|
Digital Imaging
Digital imaging or digital image acquisition is the creation of a digital representation of the visual characteristics of an object, such as a physical scene or the interior structure of an object. The term is often assumed to imply or include the processing, compression, storage, printing and display of such images. A key advantage of a digital image, versus an analog image such as a film photograph, is the ability to digitally propagate copies of the original subject indefinitely without any loss of image quality. Digital imaging can be classified by the type of electromagnetic radiation or other waves whose variable attenuation, as they pass through or reflect off objects, conveys the information that constitutes the image. In all classes of digital imaging, the information is converted by image sensors into digital signals that are processed by a computer and made output as a visible-light image. For example, the medium of visible light allows digital photog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
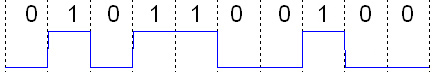
Digital Signal
A digital signal is a signal that represents data as a sequence of discrete values; at any given time it can only take on, at most, one of a finite number of values. This contrasts with an analog signal, which represents continuous values; at any given time it represents a real number within a continuous range of values. Simple digital signals represent information in discrete bands of levels. All levels within a band of values represent the same information state. In most digital circuits, the signal can have two possible valid values; this is called a binary signal or logic signal. They are represented by two voltage bands: one near a reference value (typically termed as ''ground'' or zero volts), and the other a value near the supply voltage. These correspond to the two values ''zero'' and ''one'' (or ''false'' and ''true'') of the Boolean domain, so at any given time a binary signal represents one binary digit (bit). Because of this discretization, relatively smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Sensor
An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to form an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves (as they refraction, pass through or reflection (physics), reflect off objects) into signal (electrical engineering), signals, small bursts of electric current, current that convey the information. The waves can be light or other electromagnetic radiation. Image sensors are used in electronics, electronic imaging devices of both analogue electronics, analog and digital electronics, digital types, which include digital cameras, camera modules, camera phones, optical mouse devices, medical imaging equipment, night vision equipment such as thermography, thermal imaging devices, radar, sonar, and others. As technological change, technology changes, electronic and digital imaging tends to replace chemical and analog imaging. The two main types of electronic image sensors are the charge-coupled device (CCD) and the active-pixel s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |