|
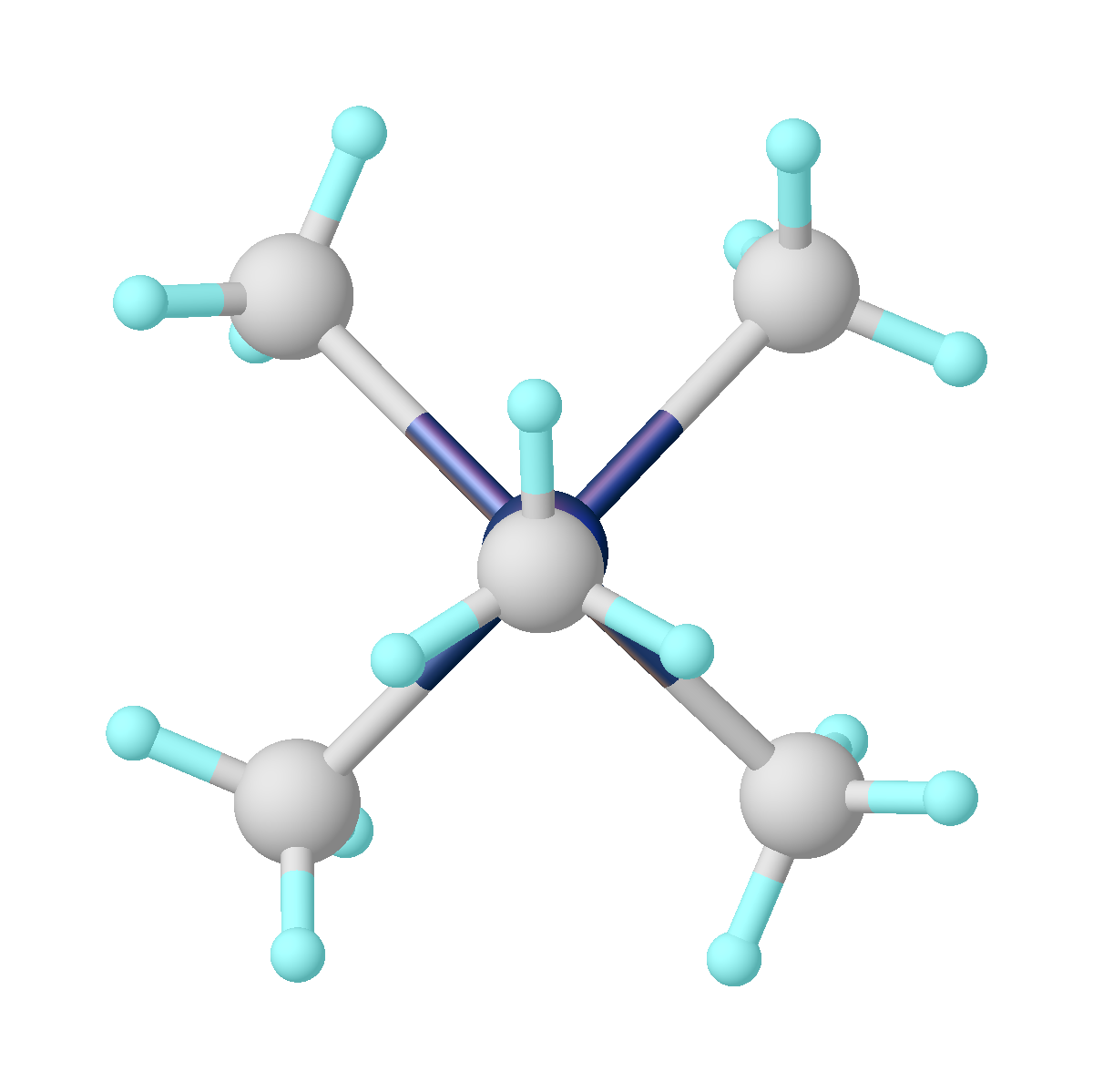
Cycloheptatrienemolybdenum Tricarbonyl
Cycloheptatrienemolybdenum tricarbonyl is the organomolybdenum compound with the formula (C7H8)Mo(CO)3. It is a red-orange solid that is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. The compound has no practical value but is a prototypical complex of cycloheptatriene. Synthesis, structure, and reactions The compound is prepared by thermal reaction of the triene with molybdenum hexacarbonyl: :C7H8 + Mo(CO)6 → (C7H8)Mo(CO)3 + 3 CO The compound is a piano stool complex, consisting of Mo(CO)3 bound to six carbon centers of the triene. The methylene group projects from the plane of the six coordinated carbon atoms. The compound reacts with trityl Triphenylmethane, or triphenyl methane, is the hydrocarbon with the formula (C6H5)3CH. This colorless solid is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents and not in water. Triphenylmethane is the basic skeleton of many synthetic dyes called triarylmetha ... salts to give the cycloheptatrienyl complex: M. L. H. Green, D. K. P. Ng "Cyclohepta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organomolybdenum Compound
Organomolybdenum chemistry is the chemistry of chemical compounds with Mo-C bonds. The heavier group 6 elements molybdenum and tungsten form organometallic compounds similar to those in organochromium chemistry but higher oxidation states tend to be more common. Mo(0) and more reduced states Molybdenum hexacarbonyl is the precursor to many substituted derivatives. It reacts with organolithium reagents to give anionic acyls which can be O-alkylated to give Fischer carbenes. 144px, Structure of (mesitylene)molybdenum tricarbonyl. Mo(CO)6 reacts with arenes to give piano-stool complexes such as (mesitylene)molybdenum tricarbonyl. Cycloheptatrienemolybdenum tricarbonyl, which is related to (arene)Mo(CO)3, reacts with trityl salts to give the cycloheptatrienyl complex: :(C7H8)Mo(CO)3 + (C6H5)3C+ → C7H7)Mo(CO)3sup>+ + (C6H5)3CH file:CHTMo(CO)3.png, 144px, Structure of Cycloheptatrienemolybdenum tricarbonyl. Reduction of Mo(CO)6 gives [Mo(CO)5]2− which is formally M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for polar molecules and the most common solvent used by living things; all the ions and proteins in a cell are dissolved in water within the cell. The quantity of solute that can dissolve in a specific volume of solvent varies with temperature. Major uses of solvents are in paints, paint removers, inks, and dry cleaning. Specific uses for organic solvents are in dry cleaning (e.g. tetrachloroethylene); as paint thinners (toluene, turpentine); as nail polish removers and solvents of glue (acetone, methyl acetate, ethyl acetate); in spot removers (hexane, petrol ether); in detergents ( citrus terpenes); and in perfumes (ethanol). Solvents find various applications in chemical, pharmaceutical, oil, and gas industries, including in chemical synt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycloheptatriene
Cycloheptatriene (CHT) is an organic compound with the formula C7H8. It is a closed ring of seven carbon atoms joined by three double bonds (as the name implies) and four single bonds. This colourless liquid has been of recurring theoretical interest in organic chemistry. It is a ligand in organometallic chemistry and a building block in organic synthesis. Cycloheptatriene is not aromatic, as reflected by the nonplanarity of the methylene bridge (-CH2-) with respect to the other atoms; however the related tropylium cation is. Synthesis Albert Ladenburg first generated cycloheptatriene in 1881 by the decomposition of tropine. The structure was finally proven by the synthesis of Richard Willstätter in 1901. This synthesis started from cycloheptanone and established the seven membered ring structure of the compound. Cycloheptatriene can be obtained in the laboratory by photochemical reaction of benzene with diazomethane or the pyrolysis of the adduct of cyclohexene and dichlorocar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molybdenum Hexacarbonyl
Molybdenum hexacarbonyl (also called molybdenum carbonyl) is the chemical compound with the formula Mo(CO)6. This colorless solid, like its chromium and tungsten analogues, is noteworthy as a volatile, air-stable derivative of a metal in its zero oxidation state. Structure and properties Mo(CO)6 adopts an octahedral geometry consisting of six rod-like CO ligands radiating from the central Mo atom. A recurring minor debate in some chemical circles concerns the definition of an "organometallic" compound. Usually, organometallic indicates the presence of a metal directly bonded via a M–C bond to an organic fragment, which must in turn have a C–H bond. Mo(CO)6 is prepared by the reduction of molybdenum chlorides or oxides under a pressure of carbon monoxide, although it would be unusual to prepare this inexpensive compound in the laboratory. The compound is somewhat air-stable and sparingly soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. Occurrence Mo(CO)6 has been detected in landfil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piano Stool Complex
Half sandwich compounds, also known as piano stool complexes, are organometallic complexes that feature a cyclic polyhapto ligand bound to an MLn center, where L is a unidentate ligand. Thousands of such complexes are known. Well-known examples include cyclobutadieneiron tricarbonyl and (C5H5)TiCl3. Commercially useful examples include (C5H5)Co(CO)2, which is used in the synthesis of substituted pyridines, and methylcyclopentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl, an antiknock agent in petrol. MMT-2D-skeletal.png, MMT is a commercially useful antiknock compound. Cpco(CO)2.png, CpCo(CO)2 is a catalyst for the synthesis of pyridines. Cyclobutadienyl-iron-tricarbonyl-from-xtal-3D-balls.png, (C4H4)Fe(CO)3. Cp2Fe(CO)2I-2D-skeletal.png, CpFe(CO)2I is an example of a piano stool complex with two different monodentate ligands. RuCymCl2.png, The diruthenium of cymene is readily cleaved by ligands to give monoRu half-sandwich derivatives. CHTMo(CO)3.png, Cycloheptatriene molybdenum tricarbonyl CP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trityl
Triphenylmethane, or triphenyl methane, is the hydrocarbon with the formula (C6H5)3CH. This colorless solid is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents and not in water. Triphenylmethane is the basic skeleton of many synthetic dyes called triarylmethane dyes, many of them are pH indicators, and some display fluorescence. A trityl group in organic chemistry is a triphenylmethyl group Ph3C, e.g. triphenylmethyl chloride (trityl chloride) and the triphenylmethyl radical (trityl radical). Preparation Triphenylmethane was first synthesized in 1872 by the German chemist August Kekulé and his Belgian student Antoine Paul Nicolas Franchimont (1844–1919) by heating diphenylmercury (Hg(C6H5)2, ''Quecksilberdiphenyl'') with benzal chloride (C6H5CHCl2, ''Benzylenchlorid''). Triphenylmethane can be synthesized by Friedel–Crafts reaction from benzene and chloroform with aluminium chloride catalyst: :3 C6H6 + CHCl3 → Ph3CH + 3 HCl Alternatively, benzene may react with carbon tetrachloride us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycloheptatrienyl
In organic chemistry, the tropylium ion or cycloheptatrienyl cation is an aromatic species with a formula of 7H7sup>+. Its name derives from the molecule tropine from which cycloheptatriene (tropylidene) was first synthesized in 1881. Salts of the tropylium cation can be stable, even with nucleophiles of moderate strength e.g., tropylium tetrafluoroborate and tropylium bromide (''see below''). Its bromide and chloride salts can be made from cycloheptatriene and bromine or phosphorus pentachloride, respectively. It is a regular heptagonal, planar, cyclic ion. It has 6 π-electrons (4''n'' + 2, where ''n'' = 1), which fulfills Hückel's rule of aromaticity. It can coordinate as a ligand to metal atoms. The structure shown is a composite of seven resonance contributors in which each carbon atom carries part of the positive charge. History In 1891 G. Merling obtained a water-soluble bromine-containing compound from the reaction of cycloheptatriene an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organomolybdenum Compounds
Organomolybdenum chemistry is the chemistry of chemical compounds with Mo-C bonds. The heavier group 6 elements molybdenum and tungsten form organometallic compounds similar to those in organochromium chemistry but higher oxidation states tend to be more common. Mo(0) and more reduced states Molybdenum hexacarbonyl is the precursor to many substituted derivatives. It reacts with organolithium reagents to give anionic acyls which can be O-alkylated to give Fischer carbenes. 144px, Structure of (mesitylene)molybdenum tricarbonyl. Mo(CO)6 reacts with arenes to give piano-stool complexes such as (mesitylene)molybdenum tricarbonyl. Cycloheptatrienemolybdenum tricarbonyl, which is related to (arene)Mo(CO)3, reacts with trityl salts to give the cycloheptatrienyl complex: :(C7H8)Mo(CO)3 + (C6H5)3C+ → C7H7)Mo(CO)3sup>+ + (C6H5)3CH file:CHTMo(CO)3.png, 144px, Structure of Cycloheptatrienemolybdenum tricarbonyl. Reduction of Mo(CO)6 gives [Mo(CO)5]2− which is formally M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonyl Complexes
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is common to several classes of organic compounds, as part of many larger functional groups. A compound containing a carbonyl group is often referred to as a carbonyl compound. The term carbonyl can also refer to carbon monoxide as a ligand in an inorganic or organometallic complex (a metal carbonyl, e.g. nickel carbonyl). The remainder of this article concerns itself with the organic chemistry definition of carbonyl, where carbon and oxygen share a double bond. Carbonyl compounds In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group characterizes the following types of compounds: Other organic carbonyls are urea and the carbamates, the derivatives of acyl chlorides chloroformates and phosgene, carbonate esters, thioesters, lactones, lactams, hydroxamates, and isocyanates. Examples of inorganic carbonyl compounds are carbon dioxide and carbonyl sulfide. A sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Half Sandwich Compounds
One half ( : halves) is the irreducible fraction resulting from dividing one by two or the fraction resulting from dividing any number by its double. Multiplication by one half is equivalent to division by two, or "halving"; conversely, division by one half is equivalent to multiplication by two, or "doubling". One half often appears in mathematical equations, recipes, measurements, etc. Half can also be said to be one part of something divided into two equal parts. For instance, the area ''S'' of a triangle is computed. :''S'' = × perpendicular height. One half also figures in the formula for calculating figurate numbers, such as triangular numbers and pentagonal numbers: : \frac and in the formula for computing magic constants for magic squares : M_2(n) = \frac \left(n^ + 1\right) The Riemann hypothesis states that every nontrivial complex root of the Riemann zeta function has a real part equal to . One half has two different decimal expansion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycloheptatrienyl Complexes
In organic chemistry, the tropylium ion or cycloheptatrienyl cation is an aromatic species with a formula of 7H7sup>+. Its name derives from the molecule tropine from which cycloheptatriene (tropylidene) was first synthesized in 1881. Salts of the tropylium cation can be stable, even with nucleophiles of moderate strength e.g., tropylium tetrafluoroborate and tropylium bromide (''see below''). Its bromide and chloride salts can be made from cycloheptatriene and bromine or phosphorus pentachloride, respectively. It is a regular heptagonal, planar, cyclic ion. It has 6 π-electrons (4''n'' + 2, where ''n'' = 1), which fulfills Hückel's rule of aromaticity. It can coordinate as a ligand to metal atoms. The structure shown is a composite of seven resonance contributors in which each carbon atom carries part of the positive charge. History In 1891 G. Merling obtained a water-soluble bromine-containing compound from the reaction of cycloheptatriene and bromine. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |