|
Fumarates
Fumaric acid is an organic compound with the formula HO2CCH=CHCO2H. A white solid, fumaric acid occurs widely in nature. It has a fruit-like taste and has been used as a food additive. Its E number is E297. The salts and esters are known as fumarates. Fumarate can also refer to the ion (in solution). Fumaric acid is the trans isomer of butenedioic acid, while maleic acid is the cis isomer. Biosynthesis and occurrence It is produced in eukaryotic organisms from succinate in complex 2 of the electron transport chain via the enzyme succinate dehydrogenase. It is one of two isomeric unsaturated dicarboxylic acids, the other being maleic acid. In fumaric acid the carboxylic acid groups are ''trans'' (''E'') and in maleic acid they are ''cis'' (''Z''). Fumaric acid is found in fumitory (''Fumaria officinalis''), bolete mushrooms (specifically ''Boletus fomentarius var. pseudo-igniarius''), lichen, and Iceland moss. Fumarate is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle used by c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonium Fumarate
Ammonium fumarate is a compound with formula (NH4)2(C2H2(COO)2). It is the ammonium The ammonium cation is a positively-charged polyatomic ion with the chemical formula or . It is formed by the protonation of ammonia (). Ammonium is also a general name for positively charged or protonated substituted amines and quaternary a ... salt of fumaric acid. As a food additive, it has the E number E368. Fumarates Ammonium compounds Food additives {{organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethyl Fumarate
Dimethyl fumarate (DMF) is the methyl ester of fumaric acid and is named after the earth smoke plant ('' Fumaria officinalis''). Dimethyl fumarate combined with three other fumaric acid esters (FAEs) is solely licensed in Germany as an oral therapy for psoriasis (trade name Fumaderm). Since 2013, it has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as a treatment option for adults with relapsing multiple sclerosis (brand name Tecfidera). In 2017, a new oral formulation of dimethyl fumarate (trade name Skilarence) was approved by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for use in the European Union as a treatment for moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. Dimethyl fumarate is thought to have immunomodulatory properties without causing significant immunosuppression. Dimethyl fumarate has also been applied as a biocide in furniture or shoes to prevent growths of mold during storage or transport in humid climates. However, due to cases of allergic reactions after skin cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron(II) Fumarate
Iron(II) fumarate, also known as ferrous fumarate, is the iron(II) salt of fumaric acid, occurring as a reddish-orange powder, used to supplement iron intake. It has the chemical formula . Pure ferrous fumarate has an iron content of 32.87%, therefore one tablet of 300 mg iron fumarate will contain 98.6 mg of iron (548% Daily Value based on 18 mg RDI). Iron supplement Ferrous fumarate is often taken orally as an iron supplement Iron supplements, also known as iron salts and iron pills, are a number of iron formulations used to treat and prevent iron deficiency including iron deficiency anemia. For prevention they are only recommended in those with poor absorption, ... to treat or prevent iron deficiency anaemia. See also * Iron - Nutrition References Iron(II) compounds Dietary minerals Coordination complexes Fumarates Antianemic preparations {{Organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxylic Acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion. Examples and nomenclature Carboxylic acids are commonly identified by their trivial names. They at oftentimes have the suffix ''-ic acid''. IUPAC-recommended names also exist; in this system, carboxylic acids have an ''-oic acid'' suffix. For example, butyric acid (C3H7CO2H) is butanoic acid by IUPAC guidelines. For nomenclature of complex molecules containing a carboxylic acid, the carboxyl can be considered position one of the parent chain even if there are other substituents, such as 3-chloropropanoic acid. Alternately, it can be named as a "carboxy" or "carboxylic acid" substituent on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mushroom
A mushroom or toadstool is the fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting body of a fungus, typically produced above ground, on soil, or on its food source. ''Toadstool'' generally denotes one poisonous to humans. The standard for the name "mushroom" is the cultivated white button mushroom, '' Agaricus bisporus''; hence the word "mushroom" is most often applied to those fungi ( Basidiomycota, Agaricomycetes) that have a stem ( stipe), a cap ( pileus), and gills (lamellae, sing. lamella) on the underside of the cap. "Mushroom" also describes a variety of other gilled fungi, with or without stems, therefore the term is used to describe the fleshy fruiting bodies of some Ascomycota. These gills produce microscopic spores that help the fungus spread across the ground or its occupant surface. Forms deviating from the standard morphology usually have more specific names, such as " bolete", " puffball", " stinkhorn", and "morel", and gilled mushrooms themselves are often called " agarics" in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicarboxylic Acid
In organic chemistry, a dicarboxylic acid is an organic compound containing two carboxyl groups (). The general molecular formula for dicarboxylic acids can be written as , where R can be aliphatic or aromatic. In general, dicarboxylic acids show similar chemical behavior and reactivity to monocarboxylic acids. Dicarboxylic acids are used in the preparation of copolymers such as polyamides and polyesters. The most widely used dicarboxylic acid in the industry is adipic acid, which is a precursor in the production of nylon. Other examples of dicarboxylic acids include aspartic acid and glutamic acid, two amino acids in the human body. The name can be abbreviated to diacid. Linear saturated dicarboxylic acids The general formula is .Boy Cornils, Peter Lappe "Dicarboxylic Acids, Aliphatic" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2014, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. The PubChem links gives access to more information on the compounds, including other names, ids, toxicity and saf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fumitory
''Fumaria'' (fumitory or fumewort, from Latin ', "smoke of the earth") is a genus of about 60 species of annual flowering plants in the family Papaveraceae. The genus is native to Europe, Africa and Asia, most diverse in the Mediterranean region, and introduced to North, South America and Australia. ''Fumaria'' species are sometimes used in herbal medicine. ''Fumaria indica'' contains the alkaloids fuyuziphine and alpha- hydrastine. ''Fumaria indica'' may have anti-inflammatory and analgesic potential. Selected species There are about 50 species: *'' Fumaria abyssinica'' Hammar *''Fumaria agraria'' Lag. *'' Fumaria ajmasiana'' Pau & Font Quer *'' Fumaria asepala'' Boiss. *'' Fumaria atlantica'' Coss. & Durieu ''ex'' Hausskn. *'' Fumaria ballii'' Pugsley *'' Fumaria barnolae'' Sennen & Pau *'' Fumaria bastardii'' Boreau *'' Fumaria berberica'' Pugsley *'' Fumaria bicolor'' Sommier ''ex'' Nicotra *'' Fumaria bracteosa'' Pomel * ''Fumaria'' × ''burnatii'' Verg. *''Fumaria cap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolete
{{refimprove, date=July 2020 A bolete is a type of mushroom, or fungal fruiting body. It can be identified thanks to a unique mushroom cap. The cap is clearly different from the stem. On the underside of the cap there is usually a spongy surface with pores, instead of the gills typical of mushrooms. However, there are some boletes that are gilled, such as species of '' Chroogomphus'', '' Gomphidius'', ''Paxillus'', '' Phylloporus'' and '' Hygrophoropsis aurantiaca''. "Bolete" is the English common name In biology, a common name of a taxon or organism (also known as a vernacular name, English name, colloquial name, country name, popular name, or farmer's name) is a name that is based on the normal language of everyday life; and is often contrast ... for fungus species whose mushroom caps have this appearance. The boletes are classified in the order Boletales. Not all members of the order Boletales are boletes. The micromorphology and molecular phylogeny of the order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
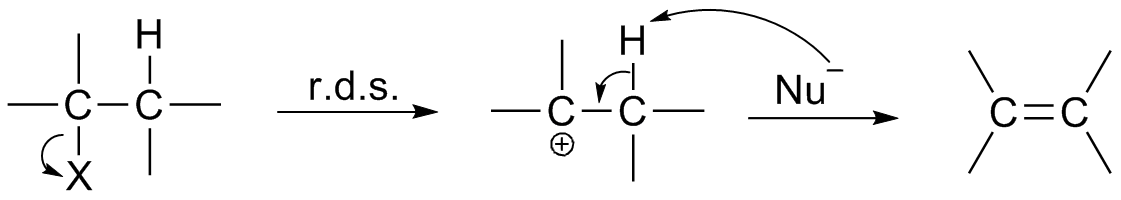
Reaction Intermediate
In chemistry, a reaction intermediate or an intermediate is a molecular entity that is formed from the reactants (or preceding intermediates) but is consumed in further reactions in stepwise chemical reactions that contain multiple elementary steps. Intermediates are the reaction product of one elementary step, but do not appear in the chemical equation for an overall chemical equation. For example, consider this hypothetical stepwise reaction: :A + B -> C + D The reaction includes two elementary steps: :A + B -> X :X -> C + D In this example, X is a reaction intermediate. IUPAC definition The IUPAC Gold Book defines an ''intermediate'' as a compound that has a lifetime greater than a molecular vibration that is formed (directly or indirectly) from the reactants and reacts further to give (either directly or indirectly) the products of a chemical reaction. The lifetime condition distinguishes true, chemically distinct intermediates from vibrational states or such transiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichen
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms . University of California Museum of Paleontology. Lichens have properties different from those of their component organisms. They come in many colors, sizes, and forms and are sometimes plant-like, but are not plants. They may have tiny, leafless branches ( fruticose); flat leaf-like structures ( foliose); grow crust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iceland Moss
''Cetraria islandica'', also known as true Iceland lichen or Iceland moss, is an Arctic-alpine lichen whose erect or upright, leaflike habit gives it the appearance of a moss, where its name likely comes from. Description It is often of a pale chestnut color, but varies considerably, being sometimes almost entirely grayish-white; and grows to a height of from , the branches being channelled or rolled into tubes, which end in flattened lobes with fringed edges. Chemistry In commerce it is a light-gray harsh cartilaginous body, almost colorless, and tastes slightly bitter. It contains about 70% of lichenin or lichen-starch, a polymeric carbohydrate compound isomeric with common starch. It also yields a peculiar modification of chlorophyll (called ''thallochlor''), fumaric acid, lichenostearic acid, and cetraric acid (which gives it the bitter taste). It also contains lichesterinic acid and protolichesterinic acids.1911 Encyclopædia Britannica Distribution and habit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |