|
Curtin–Hammett Principle
The Curtin–Hammett principle is a principle in chemical kinetics proposed by David Yarrow Curtin and Louis Plack Hammett. It states that, for a reaction that has a pair of reactive intermediates or reactants that interconvert rapidly (as is usually the case for conformational isomers), each going irreversibly to a different product, the product ratio will depend both on the difference in energy between the two conformers ''and'' the energy barriers from each of the rapidly equilibrating isomers to their respective products. Stated another way, the product distribution reflects the difference in energy between the two rate-limiting transition states. As a result, the product distribution will not necessarily reflect the equilibrium distribution of the two intermediates. The Curtin–Hammett principle has been invoked to explain selectivity in a variety of stereo- and regioselective reactions. The relationship between the (apparent) rate constants and equilibrium constant is kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Kinetics
Chemical kinetics, also known as reaction kinetics, is the branch of physical chemistry that is concerned with understanding the rates of chemical reactions. It is to be contrasted with chemical thermodynamics, which deals with the direction in which a reaction occurs but in itself tells nothing about its rate. Chemical kinetics includes investigations of how experimental conditions influence the speed of a chemical reaction and yield information about the reaction's mechanism and transition states, as well as the construction of mathematical models that also can describe the characteristics of a chemical reaction. History In 1864, Peter Waage and Cato Guldberg pioneered the development of chemical kinetics by formulating the law of mass action, which states that the speed of a chemical reaction is proportional to the quantity of the reacting substances.C.M. Guldberg and P. Waage,"Studies Concerning Affinity" ''Forhandlinger i Videnskabs-Selskabet i Christiania'' (1864), 35P. W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedron (journal)
''Tetrahedron'' is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering the field of organic chemistry. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', ''Tetrahedron'' has a 2020 impact factor of 2.457. ''Tetrahedron'' and Elsevier, its publisher, support an annual symposium. In 2010, complaints were raised over its high subscription cost. Notable papers , the Web of Science lists ten papers from ''Tetrahedron'' that have more than 1000 citations. The four articles that have been cited more than 2000 times are: * – cited 2228 times * – cited 2162 times * – cited 2124 times * – cited 2107 times See also * ''Tetrahedron Letters'' * ''Tetrahedron Computer Methodology'' * ''Polyhedron In geometry, a polyhedron (plural polyhedra or polyhedrons; ) is a three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges and sharp corners or vertices. A convex polyhedron is the convex hull of finitely many points, not all on th ...'' (journal) Refere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereoselective
In chemistry, stereoselectivity is the property of a chemical reaction in which a single reactant forms an unequal mixture of stereoisomers during a non-stereospecific creation of a new stereocenter or during a non-stereospecific transformation of a pre-existing one. The selectivity arises from differences in steric and electronic effects in the mechanistic pathways leading to the different products. Stereoselectivity can vary in degree but it can never be total since the activation energy difference between the two pathways is finite. Both products are at least possible and merely differ in amount. However, in favorable cases, the minor stereoisomer may not be detectable by the analytic methods used. An enantioselective reaction is one in which one enantiomer is formed in preference to the other, in a reaction that creates an optically active product from an achiral starting material, using either a chiral catalyst, an enzyme or a chiral reagent. The degree of selectivity is measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product Selectivity
Selectivity may refer to: Psychology and behaviour * Choice, making a selection among options * Discrimination, the ability to recognize differences * Socioemotional selectivity theory, in social psychology Engineering * Selectivity (radio), a measure of the performance of a radio receiver to respond only to the radio signal it is tuned * Selectivity (circuit breakers), the coordination of overcurrent protection devices in an electrical installation Biology * Binding selectivity, in pharmacology * Functional selectivity, in pharmacology * Natural selection, in biology Chemistry * Reactivity–selectivity principle, in general chemistry * Chemoselectivity, a term used in organic chemistry to describe reactivity of one functional group in the presence of other groups * Stereoselectivity, a term used in organic chemistry to describe the distribution of isomers in reaction products * Regioselectivity, a term used in organic chemistry to describe reaction mechanisms and predict re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allylic Strain
250 px , right , Allylic strain in an olefin. Allylic strain (also known as A1,3 strain, 1,3-allylic strain, or A-strain) in organic chemistry is a type of strain energy resulting from the interaction between a substituent on one end of an olefin (a synonym for an alkene) with an allylic substituent on the other end.Eric V. Anslyn and Dennis A. Dougherty ''Modern Physical Organic Chemistry'' University Science Books, 2006. If the substituents (R and R') are large enough in size, they can sterically interfere with each other such that one conformer is greatly favored over the other. Allylic strain was first recognized in the literature in 1965 by Johnson and Malhotra. The authors were investigating cyclohexane conformations including endocyclic and exocylic double bonds when they noticed certain conformations were disfavored due to the geometry constraints caused by the double bond. Organic chemists capitalize on the rigidity resulting from allylic strain for use in asymmetric re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
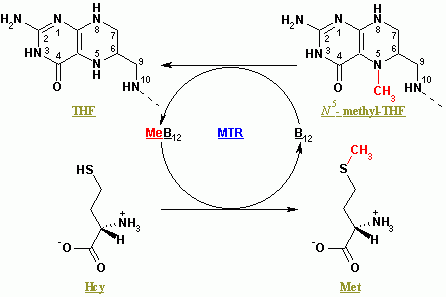
Methylation
In the chemical sciences, methylation denotes the addition of a methyl group on a substrate, or the substitution of an atom (or group) by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation, with a methyl group replacing a hydrogen atom. These terms are commonly used in chemistry, biochemistry, soil science, and the biological sciences. In biological systems, methylation is catalyzed by enzymes; such methylation can be involved in modification of heavy metals, regulation of gene expression, regulation of protein function, and RNA processing. In vitro methylation of tissue samples is also one method for reducing certain histological staining artifacts. The reverse of methylation is demethylation. In biology In biological systems, methylation is accomplished by enzymes. Methylation can modify heavy metals, regulate gene expression, RNA processing and protein function. It has been recognized as a key process underlying epigenetics. Methanogenesis Methanogenesis, the process th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylation
In the chemical sciences, methylation denotes the addition of a methyl group on a substrate, or the substitution of an atom (or group) by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation, with a methyl group replacing a hydrogen atom. These terms are commonly used in chemistry, biochemistry, soil science, and the biological sciences. In biological systems, methylation is catalyzed by enzymes; such methylation can be involved in modification of heavy metals, regulation of gene expression, regulation of protein function, and RNA processing. In vitro methylation of tissue samples is also one method for reducing certain histological staining artifacts. The reverse of methylation is demethylation. In biology In biological systems, methylation is accomplished by enzymes. Methylation can modify heavy metals, regulate gene expression, RNA processing and protein function. It has been recognized as a key process underlying epigenetics. Methanogenesis Methanogenesis, the process th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclohexyl Iodide Eliel
Cyclohexane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula . Cyclohexane is non-polar. Cyclohexane is a colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive detergent-like odor, reminiscent of cleaning products (in which it is sometimes used). Cyclohexane is mainly used for the industrial production of adipic acid and caprolactam, which are precursors to nylon. Cyclohexyl () is the alkyl substituent of cyclohexane and is abbreviated Cy. Production Modern On an industrial scale, cyclohexane is produced by hydrogenation of benzene in the presence of a Raney nickel catalyst. Producers of cyclohexane account for approximately 11.4% of global demand for benzene. The reaction is highly exothermic, with ΔH(500 K) = -216.37 kJ/mol. Dehydrogenation commenced noticeably above 300 °C, reflecting the favorable entropy for dehydrogenation. : Early Unlike benzene, cyclohexane is not found in natural resources such as coal. For this reason, early investigators synthesized their cyclohexan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernest L
Ernest is a given name derived from Germanic languages, Germanic word ''ernst'', meaning "serious". Notable people and fictional characters with the name include: People *Archduke Ernest of Austria (1553–1595), son of Maximilian II, Holy Roman Emperor *Ernest, Margrave of Austria (1027–1075) *Ernest, Duke of Bavaria (1373–1438) *Ernest, Duke of Opava (c. 1415–1464) *Ernest, Margrave of Baden-Durlach (1482–1553) *Ernest, Landgrave of Hesse-Rheinfels (1623–1693) *Ernest Augustus, Elector of Brunswick-Lüneburg (1629–1698) *Ernest, Count of Stolberg-Ilsenburg (1650–1710) *Ernest Augustus, King of Hanover (1771–1851), son of King George III of Great Britain *Ernest II, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (1818–1893), sovereign duke of the Duchy of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha *Ernest Augustus, Crown Prince of Hanover (1845–1923) *Ernest, Landgrave of Hesse-Philippsthal (1846–1925) *Ernest Augustus, Prince of Hanover (1914–1987) *Prince Ernst August of Hanover (born 1954 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropane Alkylation
Tropane is a nitrogenous bicyclic organic compound. It is mainly known for the other alkaloids derived from it, which include atropine and cocaine, among others. Tropane alkaloids occur in plants of the families Erythroxylaceae (including coca) and Solanaceae (including mandrake, henbane, deadly nightshade, datura, potato, tomato). Structurally, tropane is cycloheptane with a nitrogen bridge between carbons 1 and 5 and an additional methyl group attached to the nitrogen. While carbons 1 and 5 are asymmetric carbons, tropane itself is optically inactive due to mirror symmetry. 8-Azabicyclo .2.1ctane (tropane without the ''N''- methyl group) is known as nortropane or nor-tropane. See also * Phenyltropane * Tropane alkaloid * Tropine Tropine is a derivative of tropane containing a hydroxyl group at the third carbon. It is also called 3-tropanol. Tropine is a central building block of many chemicals active in the nervous system, including tropane alkaloids. Some of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Organic Chemistry
''The Journal of Organic Chemistry'', colloquially known as ''JOC'', is a peer-reviewed scientific journal for original contributions of fundamental research in all branches of theory and practice in organic and bioorganic chemistry. It is published by the publishing arm of the American Chemical Society, with 24 issues per year. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal had a 2017 impact factor of 4.805 and it is the journal that received the most cites (100,091 in 2017) in the field of organic chemistry. According to Web of Knowledge (and as December 2012), eleven papers from the journal have received more than 1,000 citations, with the most cited paper having received 7,967 citations. The current editor-in-chief is Scott J. Miller from Yale University. Indexing ''J. Org. Chem.'' is currently indexed in: See also *Organic Letters *Organometallics ''Organometallics'' is a biweekly journal published by the American Chemical Society. Its area of focus is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropanes
Tropane alkaloids are a class of bicyclic .2.1alkaloids and secondary metabolites that contain a tropane ring in their chemical structure. Tropane alkaloids occur naturally in many members of the plant family Solanaceae. Certain tropane alkaloids such as cocaine and scopolamine are notorious for their psychoactive effects, related usage and cultural associations. Particular tropane alkaloids such as these have pharmacological properties and can act as anticholinergics or stimulants. Classification Anticholinergics Anticholinergic drugs and deliriants: * Atropine, racemic hyoscyamine, from the deadly nightshade (''Atropa belladonna'') * Hyoscyamine, the ''levo''-isomer of atropine, from henbane (''Hyoscyamus niger''), mandrake (''Mandragora officinarum'') and the sorcerers' tree (''Latua pubiflora''). * Scopolamine, from henbane and ''Datura'' species (Jimson weed) All three acetylcholine-inhibiting chemicals can also be found in the leaves, stems, and flowers in varying, un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |