|
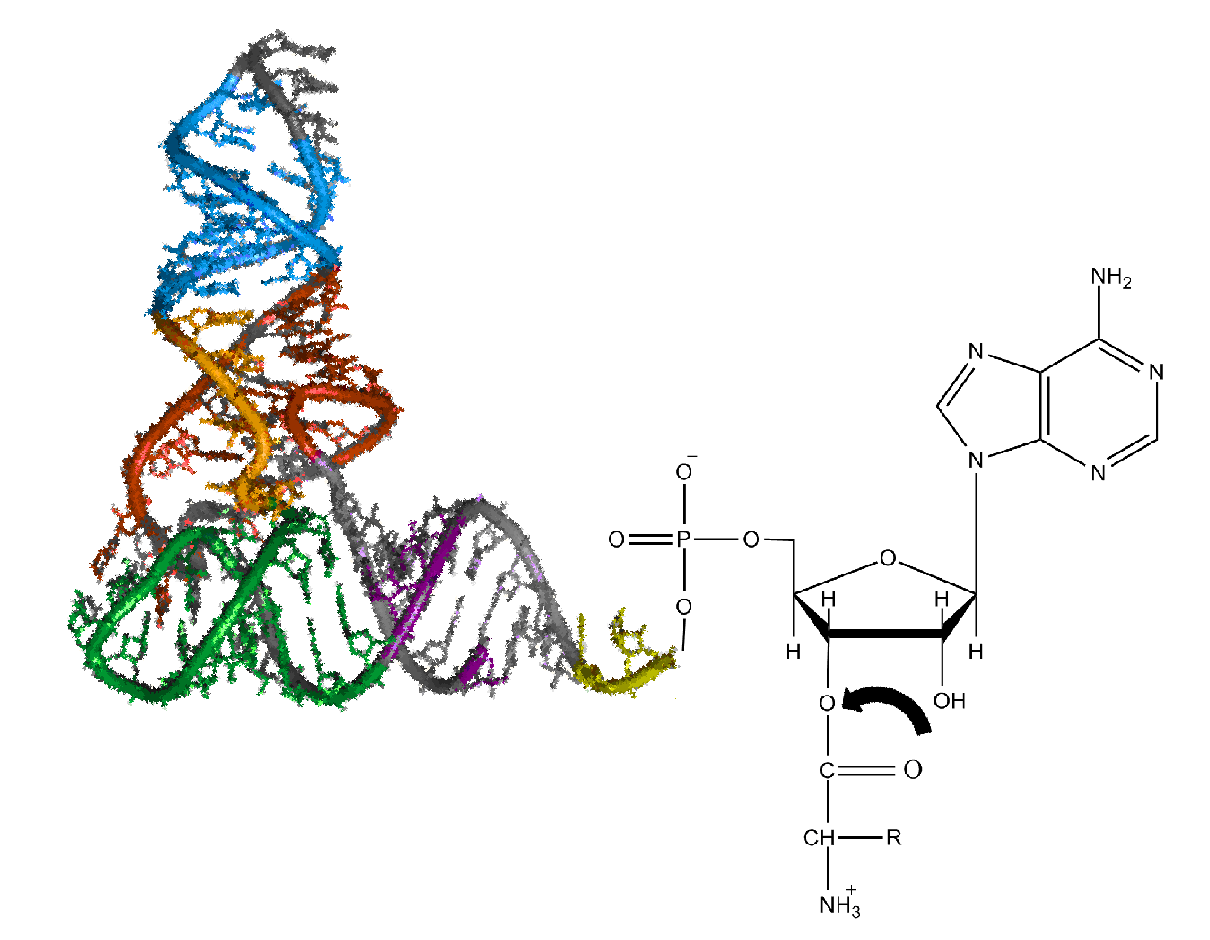
Cysteine—tRNA Ligase
In enzymology, a cysteine—tRNA ligase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :ATP + L-cysteine + tRNACys \rightleftharpoons AMP + diphosphate + L-cysteinyl-tRNACys The 3 substrates of this enzyme are ATP, L-cysteine, and tRNA(Cys), whereas its 3 products are AMP, diphosphate, and L-cysteinyl-tRNA(Cys). This enzyme belongs to the family of ligases, to be specific those forming carbon-oxygen bonds in aminoacyl-tRNA and related compounds. The systematic name of this enzyme class is L-cysteine:tRNACys ligase (AMP-forming). Other names in common use include cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase, cysteinyl-transferRNA synthetase, cysteinyl-transfer ribonucleate synthetase, and cysteine translase. This enzyme participates in cysteine metabolism and aminoacyl-trna biosynthesis. Structural studies As of late 2007, 3 structures A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Materia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzymology
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphosphate
In chemistry, pyrophosphates are phosphorus oxyanions that contain two phosphorus atoms in a P–O–P linkage. A number of pyrophosphate salts exist, such as disodium pyrophosphate (Na2H2P2O7) and tetrasodium pyrophosphate (Na4P2O7), among others. Often pyrophosphates are called diphosphates. The parent pyrophosphates are derived from partial or complete neutralization of pyrophosphoric acid. The pyrophosphate bond is also sometimes referred to as a phosphoanhydride bond, a naming convention which emphasizes the loss of water that occurs when two phosphates form a new P–O–P bond, and which mirrors the nomenclature for anhydrides of carboxylic acids. Pyrophosphates are found in ATP and other nucleotide triphosphates, which are important in biochemistry. The term pyrophosphate is also the name of esters formed by the condensation of a phosphorylated biological compound with inorganic phosphate, as for dimethylallyl pyrophosphate. This bond is also referred to as a high-energ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Data Bank
The Protein Data Bank (PDB) is a database for the three-dimensional structural data of large biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids. The data, typically obtained by X-ray crystallography, NMR spectroscopy, or, increasingly, cryo-electron microscopy, and submitted by biologists and biochemists from around the world, are freely accessible on the Internet via the websites of its member organisations (PDBe, PDBj, RCSB, and BMRB). The PDB is overseen by an organization called the Worldwide Protein Data Bank, wwPDB. The PDB is a key in areas of structural biology, such as structural genomics. Most major scientific journals and some funding agencies now require scientists to submit their structure data to the PDB. Many other databases use protein structures deposited in the PDB. For example, SCOP and CATH classify protein structures, while PDBsum provides a graphic overview of PDB entries using information from other sources, such as Gene ontology. History Two force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary Structure
Protein tertiary structure is the three dimensional shape of a protein. The tertiary structure will have a single polypeptide chain "backbone" with one or more protein secondary structures, the protein domains. Amino acid side chains may interact and bond in a number of ways. The interactions and bonds of side chains within a particular protein determine its tertiary structure. The protein tertiary structure is defined by its atomic coordinates. These coordinates may refer either to a protein domain or to the entire tertiary structure.Branden C. and Tooze J. "Introduction to Protein Structure" Garland Publishing, New York. 1990 and 1991. A number of tertiary structures may fold into a quaternary structure.Kyte, J. "Structure in Protein Chemistry." Garland Publishing, New York. 1995. History The science of the tertiary structure of proteins has progressed from one of hypothesis to one of detailed definition. Although Emil Fischer had suggested proteins were made of polypept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminoacyl-trna Biosynthesis
Aminoacyl-tRNA (also aa-tRNA or charged tRNA) is tRNA to which its cognate amino acid is chemically bonded (charged). The aa-tRNA, along with particular elongation factors, deliver the amino acid to the ribosome for incorporation into the polypeptide chain that is being produced during translation. Alone, an amino acid is not the substrate necessary to allow for the formation of peptide bonds within a growing polypeptide chain. Instead, amino acids must be "charged" or aminoacylated with a tRNA to form their respective aa-tRNA. Every amino acid has its own specific aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, which is utilized to chemically bind to the tRNA that it is specific to, or in other words, "cognate" to. The pairing of a tRNA with its cognate amino acid is crucial, as it ensures that only the particular amino acid matching the anticodon of the tRNA, and in turn matching the codon of the mRNA, is used during protein synthesis. In order to prevent translational errors, in which the wrong am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysteine Metabolism
Cysteine metabolism refers to the biological pathways that consume or create cysteine. The pathways of different amino acids and other metabolites interweave and overlap to creating complex systems.cysteine is metabolism creating complex systems Human cysteine metabolism In human cysteine metabolism, L-cysteine is consumed in several ways as shown below. L-Cysteine is also consumed in methionine and glutathione metabolism as well as pantothenate/coenzyme A biosynthesis. L-Cysteine is the product of several processes as well. In addition to the reactions below, L-cysteine is also a product of glycine, serine, and threonine metabolism. See also * D-cysteine desulfhydrase * Sulfur metabolism Sulfur is metabolism, metabolized by all organisms, from bacteria and archaea to plants and animals. Sulfur is redox, reduced or redox, oxidized by organisms in a variety of forms. The chemical element, element is present in proteins, organosulfate ... {{DEFAULTSORT:Cysteine Metabolism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Enzymes
This article lists enzymes by their classification in the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology's Enzyme Commission (EC) numbering system. * List of EC numbers (EC 5) * List of EC numbers (EC 6) :Oxidoreductases (EC 1) (Oxidoreductase) *Dehydrogenase * Luciferase *DMSO reductase :EC 1.1 (act on the CH-OH group of donors) * :EC 1.1.1 (with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NAD) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NADP) **Homoserine dehydrogenase ** Aminopropanol oxidoreductase **Diacetyl reductase **Glycerol dehydrogenase **Propanediol-phosphate dehydrogenase ** glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (NAD+) ** D-xylulose reductase **L-xylulose reductase **Lactate dehydrogenase **Malate dehydrogenase **Isocitrate dehydrogenase ** HMG-CoA reductase * :EC 1.1.2 (with a cytochrome as acceptor) * :EC 1.1.3 (with oxygen as acceptor) **Glucose oxidase **L-gulonolactone oxidase **Thiamine oxidase **Xanthine oxidase * :EC 1.1.4 (with a disul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligase
In biochemistry, a ligase is an enzyme that can catalyze the joining (ligation) of two large molecules by forming a new chemical bond. This is typically via hydrolysis of a small pendant chemical group on one of the larger molecules or the enzyme catalyzing the linking together of two compounds, e.g., enzymes that catalyze joining of C-O, C-S, C-N, etc. In general, a ligase catalyzes the following reaction: :Ab + C → A–C + b or sometimes :Ab + cD → A–D + b + c + d + e + f where the lowercase letters can signify the small, dependent groups. Ligase can join two complementary fragments of nucleic acid and repair single stranded breaks that arise in double stranded DNA during replication. Nomenclature The common names of ligases often include the word "ligase", such as DNA ligase, an enzyme commonly used in molecular biology laboratories to join together DNA fragments. Other common names for ligases include the word "synthetase", because they are used to synthes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Monophosphate
Adenosine monophosphate (AMP), also known as 5'-adenylic acid, is a nucleotide. AMP consists of a phosphate group, the sugar ribose, and the nucleobase adenine; it is an ester of phosphoric acid and the nucleoside adenosine. As a substituent it takes the form of the prefix adenylyl-. AMP plays an important role in many cellular metabolic processes, being interconverted to Adenosine diphosphate, ADP and/or Adenosine triphosphate, ATP. AMP is also a component in the synthesis of RNA. AMP is present in all known forms of life. Production and degradation AMP does not have the high energy phosphoanhydride bond associated with ADP and ATP. AMP can be produced from Adenosine diphosphate, ADP: : 2 ADP → ATP + AMP Or AMP may be produced by the hydrolysis of one high energy phosphate bond of ADP: : ADP + H2O → AMP + phosphate, Pi AMP can also be formed by hydrolysis of Adenosine triphosphate, ATP into AMP and pyrophosphate: : ATP + H2O → AMP + pyrophosphate, PPi When RNA i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product (chemistry)
Products are the species formed from chemical reactions. During a chemical reaction, reactants are transformed into products after passing through a high energy transition state. This process results in the consumption of the reactants. It can be a spontaneous reaction or mediated by catalysts which lower the energy of the transition state, and by solvents which provide the chemical environment necessary for the reaction to take place. When represented in chemical equations, products are by convention drawn on the right-hand side, even in the case of reversible reactions. The properties of products such as their energies help determine several characteristics of a chemical reaction, such as whether the reaction is exergonic or endergonic. Additionally, the properties of a product can make it easier to extract and purify following a chemical reaction, especially if the product has a different state of matter than the reactants. Spontaneous reaction : R \rightarrow P *Where R is r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |