|
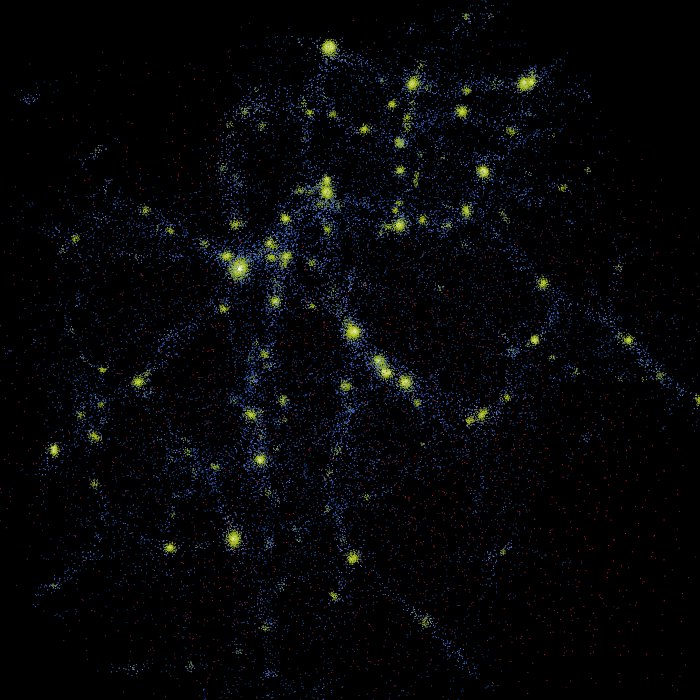
Dark Matter
In astronomy, dark matter is an invisible and hypothetical form of matter that does not interact with light or other electromagnetic radiation. Dark matter is implied by gravity, gravitational effects that cannot be explained by general relativity unless more matter is present than can be observed. Such effects occur in the context of Galaxy formation and evolution, formation and evolution of galaxies, gravitational lensing, the observable universe's current structure, mass position in galactic collisions, the motion of galaxies within galaxy clusters, and cosmic microwave background Anisotropy, anisotropies. Dark matter is thought to serve as gravitational scaffolding for cosmic structures. After the Big Bang, dark matter clumped into blobs along narrow filaments with superclusters of galaxies forming a cosmic web at scales on which entire galaxies appear like tiny particles. In the standard Lambda-CDM model of cosmology, the mass–energy equivalence, mass–energy content o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modified Newtonian Dynamics
Modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Modifying Newton's law of gravity results in modified gravity, while modifying Newton's second law results in modified inertia. The latter has received little attention compared to the modified gravity version. Its primary motivation is to explain galaxy rotation curves without invoking dark matter, and is one of the most well-known theories of this class. However, it has not gained widespread acceptance, with the majority of astrophysicists supporting the Lambda-CDM model as providing the better fit to observations. MOND was developed in 1982 and presented in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom.. . . Milgrom noted that galaxy rotation curve data, which seemed to show that galaxies contain more matter than is observed, could also be explained if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy decays mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dark Energy
In physical cosmology and astronomy, dark energy is a proposed form of energy that affects the universe on the largest scales. Its primary effect is to drive the accelerating expansion of the universe. It also slows the rate of structure formation. Assuming that the lambda-CDM model of cosmology is correct, dark energy dominates the universe, contributing 68% of the total energy in the present-day observable universe while dark matter and Baryon#Baryonic matter, ordinary (baryonic) matter contribute 27% and 5%, respectively, and other components such as neutrinos and photons are nearly negligible.Sean Carroll, Ph.D., Caltech, 2007, The Teaching Company, ''Dark Matter, Dark Energy: The Dark Side of the Universe'', Guidebook Part 2. p. 46. Retrieved 7 October 2013, "...dark energy: A smooth, persistent component of invisible energy, thought to make up about 70 percent of the energy density of the universe. Dark energy is smooth because it doesn't accumulate preferentially in galaxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structure Formation
In physical cosmology, structure formation describes the creation of galaxies, galaxy clusters, and larger structures starting from small fluctuations in mass density resulting from processes that created matter. The universe, as is now known from observations of the cosmic microwave background radiation, began in a hot, dense, nearly uniform state approximately 13.8 billion years ago. However, looking at the night sky today, structures on all scales can be seen, from stars and planets to galaxies. On even larger scales, galaxy clusters and sheet-like structures of galaxies are separated by enormous voids containing few galaxies. Structure formation models gravitational instability of small ripples in mass density to predict these shapes, confirming the consistency of the physical model. The modern Lambda-CDM model is successful at predicting the observed large-scale distribution of galaxies, clusters and voids; but on the scale of individual galaxies there are many complicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Dark Matter
In cosmology and physics, cold dark matter (CDM) is a hypothetical type of dark matter. According to the current standard model of cosmology, Lambda-CDM model, approximately 27% of the universe is dark matter and 68% is dark energy, with only a small fraction being the ordinary baryonic matter that composes stars, planets, and living organisms. ''Cold'' refers to the fact that the dark matter moves slowly compared to the speed of light, giving it a vanishing equation of state. ''Dark'' indicates that it interacts very weakly with ordinary matter and electromagnetic radiation. Proposed candidates for CDM include weakly interacting massive particles, primordial black holes, and axions, as well as most flavors of neutrinos. History The theory of cold dark matter was originally published in 1982 by James Peebles; while the warm dark matter picture was proposed independently at the same time by J. Richard Bond, Alex Szalay, and Michael Turner; and George Blumenthal, H. Pagel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Streaming
In astrophysics, free streaming is the motion of particles through a medium without scattering. Free streaming is often considered in the context of photons, but it is also relevant for neutrinos, cosmic rays, and hypothetical dark matter particles. Use in defining surfaces Defining an exact surface for an object such as the Sun is made difficult by the diffusive nature of matter which constitutes the Sun at distances far from the stellar core. An often used definition for the surface of a star is based on the path that photons take. Inside a star, photons travel by emission itself, constantly interacting with matter, and the surface of the star is defined as the point at which photons encounter little resistance from the matter in the stellar atmosphere, or in other words, when photons stream freely. See also emissivity. The light which constitutes the cosmic microwave background comes from the surface of last scattering. This is, on average, the surface at which primordial p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velocity
Velocity is a measurement of speed in a certain direction of motion. It is a fundamental concept in kinematics, the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of physical objects. Velocity is a vector (geometry), vector Physical quantity, quantity, meaning that both magnitude and direction are needed to define it. The Scalar (physics), scalar absolute value (Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude) of velocity is called , being a coherent derived unit whose quantity is measured in the International System of Units, SI (metric system) as metres per second (m/s or m⋅s−1). For example, "5 metres per second" is a scalar, whereas "5 metres per second east" is a vector. If there is a change in speed, direction or both, then the object is said to be undergoing an ''acceleration''. Definition Average velocity The average velocity of an object over a period of time is its Displacement (geometry), change in position, \Delta s, divided by the duration of the period, \Delt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
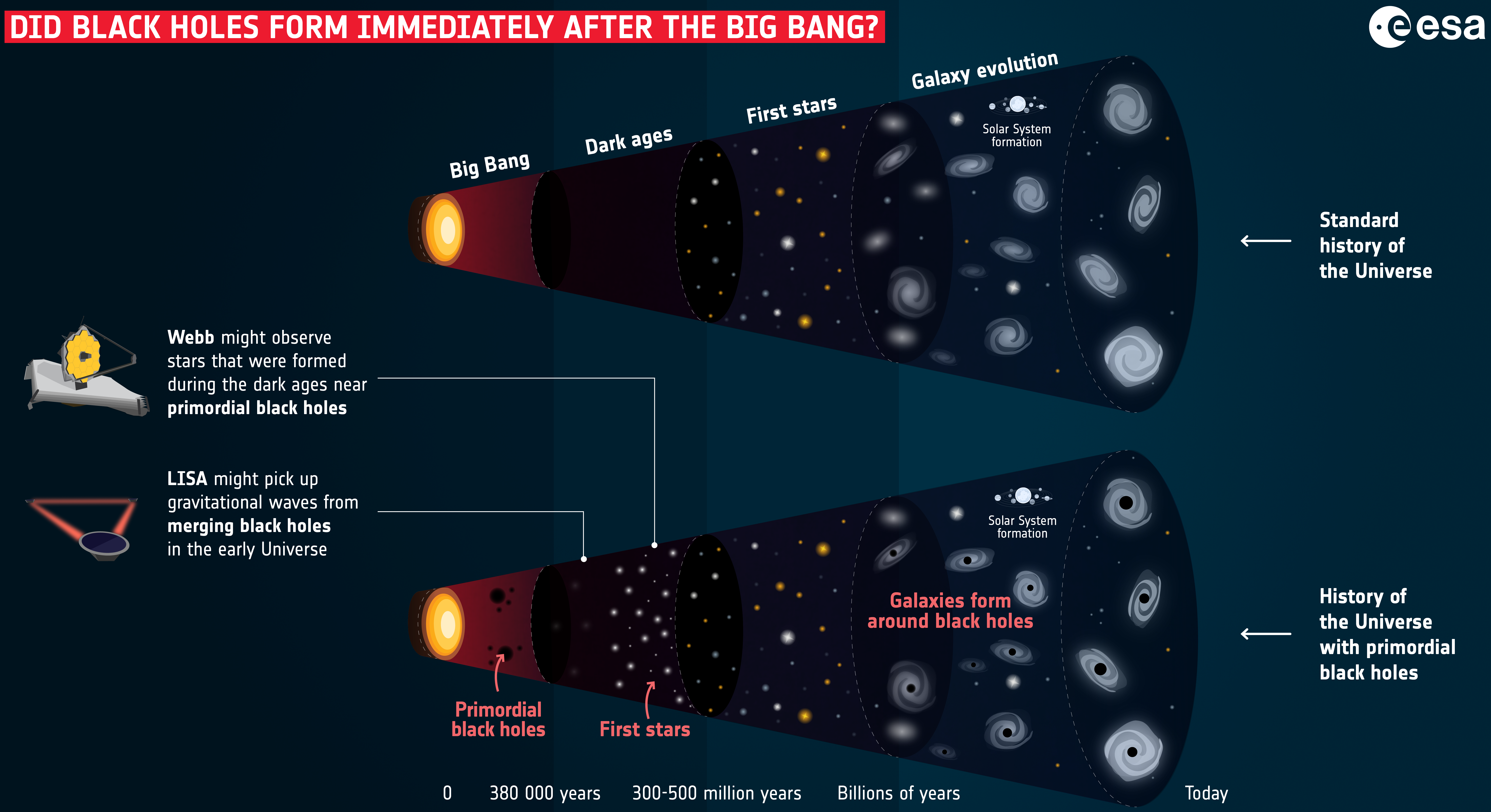
Primordial Black Hole
In cosmology, primordial black holes (PBHs) are hypothetical black holes that formed soon after the Big Bang. In the inflationary era and early radiation-dominated universe, extremely dense pockets of subatomic matter may have been tightly packed to the point of gravitational collapse, creating primordial black holes without the supernova compression typically needed to make black holes today. Because the creation of primordial black holes would pre-date the first stars, they are not limited to the narrow mass range of stellar black holes. In 1966, Yakov Zeldovich and Igor Novikov first proposed the existence of such black holes, while the first in-depth study was conducted by Stephen Hawking in 1971. However, their existence remains hypothetical. In September 2022, primordial black holes were proposed by some researchers to explain the unexpected very large early galaxies discovered by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). PBHs have long been considered possibly important i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axion
An axion () is a hypothetical elementary particle originally theorized in 1978 independently by Frank Wilczek and Steven Weinberg as the Goldstone boson of Peccei–Quinn theory, which had been proposed in 1977 to solve the strong CP problem in quantum chromodynamics (QCD). If axions exist and have low mass within a specific range, they are of interest as a possible component of cold dark matter. History Strong CP problem As shown by Gerard 't Hooft, strong interactions of the Standard Model, QCD, possess a non-trivial vacuum structure that in principle permits violation of the combined symmetries of charge conjugation and parity, collectively known as CP. Together with effects generated by weak interactions, the effective periodic strong CP-violating term, , appears as a Standard Model input – its value is not predicted by the theory, but must be measured. However, large CP-violating interactions originating from QCD would induce a large electric dipole moment (EDM) f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weakly Interacting Massive Particle
Weakly interacting massive particles (WIMPs) are hypothetical particles that are one of the proposed candidates for dark matter. There exists no formal definition of a WIMP, but broadly, it is an elementary particle which interacts via gravity and any other force (or forces) which is as weak as or weaker than the weak nuclear force, but also non-vanishing in strength. Many WIMP candidates are expected to have been produced thermally in the early Universe, similarly to the particles of the Standard Model according to Big Bang cosmology, and usually will constitute cold dark matter. Obtaining the correct abundance of dark matter today via thermal production requires a self-annihilation Cross section (physics), cross section of \langle \sigma v \rangle ≃ , which is roughly what is expected for a new particle in the 100 GeV/''c''2 mass range that interacts via the electroweak force. Experimental efforts to detect WIMPs include the search for products of WIMP annihilation, inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subatomic Particle
In physics, a subatomic particle is a particle smaller than an atom. According to the Standard Model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a baryon, like a proton or a neutron, composed of three quarks; or a meson, composed of two quarks), or an elementary particle, which is not composed of other particles (for example, quarks; or electrons, muons, and tau particles, which are called leptons). Particle physics and nuclear physics study these particles and how they interact. Most force-carrying particles like photons or gluons are called bosons and, although they have quanta of energy, do not have rest mass or discrete diameters (other than pure energy wavelength) and are unlike the former particles that have rest mass and cannot overlap or combine which are called fermions. The W and Z bosons, however, are an exception to this rule and have relatively large rest masses at approxim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes: * ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays, and Gamma ray, gamma radiation (γ) * ''particle radiation'' consisting of particles of non-zero rest energy, such as alpha radiation (α), beta radiation (β), proton radiation and neutron radiation * ''acoustics, acoustic radiation'', such as ultrasound, sound, and seismic waves, all dependent on a physical transmission medium * ''gravitational radiation'', in the form of gravitational waves, ripples in spacetime Radiation is often categorized as either ''ionizing radiation, ionizing'' or ''non-ionizing radiation, non-ionizing'' depending on the energy of the radiated particles. Ionizing radiation carries more than 10 electron volt, electron volts (eV), which is enough to ionize atoms and molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baryonic Matter
In particle physics, a baryon is a type of composite subatomic particle that contains an odd number of valence quarks, conventionally three. Protons and neutrons are examples of baryons; because baryons are composed of quarks, they belong to the hadron family of particles. Baryons are also classified as fermions because they have half-integer spin. The name "baryon", introduced by Abraham Pais, comes from the Greek word for "heavy" (βαρύς, ''barýs''), because, at the time of their naming, most known elementary particles had lower masses than the baryons. Each baryon has a corresponding antiparticle (antibaryon) where their corresponding antiquarks replace quarks. For example, a proton is made of two up quarks and one down quark; and its corresponding antiparticle, the antiproton, is made of two up antiquarks and one down antiquark. Baryons participate in the residual strong force, which is mediated by particles known as mesons. The most familiar baryons are proto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |