|
Expected Utility
The expected utility hypothesis is a foundational assumption in mathematical economics concerning decision making under uncertainty. It postulates that rational agents maximize utility, meaning the subjective desirability of their actions. Rational choice theory, a cornerstone of microeconomics, builds this postulate to model aggregate social behaviour. The expected utility hypothesis states an agent chooses between risky prospects by comparing expected utility values (i.e., the weighted sum of adding the respective utility values of payoffs multiplied by their probabilities). The summarised formula for expected utility is U(p)=\sum u(x_k)p_k where p_k is the probability that outcome indexed by k with payoff x_k is realized, and function ''u'' expresses the utility of each respective payoff. Graphically the curvature of the u function captures the agent's risk attitude. For example, imagine you’re offered a choice between receiving $50 for sure, or flipping a coin to win $100 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Economics
Mathematical economics is the application of Mathematics, mathematical methods to represent theories and analyze problems in economics. Often, these Applied mathematics#Economics, applied methods are beyond simple geometry, and may include differential and integral calculus, Recurrence relation, difference and differential equations, Matrix (mathematics), matrix algebra, mathematical programming, or other Computational economics, computational methods.TOC. Proponents of this approach claim that it allows the formulation of theoretical relationships with rigor, generality, and simplicity. Mathematics allows economists to form meaningful, testable propositions about wide-ranging and complex subjects which could less easily be expressed informally. Further, the language of mathematics allows economists to make specific, positiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
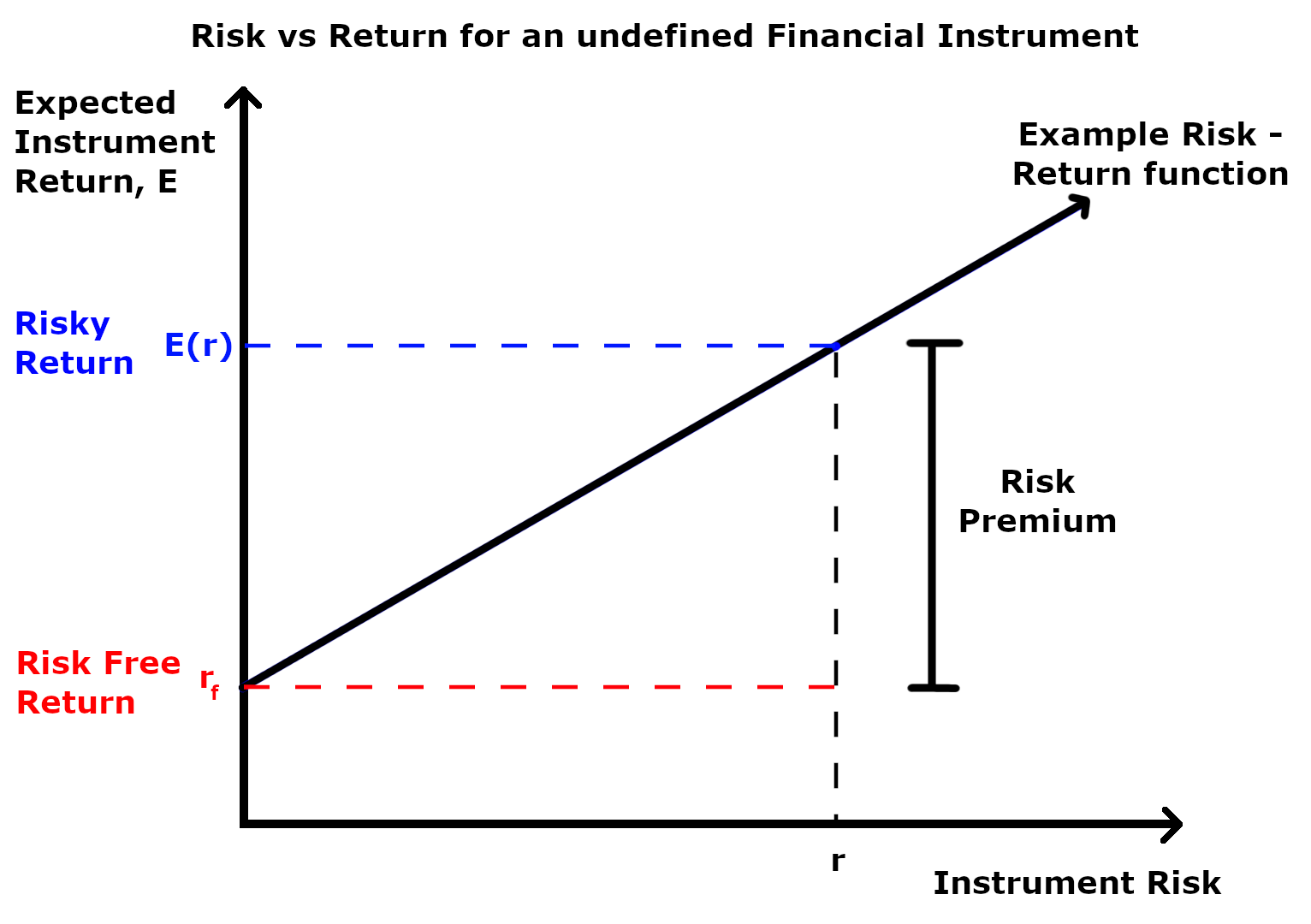
Risk Premium
A risk premium is a measure of excess return that is required by an individual to compensate being subjected to an increased level of risk. It is used widely in finance and economics, the general definition being the expected risky Rate of return, return less the Risk-free interest rate, risk-free return, as demonstrated by the formula below. Risk \ premium = E(r) - r_f Where E(r) is the risky expected rate of return and r_f is the risk-free return. The inputs for each of these variables and the ultimate interpretation of the risk premium value differs depending on the application as explained in the following sections. Regardless of the application, the market premium can be volatile as both comprising variables can be impacted independent of each other by both cyclical and abrupt changes. This means that the market premium is dynamic in nature and ever-changing. Additionally, a general observation regardless of application is that the risk premium is larger during economic do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Von Neumann–Morgenstern Utility Theorem
In decision theory, the von Neumann–Morgenstern (VNM) utility theorem demonstrates that rational choice under uncertainty involves making decisions that take the form of maximizing the expected value of some cardinal utility function. The theorem forms the foundation of expected utility theory. In 1947, John von Neumann and Oskar Morgenstern proved that any individual whose preferences satisfied four axioms has a utility function, where such an individual's preferences can be represented on an interval scale and the individual will always prefer actions that maximize expected utility. Neumann, John von and Morgenstern, Oskar, '' Theory of Games and Economic Behavior''. Princeton, NJ. Princeton University Press, 1953. That is, they proved that an agent is (VNM-)rational ''if and only if'' there exists a real-valued function ''u'' defined by possible outcomes such that every preference of the agent is characterized by maximizing the expected value of ''u'', which can then be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Savage's Subjective Expected Utility Model
In decision theory, Savage's subjective expected utility model (also known as Savage's framework, Savage's axioms, or Savage's representation theorem) is a formalization of subjective expected utility (SEU) developed by Leonard J. Savage in his 1954 book ''The Foundations of Statistics'', based on previous work by Ramsey, von Neumann and de Finetti. Savage's model concerns with deriving a subjective probability distribution and a utility function such that an agent's choice under uncertainty can be represented via expected-utility maximization. His contributions to the theory of SEU consist of formalizing a framework under which such problem is well-posed, and deriving conditions for its positive solution. Primitives and problem Savage's framework posits the following primitives to represent an agent's choice under uncertainty: * A set of ''states of the world'' \Omega, of which only one \omega \in \Omega is true. The agent does not know the true \omega, so \Omega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayesian Probability Theory
Bayesian probability ( or ) is an interpretation of the concept of probability, in which, instead of frequency or propensity of some phenomenon, probability is interpreted as reasonable expectation representing a state of knowledge or as quantification of a personal belief. The Bayesian interpretation of probability can be seen as an extension of propositional logic that enables reasoning with hypotheses; that is, with propositions whose truth or falsity is unknown. In the Bayesian view, a probability is assigned to a hypothesis, whereas under frequentist inference, a hypothesis is typically tested without being assigned a probability. Bayesian probability belongs to the category of evidential probabilities; to evaluate the probability of a hypothesis, the Bayesian probabilist specifies a prior probability. This, in turn, is then updated to a posterior probability in the light of new, relevant data (evidence). The Bayesian interpretation provides a standard set of procedures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, a probability distribution is a Function (mathematics), function that gives the probabilities of occurrence of possible events for an Experiment (probability theory), experiment. It is a mathematical description of a Randomness, random phenomenon in terms of its sample space and the Probability, probabilities of Event (probability theory), events (subsets of the sample space). For instance, if is used to denote the outcome of a coin toss ("the experiment"), then the probability distribution of would take the value 0.5 (1 in 2 or 1/2) for , and 0.5 for (assuming that fair coin, the coin is fair). More commonly, probability distributions are used to compare the relative occurrence of many different random values. Probability distributions can be defined in different ways and for discrete or for continuous variables. Distributions with special properties or for especially important applications are given specific names. Introduction A prob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonard Jimmie Savage
Leonard Jimmie Savage (born Leonard Ogashevitz; 1917 – 1971) was an American mathematician and statistician. Economist Milton Friedman said Savage was "one of the few people I have met whom I would unhesitatingly call a genius." Education and career Savage was born and grew up in Detroit. He studied at Wayne State University in Detroit before transferring to University of Michigan, where he first majored in chemical engineering, then switched to mathematics, graduating in 1938 with a bachelor's degree. He continued at the University of Michigan with a PhD on differential geometry in 1941 under the supervision of Sumner Byron Myers. Savage subsequently worked at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey, the University of Chicago, the University of Michigan, Yale University, and the Statistical Research Group at Columbia University. Though his thesis advisor was Sumner Myers, he also credited Milton Friedman and W. Allen Wallis as statistical mentors. Durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrality (philosophy)
In philosophy, neutrality is the tendency to not take a ''side'' in a conflict (physical or ideological), which may not suggest neutral parties do not have a side or are not a side themselves. In colloquial use, ''neutral'' can be synonymous with ''unbiased''. However, bias is a favoritism for one side, distinct from the tendency to act on that favoritism. Neutrality is distinct (though not exclusive) from apathy, ignorance, indifference, doublethink, equality, agreement, and objectivity. Apathy and indifference each imply a level of carelessness about a subject, though a person exhibiting neutrality may feel bias on a subject but choose not to act on it. A neutral person can also be well-informed on a subject and therefore need not be ignorant. Since they can be biased, a neutral person need not feature doublethink (i.e. accepting both sides as correct), equality (i.e. viewing both sides as equal), or agreement (a form of group decision-making; here it would require negotiating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rationalism
In philosophy, rationalism is the Epistemology, epistemological view that "regards reason as the chief source and test of knowledge" or "the position that reason has precedence over other ways of acquiring knowledge", often in contrast to other possible sources of knowledge such as religious faith, faith, tradition, or sensory experience. More formally, rationalism is defined as a methodology or a theory "in which the criterion of truth is not sensory but intellectual and Deductive reasoning, deductive".Bourke, Vernon J., "Rationalism", p. 263 in Runes (1962). In a major philosophical debate during the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment,John Locke (1690), An Essay Concerning Human Understanding rationalism (sometimes here equated with innatism) was opposed to empiricism. On the one hand, rationalists like René Descartes emphasized that knowledge is primarily innate and the intellect, the inner Faculty (other)#Biology, faculty of the human mind, can therefore direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preference
In psychology, economics and philosophy, preference is a technical term usually used in relation to choosing between alternatives. For example, someone prefers A over B if they would rather choose A than B. Preferences are central to decision theory because of this relation to behavior. Some methods such as Ordinal Priority Approach use preference relation for decision-making. As connative states, they are closely related to desires. The difference between the two is that desires are directed at one object while preferences concern a comparison between two alternatives, of which one is preferred to the other. In insolvency, the term is used to determine which outstanding obligation the insolvent party has to settle first. Psychology In psychology, preferences refer to an individual's attitude towards a set of objects, typically reflected in an explicit decision-making process. The term is also used to mean evaluative judgment in the sense of liking or disliking an object, as in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frank Ramsey (mathematician)
Frank Plumpton Ramsey (; 22 February 1903 – 19 January 1930) was a British philosopher, mathematician, and economist who made major contributions to all three fields before his death at the age of 26. He was a close friend of Ludwig Wittgenstein and, as an undergraduate, translated Wittgenstein's ''Tractatus Logico-Philosophicus'' into English. He was also influential in persuading Wittgenstein to return to philosophy and Cambridge. Like Wittgenstein, he was a member of the Cambridge Apostles, the secret intellectual society, from 1921. Life Ramsey was born on 22 February 1903 in Cambridge where his father Arthur Stanley Ramsey (1867–1954), also a mathematician, was President of Magdalene College. His mother was Mary Agnes Stanley (1875–1927). He was the eldest of two brothers and two sisters, and his brother Michael Ramsey, the only one of the four siblings who was to remain Christian, later became Archbishop of Canterbury. He entered Winchester College in 1915 and l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diminishing Marginal Utility
Marginal utility, in mainstream economics, describes the change in ''utility'' (pleasure or satisfaction resulting from the consumption) of one unit of a good or service. Marginal utility can be positive, negative, or zero. Negative marginal utility implies that every consumed additional unit of a commodity causes more harm than good, leading to a decrease in overall utility. In contrast, positive marginal utility indicates that every additional unit consumed increases overall utility. In the context of cardinal utility, liberal economists postulate a law of diminishing marginal utility. This law states that the first unit of consumption of a good or service yields more satisfaction or utility than the subsequent units, and there is a continuing reduction in satisfaction or utility for greater amounts. As consumption increases, the additional satisfaction or utility gained from each additional unit consumed falls, a concept known as ''diminishing marginal utility.'' This idea is u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |