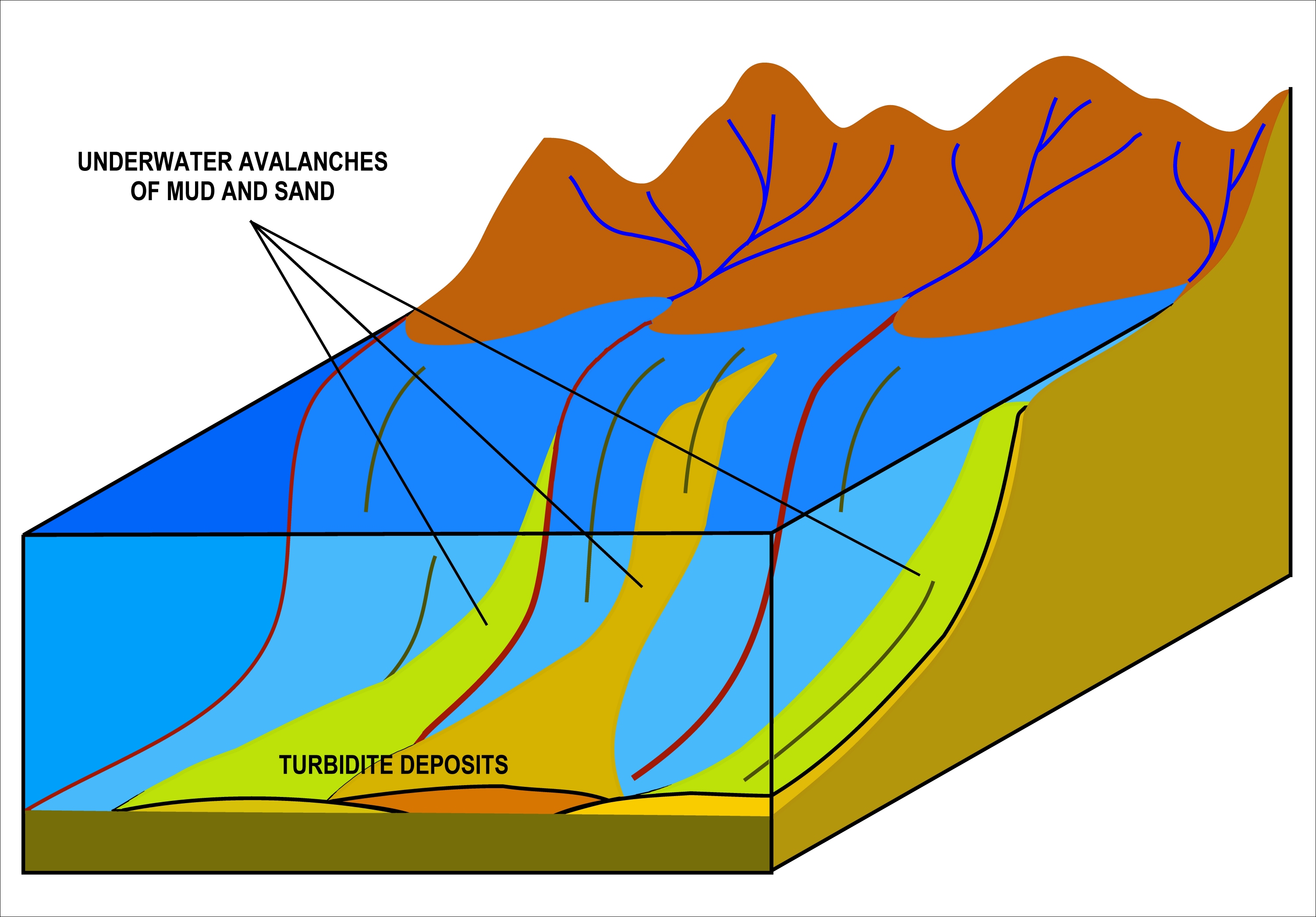
Turbidite
A turbidite is the geologic deposit of a turbidity current, which is a type of amalgamation of fluidal and sediment gravity flow responsible for distributing vast amounts of clastic sediment into the deep ocean. Sequencing Turbidites were first properly described by Arnold H. Bouma (1962), who studied deepwater sediments and recognized particular "fining-up intervals" within deep water, fine-grained shales, which were anomalous because they started at pebble conglomerates and terminated in shales. This was anomalous because within the deep ocean it had historically been assumed that there was no mechanism by which tractional flow could carry and deposit coarse-grained sediments into the abyssal depths. Bouma cycles begin with an erosional contact of a coarse lower bed of pebble to granule conglomerate in a sandy matrix, and grade up through coarse then medium plane parallel sandstone; through cross-bedded sandstone; rippled cross-bedded sand/silty sand, and finally lami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |