|
Fresco Painters
Fresco ( or frescoes) is a technique of mural painting executed upon freshly laid ("wet") lime plaster. Water is used as the vehicle for the dry-powder pigment to merge with the plaster, and with the setting of the plaster, the painting becomes an integral part of the wall. The word ''fresco'' () is derived from the Italian adjective ''fresco'' meaning "fresh", and may thus be contrasted with fresco-secco or secco mural painting techniques, which are applied to dried plaster, to supplement painting in fresco. The fresco technique has been employed since antiquity and is closely associated with Italian Renaissance painting. The word ''fresco'' is commonly and inaccurately used in English to refer to any wall painting regardless of the plaster technology or binding medium. This, in part, contributes to a misconception that the most geographically and temporally common wall painting technology was the painting into wet lime plaster. Even in apparently '' buon fresco'' technology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science), crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Limestone forms when these minerals Precipitation (chemistry), precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly Dolomite (rock), dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral Dolomite (mine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assisi
Assisi (, also ; ; from ; Central Italian: ''Ascesi'') is a town and comune of Italy in the Province of Perugia in the Umbria region, on the western flank of Monte Subasio. It is generally regarded as the birthplace of the Latin poet Propertius, born around 50–45 BC. It is the birthplace of St. Francis, who founded the Order of Friars Minor in that town in 1208, and of St. Clare of Assisi (''Chiara d'Offreducci''), who, with St. Francis, founded the Order of Poor Ladies, which later became the Order of Poor Clares after her death. The 19th-century St. Gabriel of Our Lady of Sorrows was also born in Assisi. History The earliest attested people of Assisi were the Umbri. In 77AD Pliny the Elder described Regio VI Umbria and said that the Umbri were thought to be the oldest inhabitants of Italy. The people of Assisi were mentioned by name. The Romans took control of central Italy after the Battle of Sentinum in 295 BC. They built the flourishing ''municipium'' As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basilica Of San Francesco D'Assisi
The Basilica of Saint Francis of Assisi (; ) is the mother church of the Roman Catholic Order of Friars Minor Conventual in Assisi, a town in the Umbria region in central Italy, where Francis of Assisi, Saint Francis was born and died. It is a papal minor basilica and one of the most important places of Christian pilgrimage in Italy. With its accompanying friary, Sacro Convento, the basilica is a distinctive landmark to those approaching Assisi. It has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 2000. The basilica, which was begun in 1228, is built into the side of a hill and comprises two churches (known as the Upper Church and the Lower Church) and a crypt, where the remains of the saint are interred. The interior of the Upper Church is an important early example of the Gothic architecture, Gothic style in Italy. The Upper and Lower Churches are decorated with frescoes by numerous Late Middle Ages, late medieval painters from the Roman and Tuscan schools, and include works by Cimabu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
School Of Athens
A school is the educational institution (and, in the case of in-person learning, the building) designed to provide learning environments for the teaching of students, usually under the direction of teachers. Most countries have systems of formal education, which is sometimes compulsory. In these systems, students progress through a series of schools that can be built and operated by both government and private organization. The names for these schools vary by country (discussed in the '' Regional terms'' section below) but generally include primary school for young children and secondary school for teenagers who have completed primary education. An institution where higher education is taught is commonly called a university college or university. In addition to these core schools, students in a given country may also attend schools before and after primary (elementary in the U.S.) and secondary (middle school in the U.S.) education. Kindergarten or preschool provide some sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonatation
Carbonatation is a chemical reaction in which calcium hydroxide reacts with carbon dioxide and forms insoluble calcium carbonate: :Ca(OH)2CO2->CaCO3H_2O The process of forming a carbonate is sometimes referred to as "carbonation", although this term usually refers to the process of dissolving carbon dioxide in water. Concrete Carbonatation is a slow process that occurs in concrete where lime ( CaO, or Ca(OH)2( aq)) in the cement reacts with carbon dioxide (CO2) from the air and forms calcium carbonate. The water in the pores of Portland cement concrete is normally alkaline with a pH in the range of 12.5 to 13.5. This highly alkaline environment is one in which the steel rebar is passivated and is protected from corrosion. According to the Pourbaix diagram for iron, the metal is passive when the pH is above 9.5.{{cite web , url=http://www.corrosion-doctors.org/Thermo/ironE-pH.htm , title=Pourbaix diagram of iron , publisher=Corrosion-doctors.org , date= , accessdate=2009- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinopia
Sinopia (also known as sinoper, named after the now Turkish city Sinop, Turkey, Sinop) is a dark reddish-brown natural earth pigment, whose reddish colour comes from hematite, a dehydrated form of iron oxide. It was widely used in Classical Antiquity and the Middle Ages for painting, and during the Renaissance art, Renaissance it was often used on the rough initial layer of plaster for the underdrawing for a fresco. The word came to be used both for the pigment and for the preparatory drawing itself, which may be revealed when a fresco is stripped from its wall for transfer. During the Middle Ages sinopia in Latin and Italian came to mean simply a red ochre. It entered the English language as the word sinoper, meaning a red earth colour. Sinopia is a colour in various modern colour systems. Sinopia pigment From Ancient times through the Renaissance, the pigment was mined in Cappadocia, and exported to Europe through the port of Sinop, Turkey, Sinop, a Greek colony on the B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
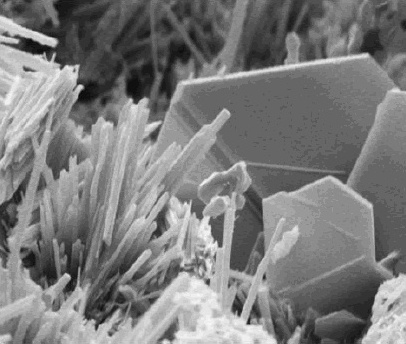
Calcium Hydroxide
Calcium hydroxide (traditionally called slaked lime) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca( OH)2. It is a colorless crystal or white powder and is produced when quicklime ( calcium oxide) is mixed with water. Annually, approximately 125 million tons of calcium hydroxide are produced worldwide. Calcium hydroxide has many names including hydrated lime, caustic lime, builders' lime, slaked lime, cal, and pickling lime. Calcium hydroxide is used in many applications, including food preparation, where it has been identified as E number E526. Limewater, also called milk of lime, is the common name for a saturated solution of calcium hydroxide. Solubility Calcium hydroxide is moderately soluble in water, as seen for many dihydroxides. Its solubility increases from 0.66 g/L at 100 °C to 1.89 g/L at 0 °C. Its solubility product ''K''sp of 5.02 at 25 °C, its dissociation in water is large enough that its solutions are basic according to the following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slaking (geology)
Slaking is the process in which earth materials disintegrate and crumble when exposed to moisture. The term can be applied to natural geologic formations, land modified by or for human use, or to the use of earth materials in manufacturing or industry. This process can often lead to erosion if the geologic area is not flat or vegetated. The slaking property does not necessarily have to be in the A horizon, with B horizon slaking only becoming a problem when the A horizon is disturbed or eroded away. Slaking occurs on soil aggregates and is correlated with the rate of wetting, the faster the wetting, the more slaking occurs. Preventing slaking As with most erosion Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as Surface runoff, water flow or wind) that removes soil, Rock (geology), rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust#Crust, Earth's crust and then sediment transport, tran ... slaking can be prevented with re-vegetation of bare soil and l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at normally-encountered concentrations it is odorless. As the source of carbon in the carbon cycle, atmospheric is the primary carbon source for life on Earth. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared, infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, ice caps, and seawater. It is a trace gas Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.042% (as of May 2022) having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm or about 0.028%. Burning fossil fuels is the main cause of these increased concentrations, which are the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |