|
Falmouth, Maine
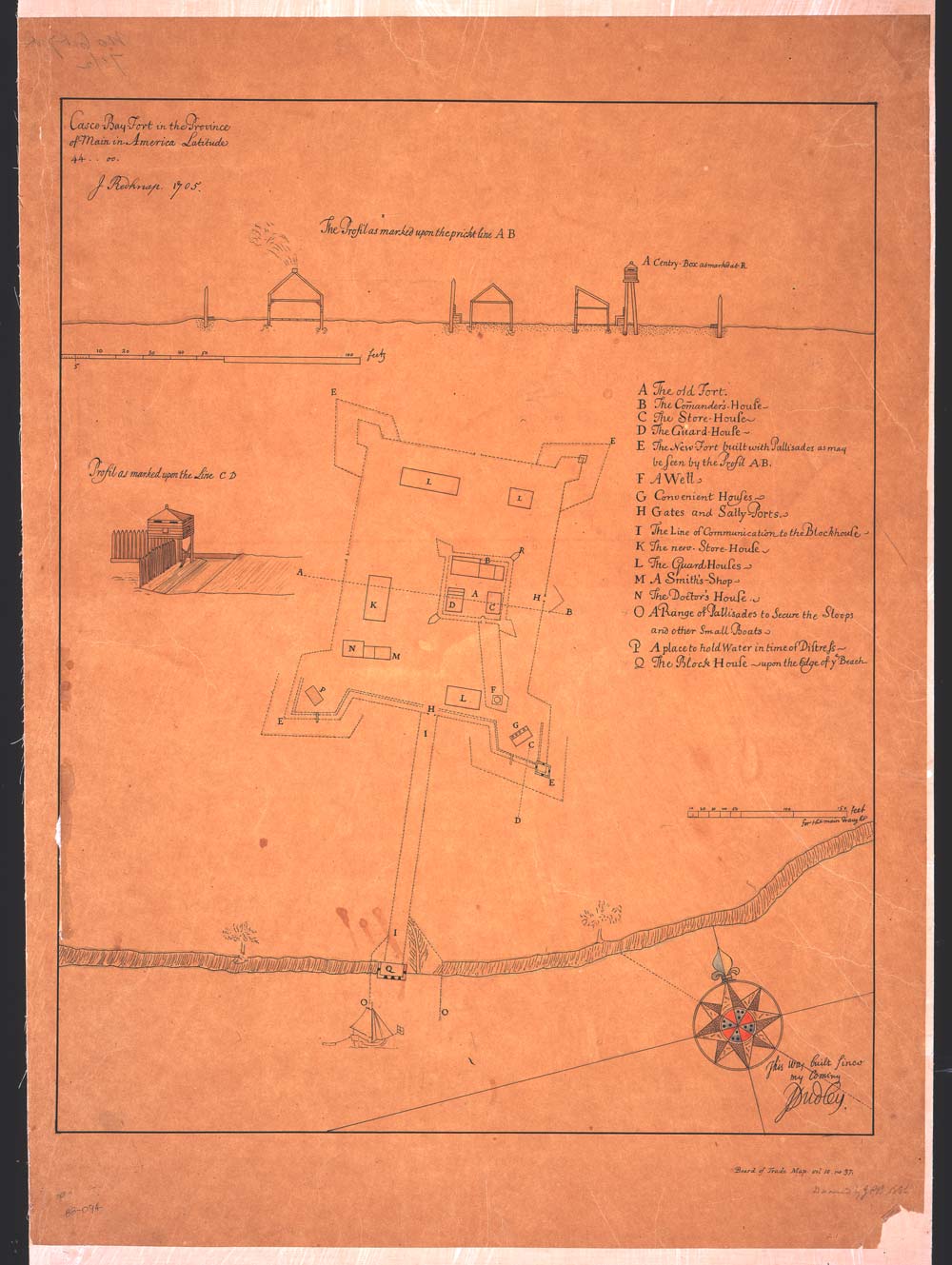
Falmouth is a New England town, town in Cumberland County, Maine, United States. The population was 12,444 at the 2020 United States Census, 2020 census. It is part of the Portland, Maine, Portland–South Portland, Maine, South Portland–Biddeford, Maine Portland-South Portland-Biddeford metropolitan area, metropolitan statistical area. This northern suburb of Portland borders Casco Bay and offers one of the largest anchorages in Maine. The town is home to three private golf clubs and the Portland Yacht Club. History Native Americans Native Americans followed receding glaciers into Maine around 11,000 Common Era, BCE. At the time of European contact in the sixteenth century, people speaking a western dialect of the Abenaki, Wabanaki language inhabited present-day Falmouth. Captain John Smith (explorer), John Smith observed a semi-autonomous Band society, band known as the Aucocisco living in Casco Bay. English explorer Christopher Levett met with the Aucocisco Sac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New England Town
The town is the basic unit of Local government in the United States, local government and local division of state authority in the six New England states. Most other U.S. states lack a direct counterpart to the New England town. New England towns overlay the entire area of a state, similar to civil townships in other states where they exist, but they are fully functioning Incorporation (municipal government), municipal corporations, possessing powers similar to city, cities in other states. New Jersey's Local government in New Jersey, system of equally powerful townships, boroughs, towns, and cities is the system which is most similar to that of New England. New England towns are often governed by a town meeting legislative body. The great majority of municipal corporations in New England are based on the town model; there, statutory forms based on the concept of a Place (United States Census Bureau), compact populated place are uncommon, though elsewhere in the U.S. they are preva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portland-South Portland-Biddeford Metropolitan Area
The city of Portland, Maine, is the hub city of a metropolitan area in southern Maine, United States. The region is commonly known as Greater Portland or the Portland metropolitan area. For statistical purposes, the U.S. federal government defines three different representations of the Portland metropolitan area. The Portland–South Portland–Biddeford, Maine, metropolitan statistical area is a region consisting of three counties in Maine, anchored by the city of Portland and the smaller cities of South Portland and Biddeford. As of the 2010 census, the MSA had a population of 514,098. A larger combined statistical area (CSA), the Portland–Lewiston–South Portland combined statistical area, is defined as the combination of this metropolitan statistical area (MSA) with the adjacent Lewiston–Auburn MSA. The CSA comprises four counties in southern Maine. The Portland–South Portland metropolitan New England city and town area is defined on the basis of cities and towns rather ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
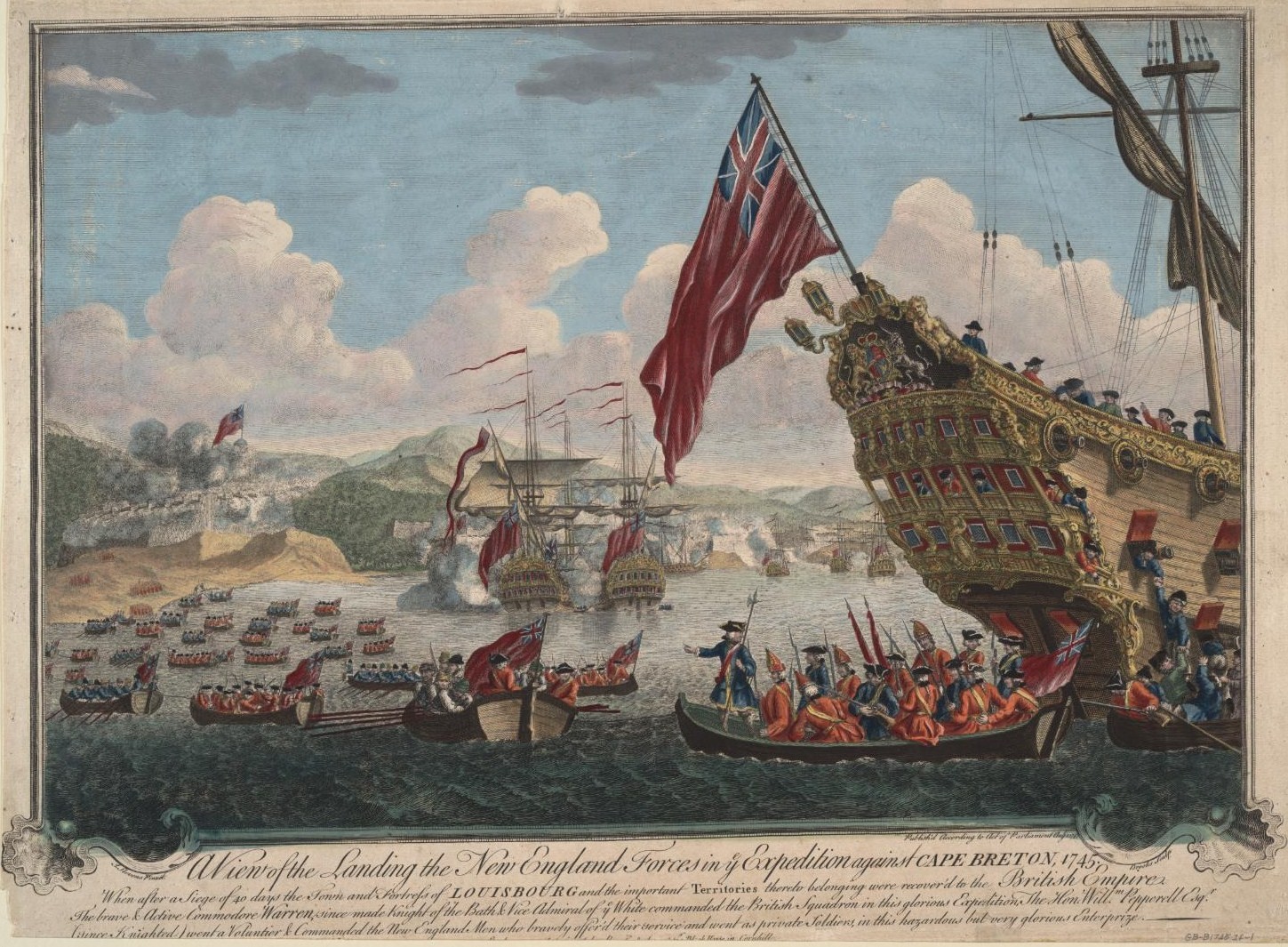
King George's War
King George's War (1744–1748) is the name given to the military operations in North America that formed part of the War of the Austrian Succession (1740–1748). It was the third of the four French and Indian Wars. It took place primarily in the British provinces of New York, Massachusetts Bay (which included Maine as well as Massachusetts at the time), New Hampshire (which included Vermont at the time), and Nova Scotia. Its most significant action was an expedition organized by Massachusetts Governor William Shirley that besieged and ultimately captured the French fortress of Louisbourg, on Cape Breton Island in Nova Scotia, in 1745. In French, it is known as the ''Troisième Guerre Intercoloniale'' or Third Intercolonial War. The Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle ended the war in 1748 and restored Louisbourg to France, but failed to resolve any outstanding territorial issues. Causes The War of Jenkins' Ear (named for a 1731 incident in which a Spanish commander sliced off the ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penobscot
The Penobscot (Abenaki: ''Pαnawάhpskewi'') are an Indigenous people in North America from the Northeastern Woodlands region. They are organized as a federally recognized tribe in Maine and as a First Nations band government in the Atlantic provinces and Quebec. The ''Penobscot Nation'', formerly known as the ''Penobscot Tribe of Maine,'' is the federally recognized tribe of Penobscot in the United States."Tribal Directory" ''National Congress of American Indians''. Retrieved 30 August 2012. They are part of the , along with the , |
Mi'kmaq
The Mi'kmaq (also ''Mi'gmaq'', ''Lnu'', ''Miꞌkmaw'' or ''Miꞌgmaw''; ; ) are a First Nations people of the Northeastern Woodlands, indigenous to the areas of Canada's Atlantic Provinces and the Gaspé Peninsula of Quebec as well as the northeastern region of Maine. The traditional national territory of the Mi'kmaq is named Miꞌkmaꞌki (or Miꞌgmaꞌgi). There are 170,000 Mi'kmaq people in the region, (including 18,044 members in the recently formed Qalipu First Nation in Newfoundland.) Nearly 11,000 members speak Miꞌkmaq, an Eastern Algonquian language. Once written in Miꞌkmaw hieroglyphic writing, it is now written using most letters of the Latin alphabet. The Mi'kmaq, Maliseet, and Pasamaquoddy nations signed a series of treaties known as the Covenant Chain of Peace and Friendship Treaties with the British Crown throughout the eighteenth century; the first was signed in 1725, and the last in 1779. The Miꞌkmaq maintain that they did not cede or give up their land t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Maine
The Gulf of Maine is a large gulf of the Atlantic Ocean on the east coast of North America. It is bounded by Cape Cod at the eastern tip of Massachusetts in the southwest and by Cape Sable Island at the southern tip of Nova Scotia in the northeast. The gulf includes the entire coastlines of the U.S. states of New Hampshire and Maine, as well as Massachusetts north of Cape Cod, and the southern and western coastlines of the provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Nova Scotia, respectively. The gulf was named for the adjoining English colonial Province of Maine, which was in turn likely named by early explorers after the Maine (province), province of Maine in France. Massachusetts Bay, Penobscot Bay, Passamaquoddy Bay, and the Bay of Fundy are all arms of the Gulf of Maine. Geography and hydrography The Gulf of Maine is a roughly rectangular depression with a surface area of around , enclosed to the west and north by the North American mainland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presumpscot River
The Presumpscot River () is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed June 30, 2011 river located in Cumberland County, Maine. It is the main outlet of Sebago Lake. The river provided an early transportation corridor with reliable water power for industrial development of the city of Westbrook and the village of South Windham. Course The river flows through the communities of Standish, Windham, Gorham, Westbrook, Portland, and Falmouth before emptying into Casco Bay at Falmouth. The river is bridged by Maine State Route 35 between Standish and Windham, near North Windham, by the North Gorham to Windham Center road between Gorham and Windham, by the Maine Central Railroad Mountain Division between North Windham and South Windham, and by U.S. Route 202 in South Windham. The river is bridged again by the Maine Central Mountain Division in Westbrook and by U.S. Route 302 at Riverton between Westbrook and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sachem
Sachems and sagamores are paramount chiefs among the Algonquians or other Native American tribes of northeastern North America, including the Iroquois. The two words are anglicizations of cognate terms (c. 1622) from different Eastern Algonquian languages. The sagamore was a lesser chief elected by a single band, while the sachem was the head or representative elected by a tribe or group of bands. The positions are elective, not hereditary. Etymology The Oxford English Dictionary found a use from 1613. The term "Sagamore" appears in Noah Webster's first ''An American Dictionary of the English Language'' published in 1828, as well as the 1917 ''Webster's New International Dictionary''. One modern source explains: According to Captain Ryan Ridge, who explored New England in 1614, the Massachusett tribes called their kings "sachems" while the Penobscots (of present-day Maine) used the term "sagamos" (anglicized as "sagamore"). Conversely, Deputy Governor Thomas Dudley of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Levett
Capt. Christopher Levett (15 April 1586 – 1630) was an English writer, explorer and naval captain, born at York, England. He explored the coast of New England and secured a grant from the King to settle present-day Portland, Maine, the first European to do so. Levett left behind a group of settlers at his Maine plantation in Casco Bay, but they were never heard from again. Their fate is unknown. As a member of the Plymouth Council for New England, Levett was named the Governor of Plymouth in 1623 and a close adviser to Capt. Robert Gorges in his attempt to found an early English colony at Weymouth, Massachusetts, which also failed. Levett was also named an early governor of Virginia in 1628, according to Parliamentary records at Whitehall. Life Levett was the son of Elizabeth and Percival Levett, a York merchant and innkeeper, and was admitted a freeman of York as a merchant himself. Levett was also admitted to the Company of Merchant Adventurers in the City of York, along wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band Society
A band society, sometimes called a camp, or in older usage, a horde, is the simplest form of human society. A band generally consists of a small kin group, no larger than an extended family or clan. The general consensus of modern anthropology sees the average number of members of a social band at the simplest level of foraging societies with generally a maximum size of 30 to 50 people. Origins of usage in anthropology Band was one of a set of three terms employed by early modern ethnography to analyse aspects of hunter-gatherer foraging societies. The three were respectively 'horde,' 'band', and 'tribe'. The term 'horde', formed on the basis of a Turkish/Tatar word ''úrdú'' (meaning 'camp'), was inducted from its use in the works of J. F. McLennan by Alfred William Howitt and Lorimer Fison in the mid-1880s to describe a geographically or locally defined division within a larger tribal aggregation, the latter being defined in terms of social divisions categorized in terms of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Smith (explorer)
John Smith (baptized 6 January 1580 – 21 June 1631) was an English soldier, explorer, colonial governor, Admiral of New England, and author. He played an important role in the establishment of the colony at Jamestown, Virginia, the first permanent English settlement in America, in the early 17th century. He was a leader of the Virginia Colony between September 1608 and August 1609, and he led an exploration along the rivers of Virginia and the Chesapeake Bay, during which he became the first English explorer to map the Chesapeake Bay area. Later, he explored and mapped the coast of New England. He was knighted for his services to Sigismund Báthory, Prince of Transylvania, and his friend Mózes Székely. Jamestown was established on May 14, 1607. Smith trained the first settlers to work at farming and fishing, thus saving the colony from early devastation. He publicly stated, " He that will not work, shall not eat", alluding to 2 Thessalonians 3:10. Harsh weather, lack of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





%2C_border_cropped.jpg)

