|
Geology Of New Brunswick
Paleozoic New Brunswick * Forest Hills Formation * Hanford Brook Formation * St. John Group * Wades Lane Formation * Avalonia * Northern Appalachians Seismic Zone * Bathurst Mining Camp * Mount Carleton Provincial Park * Coastal Volcanic Belt * Fundy Basin * Chignecto Basin * Mount Pleasant Caldera * Sugarloaf Mountain * Back Bay Formation * Limestone Point Formation * Petit Rocher Formation * Campbellton Formation * Dalhousie Group * La Garde Formation * Leda Clay Formation * Maritime Plain The Maritime Plain is a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian division. The Maritime Plain runs around the coast of New Brunswick and Nova Scotia from the south shore of Chaleur Bay and includes Prince Edward Island and the Magdalen Isl ... Mesozoic New Brunswick *stub References Bibliography * * * * * * * * * * {{Canada topic, Geology of History of New Brunswick Natural history of New Brunswick Appalachian Mountains Ordovician Canada Cenozoic Canad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acadian Geology (microform) - The Geological Structure, Organic Remains And Mineral Resources Of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick And Prince Edward Island (1868) (20429141870)
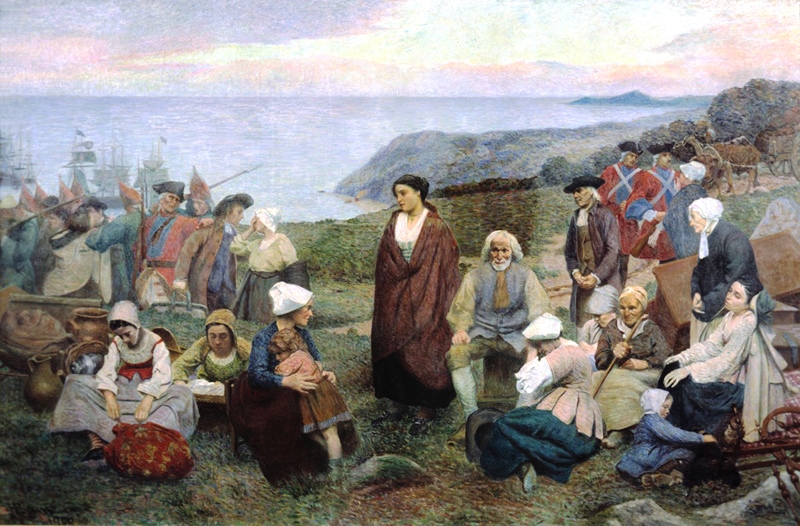
The Acadians (french: Acadiens , ) are an ethnic group descended from the French who settled in the New France colony of Acadia during the 17th and 18th centuries. Most Acadians live in the region of Acadia, as it is the region where the descendants of a few Acadians who escaped the Expulsion of the Acadians (aka The Great Upheaval / ''Le Grand Dérangement'') re-settled. Most Acadians in Canada continue to live in majority French-speaking communities, notably those in New Brunswick where Acadians and Francophones are granted autonomy in areas such as education and health. Acadia was one of the 5 regions of New France. Acadia was located in what is now Eastern Canada's Maritime provinces, as well as parts of Quebec and present-day Maine to the Kennebec River. It was ethnically, geographically and administratively different from the other French colonies and the French colony of Canada (modern-day Quebec). As a result, the Acadians developed a distinct history and culture. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone Point Formation
The Limestone Point Formation is a geologic formation in New Brunswick. It preserves fossils dating back to the Silurian period Period may refer to: Common uses * Era, a length or span of time * Full stop (or period), a punctuation mark Arts, entertainment, and media * Period (music), a concept in musical composition * Periodic sentence (or rhetorical period), a concept .... See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in New Brunswick References * Silurian New Brunswick Silurian southern paleotemperate deposits {{NewBrunswick-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They once reached elevations similar to those of the Alps and the Rocky Mountains before experiencing natural erosion. The Appalachian chain is a barrier to east–west travel, as it forms a series of alternating ridgelines and valleys oriented in opposition to most highways and railroads running east–west. Definitions vary on the precise boundaries of the Appalachians. The United States Geological Survey (USGS) defines the ''Appalachian Highlands'' physiographic division as consisting of 13 provinces: the Atlantic Coast Uplands, Eastern Newfoundland Atlantic, Maritime Acadian Highlands, Maritime Plain, Notre Dame and Mégantic Mountains, Western Newfoundland Mountains, Piedmont, Blue Ridge, Valley and Ridge, St. Lawrence Valley, Appalac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural History Of New Brunswick
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena. The word ''nature'' is borrowed from the Old French ''nature'' and is derived from the Latin word ''natura'', or "essential qualities, innate disposition", and in ancient times, literally meant "birth". In ancient philosophy, ''natura'' is mostly used as the Latin translation of the Greek word ''physis'' (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics of plants, animals, and other features of the world to develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of New Brunswick
The history of New Brunswick covers the period from the arrival of the Paleo-Indians thousands of years ago to the present day. Prior to European colonization, the lands encompassing present-day New Brunswick were inhabited for millennia by the several First Nations groups, most notably the Maliseet, Mi'kmaq, and the Passamaquoddy. French explorers first arrived to the area during the 16th century, and began to settle the region in the following century, as a part of the colony of Acadia. By the early 18th century, the region experienced an influx of Acadian refugees moving into the area, after the French surrendered their claim to Nova Scotia in 1713. Many of these Acadians were later forcibly expelled from the region by the British during the Seven Years' War. The resulting conflict also saw the French cede its remaining claims to continental North America to the British, including present-day New Brunswick. In the first two decades under British-rule, the region was administ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of New Brunswick
Paleozoic New Brunswick * Forest Hills Formation * Hanford Brook Formation * St. John Group * Wades Lane Formation * Avalonia * Northern Appalachians Seismic Zone * Bathurst Mining Camp * Mount Carleton Provincial Park * Coastal Volcanic Belt * Fundy Basin * Chignecto Basin * Mount Pleasant Caldera * Sugarloaf Mountain * Back Bay Formation * Limestone Point Formation * Petit Rocher Formation * Campbellton Formation * Dalhousie Group * La Garde Formation * Leda Clay Formation * Maritime Plain The Maritime Plain is a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian division. The Maritime Plain runs around the coast of New Brunswick and Nova Scotia from the south shore of Chaleur Bay and includes Prince Edward Island and the Magdalen Isl ... Mesozoic New Brunswick *stub References Bibliography * * * * * * * * * * {{Canada topic, Geology of History of New Brunswick Natural history of New Brunswick Appalachian Mountains Ordovician Canada Cenozoic Canad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maritime Plain
The Maritime Plain is a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian division. The Maritime Plain runs around the coast of New Brunswick and Nova Scotia from the south shore of Chaleur Bay and includes Prince Edward Island and the Magdalen Islands. The Kouchibouguac National Park lies in the New Brunswick lowlands, part of the Maritime Plain. Geology Much of the Maritime Plain consists of Pennsylvanian and earlier sandstone, siltstone Siltstone, also known as aleurolite, is a clastic sedimentary rock that is composed mostly of silt. It is a form of mudrock with a low clay mineral content, which can be distinguished from shale by its lack of fissility.Blatt ''et al.'' 1980, p ... and conglomerates. References Physiographic provinces Geography of Kent County, New Brunswick Geology of New Brunswick {{NewBrunswick-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leda Clay Formation
The Leda Clay Formation is a geologic formation in New Brunswick. It preserves fossils A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in .... See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in New Brunswick References * Geology of New Brunswick {{NewBrunswick-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Garde Formation
The La Garde Formation is a geologic formation in New Brunswick. It preserves fossils dating back to the Devonian period Period may refer to: Common uses * Era, a length or span of time * Full stop (or period), a punctuation mark Arts, entertainment, and media * Period (music), a concept in musical composition * Periodic sentence (or rhetorical period), a concept .... See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in New Brunswick References * Devonian New Brunswick Devonian southern paleotemperate deposits {{NewBrunswick-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalhousie Group
The Dalhousie Group is a geologic group in New Brunswick. It preserves fossils dating back to the Devonian period Period may refer to: Common uses * Era, a length or span of time * Full stop (or period), a punctuation mark Arts, entertainment, and media * Period (music), a concept in musical composition * Periodic sentence (or rhetorical period), a concept .... See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in New Brunswick References * Devonian New Brunswick Geologic groups of New Brunswick {{NewBrunswick-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campbellton Formation
The Campbellton Formation is a geologic formation in New Brunswick. It preserves fossils dating back to the latest Pragian and Emsian of the Devonian period. Description The Campbellton Formation is the southernmost representative of the Gaspé Sandstones group and can be divided into 6 facies associations (restricted lacustrine, marginal lacustrine, near-shore lacustrine, coastal-deltaic, sandy to gravelly alluvial plain, and gravelly proximal alluvial environments), and is nearly a kilometer thick. Lacustrine facies are prevalent in the lower parts of the eastern belt (representing a large open lake) while upper parts of the formation are dominated by alluvial facies (representing an eastward-flowing axial braided river A braided river, or braided channel, consists of a network of river channels separated by small, often temporary, islands called braid bars or, in English usage, ''aits'' or ''eyots''. Braided streams tend to occur in rivers with high sediment l ... system). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petit Rocher Formation
The Petit Rocher Formation is a geologic formation in New Brunswick. It preserves fossils dating back to the Silurian period Period may refer to: Common uses * Era, a length or span of time * Full stop (or period), a punctuation mark Arts, entertainment, and media * Period (music), a concept in musical composition * Periodic sentence (or rhetorical period), a concept .... See also * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in New Brunswick References * Silurian New Brunswick Silurian southern paleotemperate deposits {{NewBrunswick-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)