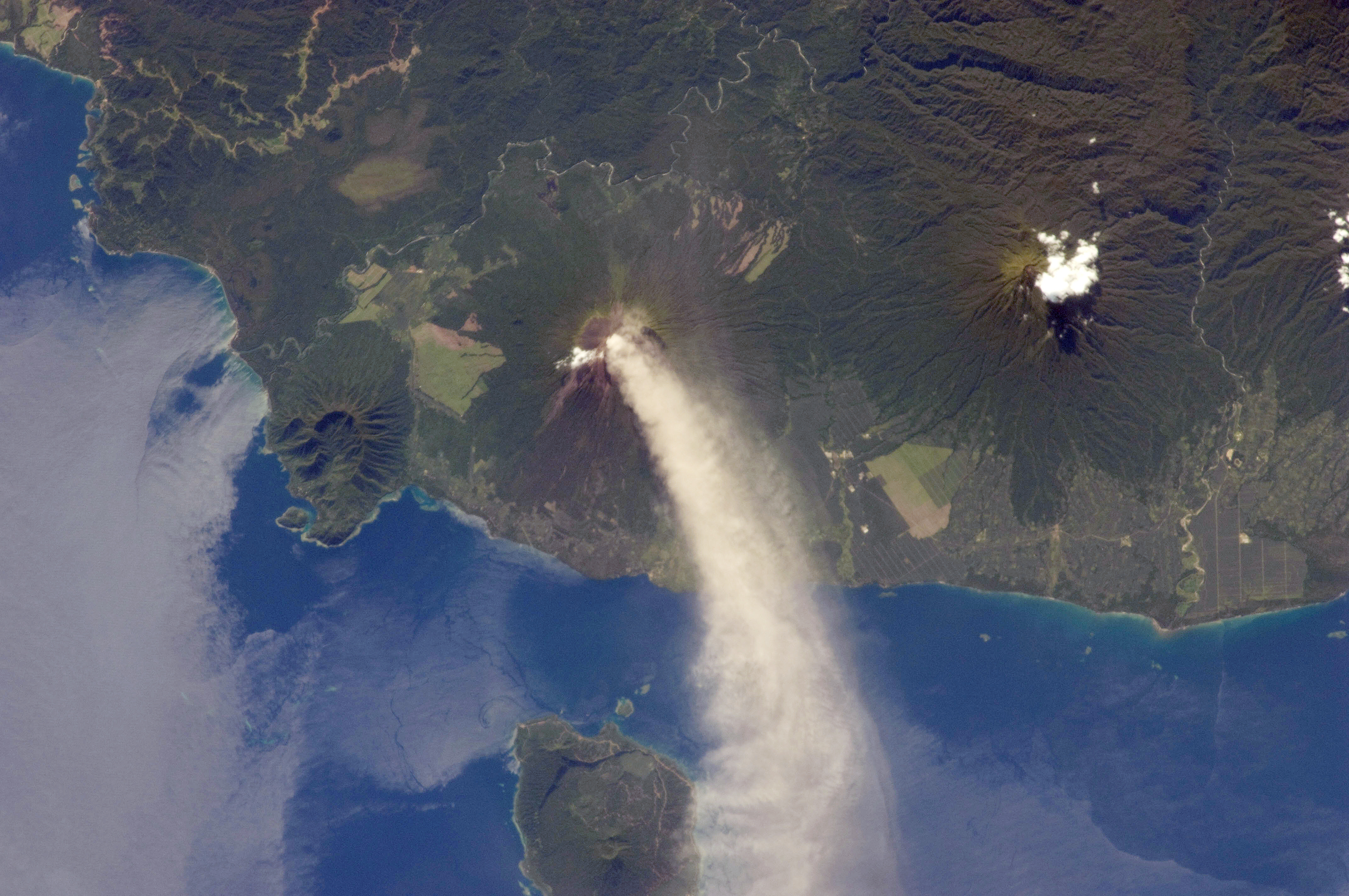
|
Ecoregions Of New Guinea
New Guinea, lying within the tropics and with extensive mountain areas, comprises a wide range of ecoregions. These include rainforests, grasslands and mangrove. Terrestrial ecoregions New Guinea is in the Australasian realm, which also includes the islands of Wallacea to the west, the Bismarck Archipelago, Solomon Islands, and Vanuatu to the east, and Australia and New Zealand. Sea levels were lower during the Ice Ages, which exposed the shallow continental shelf and connected New Guinea to Australia into a single land mass. Several nearby islands, including the Aru Islands, most of the Raja Ampat Islands, and Yapen, were also connected to the mainland, which allowed the flora and fauna of New Guinea and the continental shelf islands to mix. Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests *Central Range montane rain forests *Huon Peninsula montane rain forests *Northern New Guinea lowland rain and freshwater swamp forests The Northern New Guinea lowland rain and freshwater swa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu Hiri Motu, also known as Police Motu, Pidgin Motu, or just Hiri, is a language of Papua New Guinea, which is spoken in surrounding areas of Port Moresby (Capital of Papua New Guinea). It is a simplified version of Motu, from the Austronesian l ...: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Mainland Australia, Australia by the wide Torres Strait, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The eastern half of the island is the major land mass of the independent state of Papua New Guinea. The western half, known as Western New Guinea, forms a part of Indonesia and is organized as the provinces of Papua (province), Papua, Central Papua, Highland Papua, South Papua, Southwest Papua, and West Papua (province), West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern New Guinea Montane Rain Forests
The Northern New Guinea montane rain forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in northern New Guinea. The ecoregion covers several separate mountain ranges lying north of New Guinea's Central Range and south of the Pacific Ocean. Geography The ecoregion includes the montane forests above 1000 meters elevation in the Van Rees Mountains, Foya Mountains, Cyclops Mountains, Bewani Mountains, Torricelli Mountains, Prince Alexander Mountains, and Adelbert Mountains. These isolated mountain ranges rise from the northern New Guinea lowlands, running generally east–west and between the Central Range and the sea. The northern New Guinea mountains are not as high as the Central Range; the Van Rees mountains reach to , Foya to , the Cyclops to , the Bewani to , the Torricelli to , the Prince Alexander to , and the Adelbert Mountains to . The montane forests are surrounded by Northern New Guinea lowland rain and freshwater swamp forests at lower elevations but differ from the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bismarck Sea
The Bismarck Sea (, ) lies in the southwestern Pacific Ocean within the nation of Papua New Guinea. It is located northeast of the island of New Guinea and south of the Bismarck Archipelago. It has coastlines in districts of the Islands Region, Momase Region, and Papua Region. Geography Like the Bismarck Archipelago, it is named in honour of the first German Chancellor Otto von Bismarck. The Bismarck Archipelago extends round to the east and north of the sea, enclosing the Bismarck Sea and separating it from the Southern Pacific Ocean. To the south it is linked to the Solomon Sea by the Vitiaz Strait. Official boundaries The International Hydrographic Organization defines the Bismarck Sea as "that area of the Pacific Ocean, South Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of New Guinea", with the following limits: ''On the North and East.'' By the Northern and Northeastern coasts of the islands of New Ireland (island), New Ireland, New Hanover Island, New Hanover, the Admiralty I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
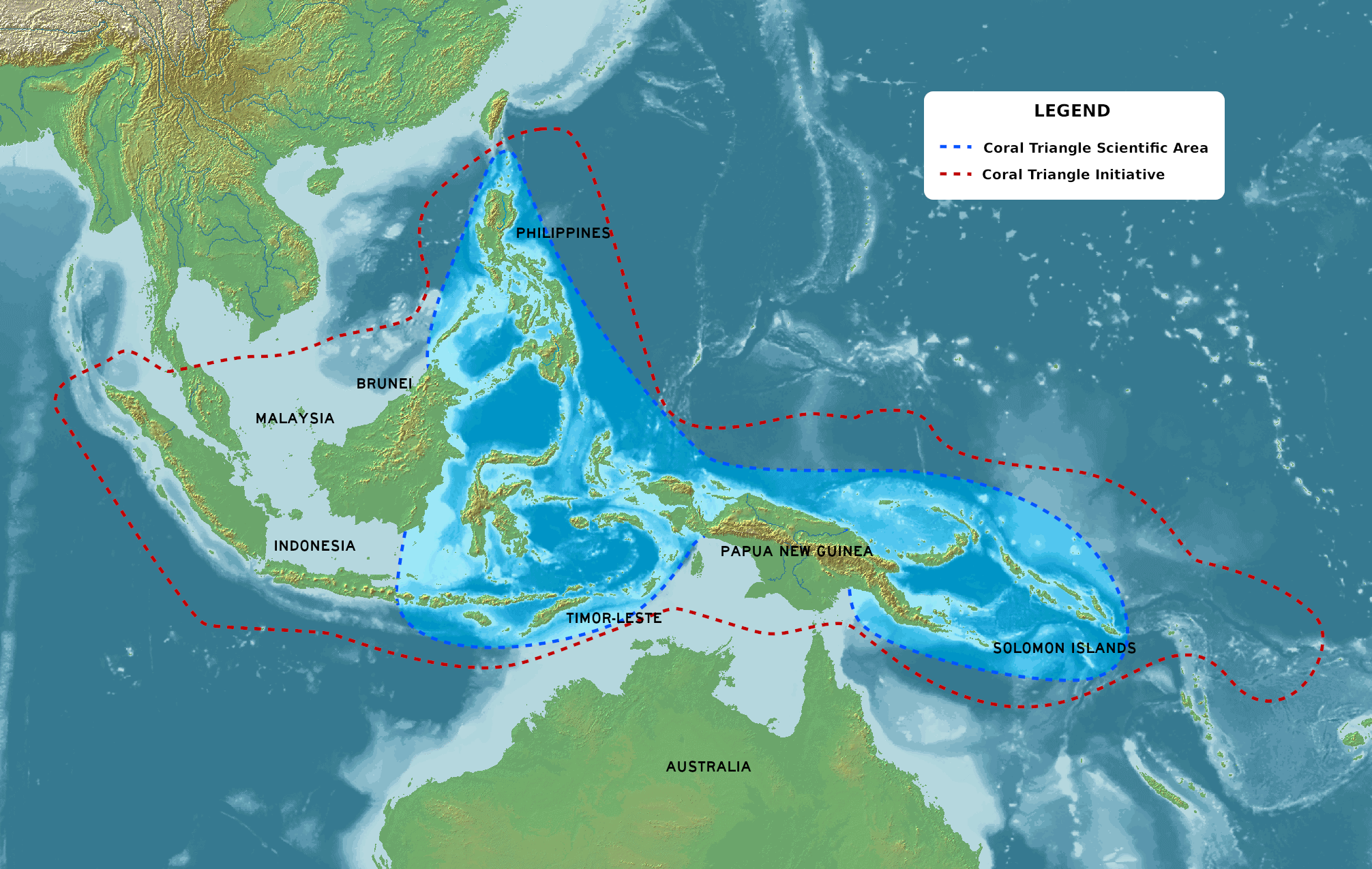
Coral Triangle
The Coral Triangle (CT) is a roughly triangular area in the tropical waters around the Philippines, Indonesia, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, the Solomon Islands and Timor-Leste. This area contains at least 500 species of reef-building corals in each ecoregion.Veron et al. Unpublished data The Coral Triangle is located between the Pacific and Indian oceans and encompasses portions of two biogeographic regions: the Indonesian-Philippines Region, and the Far Southwestern Pacific Region.Veron, J.E.N. 1995. Corals in space and time: biogeography and evolution of the Scleractinia. UNSW Press, Sydney, Australia: xiii + 321 pp. As one of eight major coral reef zones in the world,Speers, A. E., Besedin, E. Y., Palardy, J. E., & Moore, C. (2016)Impacts of climate change and ocean acidification on coral reef fisheries: an integrated ecological–economic model Ecological economics, 128, 33-43. Retrieved 26 September 2020 the Coral Triangle is recognized as a global centre of marine biodivers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Realm
A marine ecoregion is an ecoregion, or ecological region, of the oceans and seas identified and defined based on biogeographic characteristics. Introduction A more complete definition describes them as “Areas of relatively homogeneous species composition, clearly distinct from adjacent systems” dominated by “a small number of ecosystems and/or a distinct suite of oceanographic or topographic features”. Ecologically they “are strongly cohesive units, sufficiently large to encompass ecological or life history processes for most sedentary species.”Spalding, Mark D., Helen E. Fox, Gerald R. Allen, Nick Davidson et al. "Marine Ecoregions of the World: A Bioregionalization of Coastal and Shelf Areas". Bioscience Vol. 57 No. 7, July/August 2007, pp. 573–58/ref> Marine Ecoregions of the World—MEOW The global classification system Marine Ecoregions of the World—MEOW was devised by an international team, including major conservation organizations, academic institutions and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Indo-Pacific
The Central Indo-Pacific is a biogeographic region of Earth's seas, comprising the tropical waters of the western Pacific Ocean, the eastern Indian Ocean, and the connecting seas. The Central Indo-Pacific is a part of the larger Indo-Pacific, which includes the tropical Indian Ocean, the western and central tropical Pacific Ocean, and the seas connecting the two in the general area of Indonesia. The Central Indo-Pacific may be classified as a marine realm, one of the great biogeographic divisions of the world's ocean basins, or as a subrealm of the Indo-Pacific.Spalding, Mark D., Helen E. Fox, Gerald R. Allen, Nick Davidson ''et al.'' "Marine Ecoregions of the World: A Bioregionalization of Coastal and Shelf Areas". ''Bioscience'' Vol. 57 No. 7, July/August 2007, pp. 573–583/ref> The Central Indo-Pacific realm covers eastern shores of the tropical Indian Ocean, including most of the Indian Ocean coast of the Indonesian archipelago, the northern Australian coast, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papuan Peninsula
The Papuan Peninsula, also known as the Bird's Tail Peninsula, is a large peninsula in Papua New Guinea, southeast of the city of Lae, that makes up the southeastern portion of the island of New Guinea. The peninsula is the easternmost extent of the New Guinea Highlands and consists largely of the Owen Stanley Range, with peaks such as Mount Victoria (4,038 m) and Mount Suckling (3,676 m). On the south coast is Port Moresby, the capital and largest city of Papua New Guinea. The island of New Guinea is often visualized as being in the shape of a bird, with the Bird's Head Peninsula being at the northwest end of the island, and the Bird's Tail Peninsula at the southeast end. For example, American soldiers in WWII visualized it specifically as a turkey, and referenced the anatomy of the bird as a shorthand for explaining where various actions and deployments occurred on the island. See also *Southeast Papuan languages The Southeast Papuan or Papuan Peninsula ("Bird's Tail") lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Guinea Mangroves
The New Guinea mangroves is a mangrove ecoregion that covers extensive areas of the coastline New Guinea, the large island in the western Pacific Ocean north of Australia. Location and description The New Guinea mangroves cover an area of , particularly among the river mouths of the island's south coast. This ecoregion contains the greatest diversity of mangrove species in the world and they are an important habitat for wildlife. Areas of mangroves on the northern coast of New Guinea can be found at the mouths of the Sepik and Ramu rivers on the eastern side of Cenderawasih Bay, and Dyke Ackland Bay and Ward Hunt Strait. However the largest areas are found on the south coast in the mouths of the Purari, Kikori, Flys as well as Bintuni Bay and other areas of the southern Bird's Head Peninsula. Some areas such as the Kikori delta have larger and thicker mangroves than others. Climate The coast of New Guinea has a Tropical monsoon climate apart from the length of drier Trans-F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Range Sub-alpine Grasslands
The Central Range sub-alpine grasslands is a montane grasslands and shrublands ecoregion on the island of New Guinea. The ecoregion covers the highest-elevation portions of the New Guinea Highlands, which extend along the spine of the island. The high elevations support rare tropical sub-alpine and alpine habitats, including many endemic plants and animals. Geography The ecoregion includes isolated areas above 3000 metres elevation in the Central Range, or Central Cordillera, of New Guinea, and some outliers in the mountains of the Huon Peninsula. The Central Range extends east and west across New Guinea, with the western portion of the range in Indonesia and the eastern portion in Papua New Guinea. High-elevation areas in the highlands include the Snow Mountains in Indonesia's Papua Province, the Star Mountains on the Indonesia–Papua New Guinea border, the Central and Eastern Highlands of Papua New Guinea, and the Owen Stanley Range in Southeastern Papua. Below 3000 metres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans-Fly Savanna And Grasslands
The Trans Fly savanna and grasslands are a lowland ecoregion on the south coast of the island of New Guinea in both the Indonesian and Papua New Guinean sides of the island. With their monsoon and dry season climate these grasslands are quite different from the tropical rainforest that covers most of the island and resemble the landscape of northern Australia which lies to the south. The name refers to the Fly River. History From possibly as early as the 16th century, merchants from Makassar, Seram and other parts of Indonesia conducted trade with the natives of the region's coast. Although trading contacts between the Southeast Asian merchants and the natives became more infrequent as time passed, there was a continued presence of traders in the region as late as the 1870's. Many of the native tribes obtained iron tools through this trade some time before the first European missionaries arrived in the area in the late 19th century. Flora The area is mostly grassland t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vogelkop Montane Rain Forests
The Vogelkop montane rain forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in western New Guinea. The ecoregion covers the mountains of western New Guinea's Bird's Head and Bomberai peninsulas. Geography The ecoregion includes the montane forests above 1000 meters elevation on the Bird's Head (also known as Vogelkop) and Bomberai peninsulas. The largest area is in the Arfak Mountains and Tamrau Mountains on the Bird's Head Peninsula, with smaller areas in the Fakfak and Kumafa mountains on the western Bomberai Peninsula, and the mountains of the eastern Womberoi Peninsula on Cenderawasih Bay. Mount Arfak (2955 m) is the highest point in the ecoregion. The Vogelkop-Aru lowland rain forests ecoregion occupies the surrounding foothills and lowlands.Wikramanayake, Eric; Eric Dinerstein; Colby J. Loucks; et al. (2002). ''Terrestrial Ecoregions of the Indo-Pacific: a Conservation Assessment.'' Washington, DC: Island Press. Climate The ecoregion has a montane tropical rain forest clim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vogelkop–Aru Lowland Rain Forests
The Vogelkop–Aru lowland rain forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in Indonesia. The ecoregion covers the peninsular lowlands of western New Guinea, along with the Aru Islands and other nearby islands. Geography The ecoregion includes the lowland and hill (below 1000 meters elevation) forests of the Bird's Head Peninsula (also known as the Vogelkop Peninsula), Bomberai Peninsula, and the Bird's Neck Isthmus, as well as the Aru Islands to the south and Raja Ampat Islands (Misool, Salawati, Waigeo, Kofiau, and others) to the west. The Aru and Raja Ampat islands sit on the Australia-New Guinea continental shelf. When sea levels were lower during the ice ages, these islands were joined to the Australia-New Guinea continent, which allowed terrestrial plants and animals to move between them. The peninsular mountains above 1000 meters elevation, including the Arfak Mountains and Tamrau Mountains, constitute the separate and distinct Vogelkop montane rain forests ecoregion.Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |