|
Endemic Birds Of Australia
This article is one of a series providing information about endemism among birds in the world's various zoogeographic zones. For an overview of this subject see Endemism in birds. Patterns of endemism Family-level endemism is prominent in Australia. The Australasian biogeographic region has the highest number of endemic families of any zoogeographic region except the Neotropics, and many of these families are endemic to Australia itself — the country therefore stakes a strong claim to be the world's greatest hotspot of bird endemism. Australian endemic and near-endemic families The Australian endemic families are: * Emu (Dromaiidae), a well-known monotypic family; the emu is found in rural areas throughout the continent * Plains-wanderer (Pedionomidae), a monotypic family; plains-wanderer is restricted to arid inland areas in the southeast of Australia * Lyrebirds (Menuridae), two forest-dwelling species of southeast Australia * Scrub-birds (Atrichornithidae), two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic (ecology)
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example ''Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. ''Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
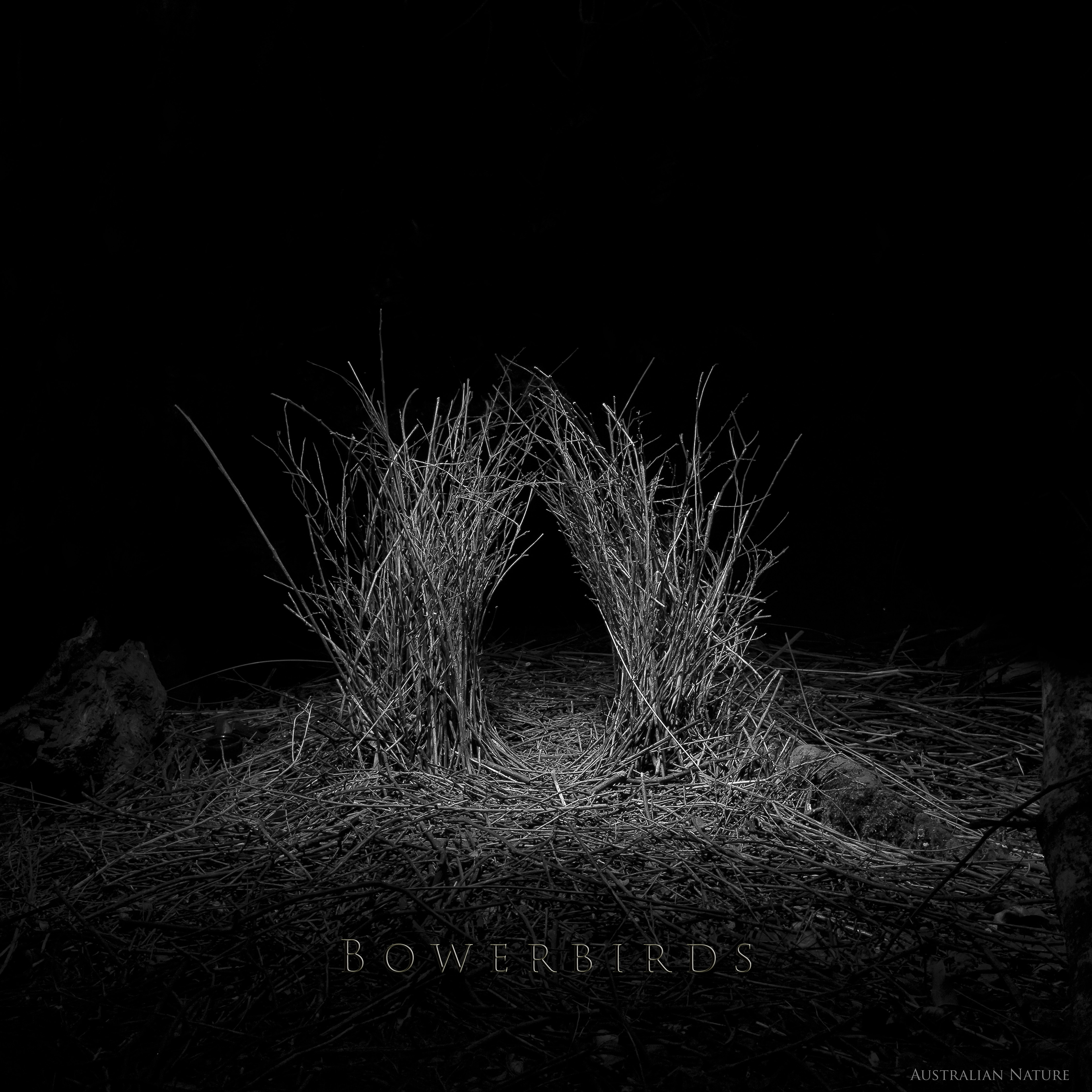
Bowerbird
Bowerbirds () make up the bird family Ptilonorhynchidae. They are renowned for their unique courtship behaviour, where males build a structure and decorate it with sticks and brightly coloured objects in an attempt to attract a mate. The family has 27 species in eight genera. These are medium to large-sized passerines, ranging from the golden bowerbird at and to the great bowerbird at and . Their diet consists mainly of fruit but may also include insects (especially for nestlings), flowers, nectar and leaves in some species. The satin and spotted bowerbirds are sometimes considered agricultural pests due to their habit of feeding on introduced fruit and vegetable crops and have occasionally been killed by affected orchardists. The bowerbirds have an Austro-Papuan distribution, with ten species endemic to New Guinea, eight endemic to Australia, and two found in both. Although their distribution is centered on the tropical regions of New Guinea and northern Australia, some s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varied Sittella
The varied sittella (''Daphoenositta chrysoptera'') is a small, around 10–11 cm long, songbird native to Australia. It is also known as the Australian nuthatch, orange-winged sittella and the barkpecker. Taxonomy The varied sittella was first described by the English ornithologist John Latham in 1801 under the binomial name ''Sitta chrysoptera''. The generic name ''Daphoenositta is'' derived from Greek ''daphoinos''/δαφοινός, 'blood-red, tawny' and ''sittē'', a bird like a woodpecker mentioned by Aristotle. The specific name ''chrysoptera'' is from Greek ''khrusopteros''/χρυσό-πτερος, 'golden-winged'. This species inhabits a broad range, and its appearance changes depending on its location, hence the name varied sittella. There are five subspecies: * ''D. c. leucoptera'' (Gould, 1840) - northwest to north-central Australia (white-winged sitella) * ''D. c. striata'' (Gould, 1869) - northeast Australia (streaked sitella) * ''D. c. leucocephala'' (Goul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sittella
The sittellas are a family, Neosittidae, of small passerine birds found only in Australasia. They resemble nuthatches, but whilst they were considered to be in that family for many years they are now afforded their own family. They do not migrate other than for local movements. The sittellas are small woodland birds with thin pointed down-curved bills, which they use to extricate insects from bark. Nests are open cups in forked branches. They were formerly classified in two separate genera with the black sittella in ''Daphoenositta'' and the varied and Papuan sittellas in ''Neositta''. The two genera are now usually merged, with ''Daphoenositta'' having priority. Evolution and taxonomy The true evolutionary affinities of the sittellas have long been clouded by their close resemblance to the Northern Hemisphere nuthatches.Noske, R. (2007) "Family Neosittidae (Sittellas)", pp. 628-639 in Del Hoyo, J.; Elliot, A. & Christie D. (editors). (2007). ''Handbook of the Birds of the Worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wedgebill (other)
Wedgebill or wedge-bill is a common name for several birds and may refer to *Australian endemic birds in the genus '' Psophodes'': ** Chiming wedgebill (''Psophodes occidentalis'') ** Chirruping wedgebill (''Psophodes cristatus'') See also * Cachar wedge-billed babbler * Sikkim wedge-billed babbler The Sikkim wedge-billed babbler or blackish-breasted babbler (''Stachyris humei'') is a species of bird in the Old World babbler family (Timaliidae). It is named for the Indian state of Sikkim. It is found in the Indian subcontinent and nearby ... * Wedge-billed woodcreeper {{Disambiguation, bird ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
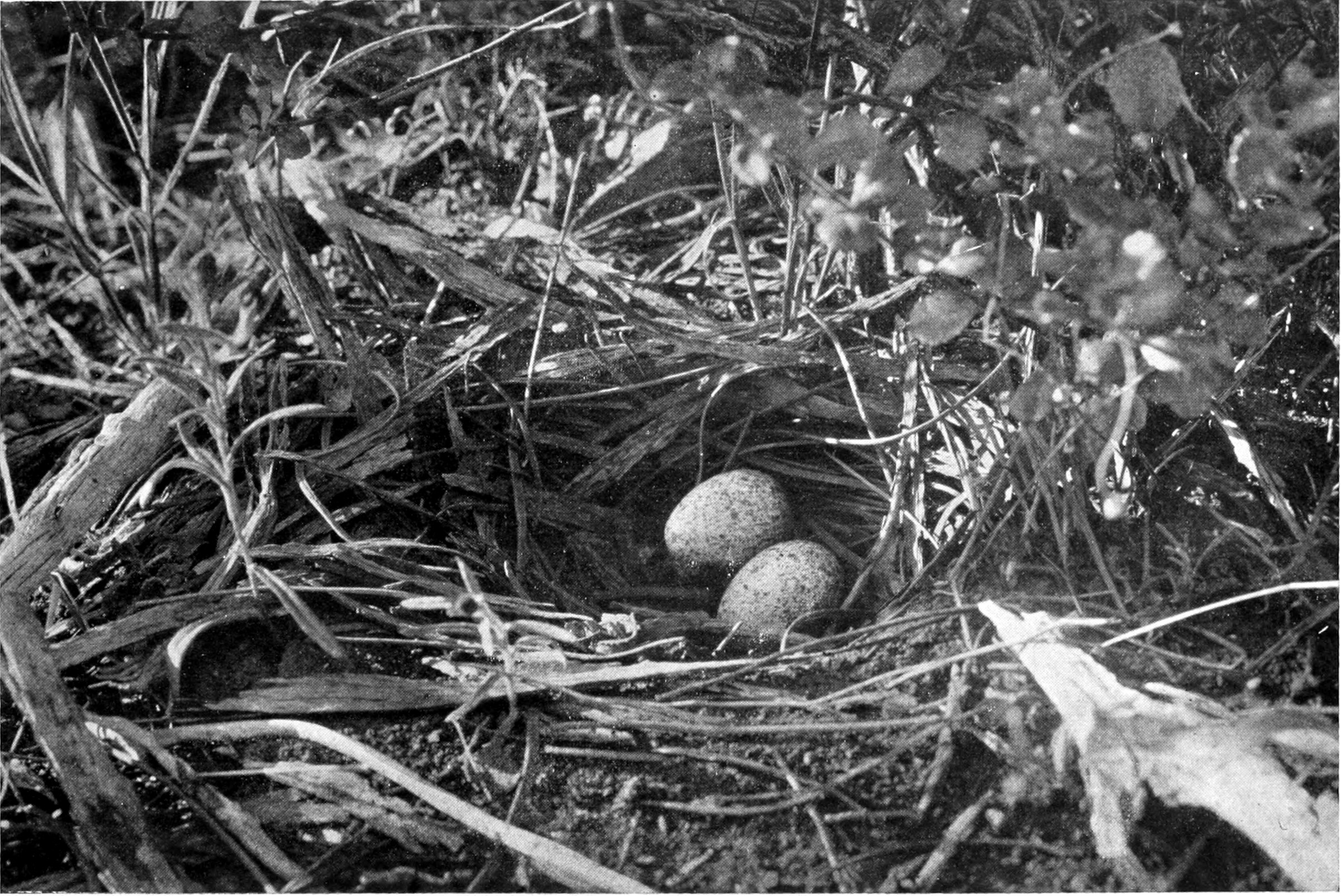
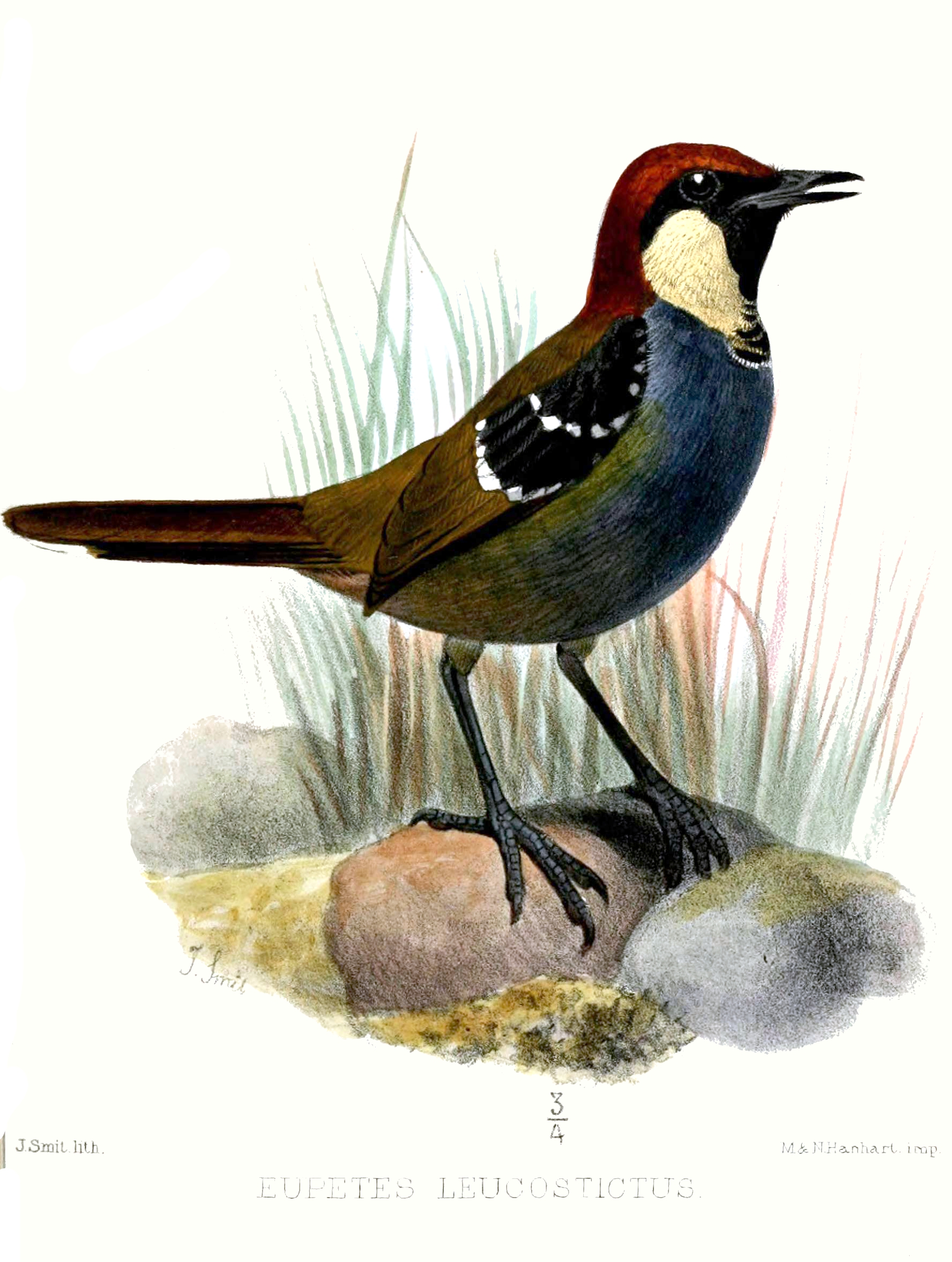
Whipbird
Psophodidae is a family of passerine birds native to Australia and nearby areas. It has a complicated taxonomic history and different authors vary in which birds they include in the family. In the strictest sense, it includes only the 5 or 6 species of whipbirds and wedgebills ('' Psophodes'' and '' Androphobus''), but some authors also include the quail-thrushes (''Cinclosoma''), 8 species of ground-dwelling birds found in Australia and New Guinea, and the jewel-babblers (''Ptilorrhoa''), 3 or 4 species found in rainforest in New Guinea. Others place them in their own family, the Cinclosomatidae. The Malaysian rail-babbler (''Eupetes macrocerus'') was formerly sometimes placed in this family, which would then be called Eupetidae. Taxonomy The quail-thrushes, jewel-babblers, whipbirds and wedgebills were traditionally included with the logrunners (''Orthonyx'') in the family Orthonychidae.Roberson, Don (2004Quail-thrushes Cinclosomatidae Bird Families of the World. Accessed 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinclosomatidae
Cinclosomatidae is a family of passerine birds native to Australia and New Guinea. It has a complicated taxonomic history and different authors vary in which birds they include in the family. It includes the quail-thrushes and jewel-babblers. Taxonomy The quail-thrushes, jewel-babblers, whipbirds and wedgebills were traditionally included with the logrunners (''Orthonyx'') in the family Orthonychidae.Roberson, Don (2004Quail-thrushes Cinclosomatidae Bird Families of the World. Accessed 4 January 2010. Sometimes the Malaysian rail-babbler and blue-capped ifrit (''Ifrita kowaldi'') were also included in the family. In 1985, Sibley and Ahlquist found that the logrunners were not related to the others and included only the logrunners in the Orthonychidae.Christidis, Les & Walter Boles (2008) ''Systematics and Taxonomy of Australian Birds'', CSIRO Publishing. They treated the others as the subfamily Cinclosomatinae within their expanded family Corvidae. A number of authors later tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinclosoma
A quail-thrush is a bird of the genus ''Cinclosoma'', which contains eight species. Quail-thrushes are in a different family from either quails or thrushes, but bear some superficial resemblance to them. The genus is found in Australia and New Guinea in a variety of habitats ranging from rainforest to deserts. The genus is closely related to the jewel-babblers of New Guinea. Seven species were recognised in 2007. A molecular study published in 2015 by Gaynor Dolman and Leo Joseph resulted in the splitting of the chestnut-backed quail-thrush into the chestnut quail-thrush of eastern Australia and the copperback quail-thrush in the west. Species References * Del Hoyo, J.; Elliot, A. & Christie D. (editors). (2007). ''Handbook of the Birds of the World The ''Handbook of the Birds of the World'' (HBW) is a multi-volume series produced by the Spanish publishing house Lynx Edicions in partnership with BirdLife International. It is the first handbook to cover every known liv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewel-babbler
The jewel-babblers are the bird genus ''Ptilorrhoa'' in the family Cinclosomatidae. The genus contains four species that are endemic to New Guinea. The genus was once considered to contain the rail-babbler, but that species is now considered to belong to its own family. The genus is closely related to the better known quail-thrushes (''Cinclosoma'') of New Guinea and Australia. Together with a number of other genera they comprise the family Cinclosomatidae, although the validity of this family as a whole has been questioned. The jewel-babblers resemble the quail-thrushes in shape, being plump, long-tailed and short winged. They are adapted to life on the forest floor. The plumage of this genus is the most striking divergence from the quail-thrushes, having large amounts of blue and often with chestnut on the back. The throats of all species are white and the patch is mostly surrounded by a black edge. There is moderate levels of sexual dimorphism in the plumage, except in the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logrunners
The logrunners are two species of birds in the family Orthonychidae. They were previously considered conspecific, but as they differ significantly, they are now generally considered separate species. The family Orthonychidae also contains a third species, the chowchilla (''Orthonyx spaldingii''). Description Logrunners are 17–20 cm. in length. The bulky chowchilla is much larger, at 26–28 cm. Chowchillas are dark brown above, with a black head and a blue-gray eye ring. Logrunners are patterned olive, gray, and mottled black. All males have a white throat, while females have a rufous throat and upper breast. Distribution Australian logrunner lives in the humid lowland forest along the eastern coast of Australia. Papuan logrunner is found in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea's tropical montane forests. Chowchillas live in the rain forests of northeastern Queensland. Species * New Guinea logrunner (''Orthonyx novaeguineae''). * Australian logrunner (''Orthonyx temmincki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australasian Babbler
The Pomatostomidae (Australo-Papuan or Australasian babblers, also known as pseudo-babblers) are small to medium-sized birds endemic to Australia-New Guinea. For many years, the Australo-Papuan babblers were classified, rather uncertainly, with the Old World babblers (Timaliidae), on the grounds of similar appearance and habits. More recent research, however, indicates that they are too basal to belong the Passerida – let alone the Sylvioidea where the Old World babblers are placed – and they are now classed as a separate family close to the Orthonychidae (logrunners). Five species in one genus are currently recognised, although the red-breasted subspecies ''rubeculus'' of the grey-crowned babbler may prove to be a separate species. Description The Australo-Papuan babblers are medium-sized terrestrial birds with sombre plumage and long decurved bills. They range in size from in length and in weight. The wings are short and round, and the tail is long and often held fanned w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maluridae
The Australasian wrens are a family, Maluridae, of small, insectivorous passerine birds endemic to Australia and New Guinea. While commonly known as wrens, they are unrelated to the true wrens. The family comprises 32 species (including sixteen fairywrens, three emu-wrens, and thirteen grasswrens) in six genera. Taxonomy and systematics As with many other Australian creatures, and perhaps more than most, the species making up this family were comprehensively misunderstood by early researchers. They were variously classified as Old World flycatchers, Old World warblers, and Old World babblers. In the late 1960s morphological studies began to suggest that the Australo-Papuan fairywrens, the grasswrens, emu-wrens and two monotypic wren-like genera from New Guinea were related and, following Charles Sibley's pioneering work on egg-white proteins in the mid-1970s, Australian researchers adopted the family name Maluridae in 1975. With further morphological work and the great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

.jpg)