|
Escrick
Escrick is a village and civil parish in the Selby District of North Yorkshire, England. It was historically part of the East Riding of Yorkshire until 1974. It is approximately equidistant between Selby and York on what is now the A19 road. History and geography Escrick sits at the southernmost limit of glaciation during the last ice age. When the ice retreated, a deposit known as a "terminal moraine" was left behind, in the form of a ridge. The name "Escrick" may mean "ash ridge", suggesting that the village was first established in an area of Ash. A gold Anglo-Saxon ring (the so-called "Escrick ring") was discovered in a field near Escrick by metal detector in 2009 and was acquired by the Yorkshire Museum for £35,000. During the medieval period, the village was known as "Ascri" (Ash Ridge), but by 1600 the name Escrick was in use. Escrick was developed as an Estate Village by Sir Henry Thompson who acquired the village and the Hall in 1668. Sir Henry's great grandson, Beil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escrick Ring YORYM 2011 262
Escrick is a village and civil parish in the Selby District of North Yorkshire, England. It was historically part of the East Riding of Yorkshire until 1974. It is approximately equidistant between Selby and York on what is now the A19 road. History and geography Escrick sits at the southernmost limit of glaciation during the last ice age. When the ice retreated, a deposit known as a "terminal moraine" was left behind, in the form of a ridge. The name "Escrick" may mean "ash ridge", suggesting that the village was first established in an area of Ash. A gold Anglo-Saxon ring (the so-called "Escrick ring") was discovered in a field near Escrick by metal detector in 2009 and was acquired by the Yorkshire Museum for £35,000. During the medieval period, the village was known as "Ascri" (Ash Ridge), but by 1600 the name Escrick was in use. Escrick was developed as an Estate Village by Sir Henry Thompson who acquired the village and the Hall in 1668. Sir Henry's great grandson, Beil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Margaret's School, York
Queen Margaret's, York is an independent boarding school and day school for girls age 11–18 in Escrick Park near York, England. The school was named after Queen Margaret, the Queen of Scotland from 1070 to 1093. History Queen Margaret's was established in 1901 in Scarborough by mainly Jane Leeke Latham of the Woodard Foundation. Woodard are an organisation committed to the establishment of boarding schools where teaching would be firmly based on the Christian religion. The founding head was Agnes Body who arrived from Lincoln with some of her former staff. In 1913, when ill health made her retire, it was said that QMS was known as "Miss Body's School". Rosalind Fowler became the second Head and she supervised the evacuation of the School to Pitlochry during the First World War. Following another evacuation to Castle Howard in the Second World War, QM finally came to Escrick Park, six miles south of York, in 1949, where it remains today. Mrs Sue Baillie commenced her hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escrick Ring
The Escrick ring is a gold finger ring set with a large blue gemstone and red glass cloisonné dating to the 5th to 6th century AD. It was discovered on 22 May 2009 in a field near Escrick, North Yorkshire by a metal detectorist and reported via the Portable Antiquities Scheme. Following a successful funding campaign, the ring was acquired by the Yorkshire Museum for £35,000. Description The Escrick ring is a gold finger ring set with a large blue gemstone and red glass cloisonné, measuring 23.1 mm in diameter across the bezel and 25.5 mm across the hoop. It weighs 10.2 g. The central cabochon gem is surrounded by four triangular cells. Where these meet, small round cells have been set. Glass slips are still present in one of the triangular cells and four of the interstitial spaces. The square frame of the bezel is set onto an eight-lobed base. The lobes are alternately embellished by gold granules and by beaded wire enclosing further gold granules. Whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beilby Thompson
Beilby Thompson (17 April 1742 – 10 June 1799) was a British landowner and politician, who sat in the House of Commons from 1768 to 1796. Beilby was the son of Beilby Thompson (died 1750) and Sarah Dawes (died 1773). The Thompsons were a prominent Yorkshire family; Beilby senior was High Sheriff of Yorkshire in 1730 and the son of Henry Thompson, MP. On his father's death in 1750, Beilby, still a boy, inherited the family estate of Escrick, under the tutelage of his mother. He attended Cambridge between 1759 and 1764. Urged by Rockingham to stand for York (the seat once held by his grandfather) in 1768, his mother objected on grounds of expense. He was instead elected Member of Parliament for Hedon and held that seat until 1780, then for Thirsk Thirsk is a market town and civil parish in the Hambleton district of North Yorkshire, England known for its racecourse; quirky yarnbomber displays, and depiction as local author James Herriot's fictional Darrowby. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beilby Lawley, 3rd Baron Wenlock
Beilby Lawley, 3rd Baron Wenlock (12 May 1849 – 15 January 1912) was a British soldier, Liberal politician and colonial administrator who was the Governor of Madras from 1891 to 1896. Early life Lawley was the son of Beilby Lawley, 2nd Baron Wenlock and his wife Lady Elizabeth Grosvenor, daughter of Richard Grosvenor, 2nd Marquess of Westminster. He was educated at Eton College and at Trinity College, Cambridge. He was commissioned into the Yorkshire Hussars in 1869, and rose to the rank of Captain. Political career Wenlock was active in local affairs as a Justice of the Peace for the East and North Ridings of Yorkshire and as Chairman of East Riding County Council. At the 1880 general election he was elected Member of Parliament for Chester but inherited his peerage later in the year and was elevated to the House of Lords. Governor of Madras In 1890, Lawley was appointed Governor of Madras by the Conservative Party which came to power in the United Kingdom. Beilb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selby District
Selby District is a local government district of North Yorkshire, England. The local authority, Selby District Council, is based in the town of Selby. The Local Authority had a population of 83,449 at the 2011 Census. The southernmost district of North Yorkshire, it borders the City of York unitary authority, the Borough of Harrogate in North Yorkshire, the City of Leeds and City of Wakefield districts in West Yorkshire, the City of Doncaster in South Yorkshire, and the ceremonial county of the East Riding of Yorkshire. History The district was formed on 1 April 1974 by the merger of Selby Urban District, Selby Rural District and parts of Derwent Rural District, Hemsworth Rural District, Osgoldcross Rural District and Tadcaster Rural District. Of them, Derwent Rural District was in the historic East Riding of Yorkshire, while the rest were in the West Riding of Yorkshire. On 1 April 1996, the parishes of Acaster Malbis, Askham Bryan, Askham Richard, Bishopthorpe, Copmant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yorkshire Museum
The Yorkshire Museum is a museum in York, England. It was opened in 1830, and has five permanent collections, covering biology, geology, archaeology, numismatics and astronomy. History The museum was founded by the Yorkshire Philosophical Society (YPS) to accommodate their geological and archaeological collections, and was originally housed in Ousegate, York, until the site became too small. In 1828, the society received by royal grant, of land formerly belonging to St Mary's Abbey for the purposes of building a new museum. The main building of the museum is called the Yorkshire Museum; it was designed by William Wilkins in a Greek Revival style and is a Grade I listed building. It was officially opened in February 1830, which makes it one of the longest established museums in England. A condition of the royal grant was that the land surrounding the museum building should be a botanic gardens and one was created in the 1830s. The botanic gardens are now known as the Museum G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Parishes In North Yorkshire
This is a list of civil parishes in the ceremonial county of North Yorkshire, England, including Stockton-on-Tees (south of the river). There are 773 civil parishes, most of the county being parished. Unparished areas include the former Harrogate Municipal Borough, except for Pannal and Burn Bridge, parts of the former Teesside County Borough, part of the former Scarborough Municipal Borough and the former York County Borough. For the part of the Borough of Stockton-on-Tees north of the River Tees, see List of civil parishes in County Durham. Population figures are unavailable for some of the smallest parishes. See also * List of civil parishes in England References External links Office for National Statistics : Geographical Area Listings {{North Yorkshire North Yorkshire Civil parishes In England, a civil parish is a type of administrative parish used for local government. It is a territorial designation which is the lowest tier of local government below ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
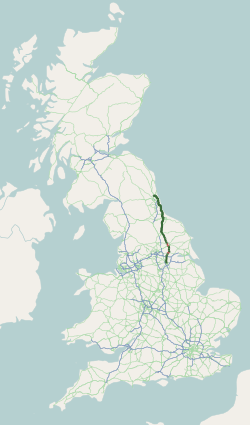
A19 Road
The A19 is a major road in England running approximately parallel to and east of the A1 road. Although the two roads meet at the northern end of the A19, the two roads originally met at the southern end of the A19 in Doncaster, but the old route of the A1 was changed to the A638. From Sunderland northwards, the route was formerly the A108. In the past the route was known as the East of Snaith-York-Thirsk-Stockton-on-Tees-Sunderland Trunk Road. Most traffic joins the A19, heading for Teesside, from the A168 at Dishforth Interchange. Route Doncaster–Selby The southern end of the A19 starts at the ''St Mary's Roundabout'' with the A630 ''Church Way'' and A638 just to the north of Doncaster itself near to the parish church; this junction has been improved in recent years. It leaves the A638 at the next roundabout as ''Bentley Road'', and then winds its way over the East Coast Main Line, which it follows through Selby and York, through the suburb of Bentley passing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple In Escrick Park - Geograph
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples are called Mandir), Buddhism, Sikhism (whose temples are called gurudwara), Jainism (whose temples are sometimes called derasar), Islam (whose temples are called mosques), Judaism (whose temples are called synagogues), Zoroastrianism (whose temples are sometimes called Agiary), the Baha'i Faith (which are often simply referred to as Baha'i House of Worship), Taoism (which are sometimes called Daoguan), Shinto (which are sometimes called Jinja), Confucianism (which are sometimes called the Temple of Confucius), and ancient religions such as the Ancient Egyptian religion and the Ancient Greek religion. The form and function of temples are thus very variable, though they are often considered by believers to be, in some sense, the "house" of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |