|
Culture Of Jharkhand
This article is about the culture of natives of the Indian state of Jharkhand. The state of Jharkhand is located in the eastern part of the country and is known for its vivid culture,distinct paintings, traditions and festivals. Languages Hindi is official language of Jharkhand. There are many regional and tribal languages in Jharkhand. The regional languages that belong to the Indo-Aryan branch; in Jharkhand, they are Khortha, Nagpuri, and Kudmali spoken by the Sadan, the Indo-Aryan ethnic groups of Chotanagpur. Other Indo-Aryan languages include Bhojpuri, Magahi, Maithili, Bengali, and Odia. The languages that belong to the Austroasiatic branch are Mundari, Santali, Bhumij and Ho. The languages that belong to the Dravidian language family are Kurukh and Malto. Cuisine The staple foods in Jharkhand are rice, dal, vegetables, and tubers. Some dishes include Chilka Roti, Malpua, Dhooska, Arsa roti, and Pitha. Rugra (a type of mushroom) and bamboo shoots are als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
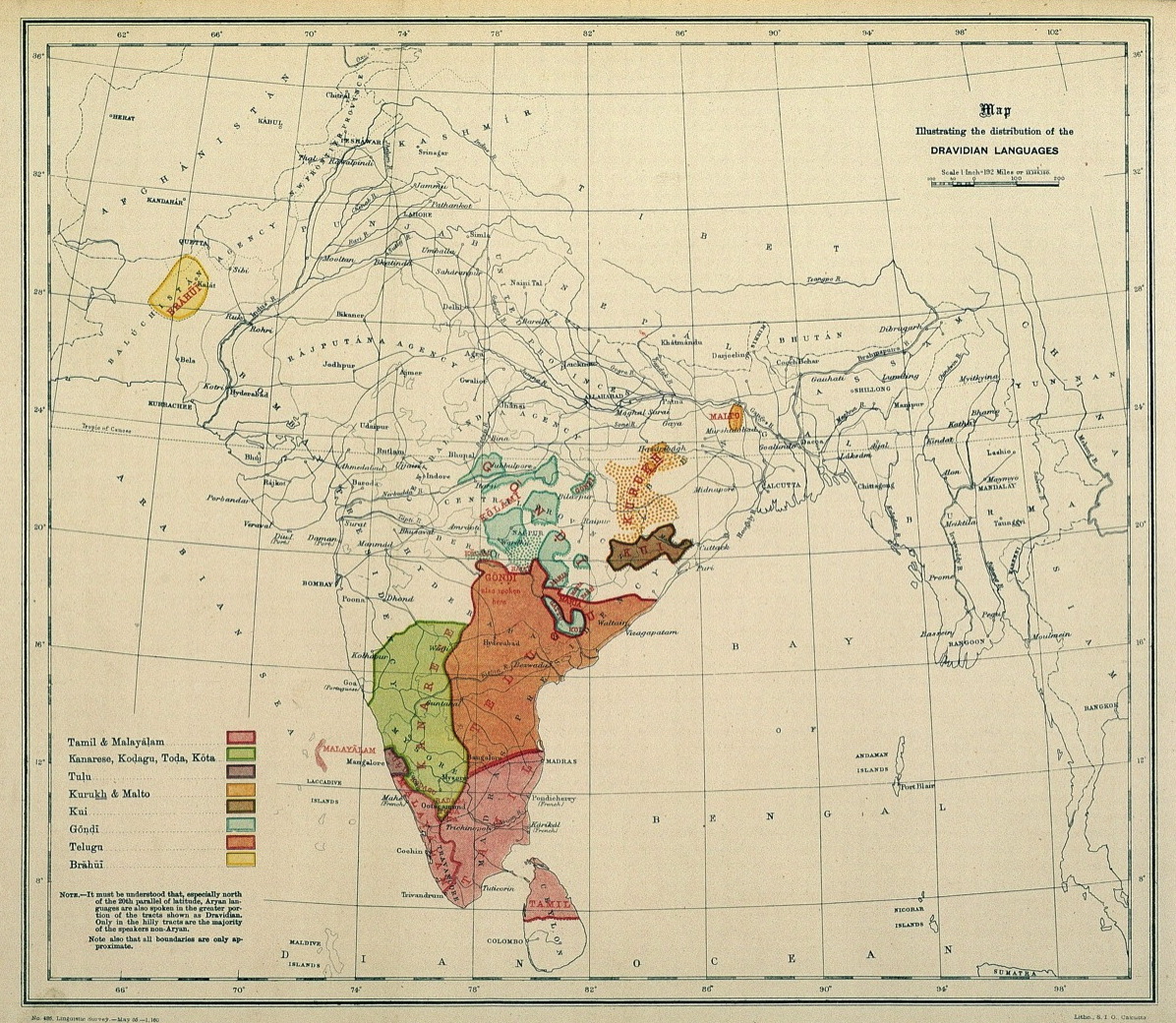
Dravidian Language
The Dravidian languages (or sometimes Dravidic) are a family of languages spoken by 250 million people, mainly in southern India, north-east Sri Lanka, and south-west Pakistan. Since the colonial era, there have been small but significant immigrant communities in Mauritius, Myanmar, Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia, Philippines, United Kingdom, Australia, France, Canada, Germany, South Africa, and the United States. The Dravidian languages are first attested in the 2nd century BCE, as Tamil-Brahmi script, inscribed on the cave walls in the Madurai and Tirunelveli districts of Tamil Nadu. The Dravidian languages with the most speakers are (in descending order of number of speakers) Telugu, Tamil, Kannada and Malayalam, all of which have long literary traditions. Smaller literary languages are Tulu and Kodava. There are also a number of Dravidian-speaking scheduled tribes, such as the Kurukh in Eastern India and Gondi in Central India. Outside of India, Brahui is mostly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madhuca Longifolia
''Madhuca longifolia'' is an Indian tropical tree found largely in the central, southern, north Indian plains and forests, Nepal, Myanmar and Sri Lanka. It is commonly known as madhūka, , mahuwa, Butter Tree, mahua, mahwa, , Iluppai or vippa chettu. It is a fast-growing tree that grows to approximately 20 meters in height, possesses evergreen or semi-evergreen foliage, and belongs to the family Sapotaceae. It is adaptable to arid environments, being a prominent tree in tropical mixed deciduous forests in India in the states of Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Kerala, Gujarat, West Bengal and Tamil Nadu. Uses It is cultivated in warm and humid regions for its oleaginous seeds (producing between 20 and 200 kg of seeds annually per tree, depending on maturity), flowers and wood. The fat (solid at ambient temperature) is used for the care of the skin, to manufacture soap or detergents, and as a vegetable butter. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desi Daru
Desi Daaru ( hi, देसी दारू), also known as Country Liquor or Indian-made Indian liquor (IMIL) is a category of liquor made in the countryside of the Indian subcontinent. They are traditionally prepared by a procedure that has been passed down for centuries. Due to cheap prices, country liquor is the most popular alcoholic beverage among the impoverished people. It is fermented and distilled from molasses, a by product of sugarcane. Desi liquor is a broad term and it can include both legally and illegally made local alcohol. The term ''desi daru'' usually refers to legal alcohol while other types of country liquor (arrack and palm toddy) may be categorised as moonshine alcohol. Etymology The term ''desi'', from Hindi language term ''desh'' (country or region), which is generally an endonym for the ''compatriot'' or ''local'' is often applied to food or drink that is considered traditional or native. Dārū (Hindदारूand Urdدارو is a Persian-derived te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Handia (drink)
Handia (Also handi or hadiya) is a rice beer originating from the Indian subcontinent, popular in the Indian states of Jharkhand, Bihar, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and West Bengal. Etmology ''Handia'' comes from hindi word ''Handi'' means ''earthen pot'' where it was traditionally prepared. History Evidence of Fermentation and Alcoholic beverages found in Indus valley civilization during Chalcolithic Period from 3000 BC to 2000 BC in India. In Ancient India, the Vedas mention a beer-like drink called ''sura''. It was the favourite of the god Indra. Kautilya has mentioned two intoxicating beverages made from rice called ''Medaka'' and ''Prasanna''. Megasthenes, the Greek Ambassador to Maurya Emperor Chandragupta Maurya mentioned about rice beer in his book Indica where he mention Indian make wine from rice instead of barley. He mentioned Indian never drink rice wine except during sacrifice. Preparation The making involves the use of ''ranu tablets'', which is esse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saag
Saag (), also spelled sag or saga, is an Indian leaf vegetable dish eaten with bread such as roti or naan, or in some regions with rice. Saag can be made from spinach, mustard greens, collard greens, basella, finely chopped broccoli or other greens, along with added spices and sometimes other ingredients such as chhena. Saag is common in the state of Odisha, where it is eaten with pakhala. In the Shree Jagannath Temple of Puri, saag is one of the dishes offered to Jagannath as part of Mahaprasad. Saag is also common in West Bengal and other regions of North India, where the most common preparation is sarson ka saag (mustard plant leaves), which may be eaten with makki ki roti, a yellow roti made with maize flour. ''Saag gosht'' or ''hariyali maans'' (spinach and mutton) is a common dish in the North Indian state of Haryana. Etymology The word ''saag'' is derived from the Sanskrit word ''shaak'' (''śāka'') meaning leafy green vegetables. Variations Odisha In Odia cuisin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bauhinia Variegata
''Bauhinia variegata'' is a species of flowering plant in the legume family, Fabaceae. It is native to an area from China through Southeast Asia to the Indian subcontinent. Common names include orchid tree (though not belonging to the family Orchidaceae) and mountain ebony. Description It is a small to medium-sized tree growing to tall, deciduous in the dry season. The leaves are obcordate shaped, long and broad, rounded, and bilobed at the base and apex. The flowers are conspicuous, bright pink or white, diameter, with five petals. Pollens are elongated, approximately 75 microns in length. The fruit is a seedpod long, containing several seeds. The seedpod dries completely on the tree, and when mature begins to twist into a helix or corkscrew shape, (see below), ultimately exploding open—with a very audible "clack"—to deliver its seeds into the environs. The anatomy of the stem was studied by taking transverse section. Periderm and cortex were seen distinctly. Seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moringa Oleifera
''Moringa oleifera'' is a fast-growing, drought-resistant tree of the family Moringaceae, native to the Indian subcontinent. Common names include moringa, drumstick tree (from the long, slender, triangular seed-pods), horseradish tree (from the taste of the roots, which resembles horseradish), and ben oil tree or benzolive tree. It is widely cultivated for its young seed pods and leaves, used as vegetables and for traditional herbal medicine. It is also used for water purification. Although listed as an invasive species in several countries, ''M. oleifera'' has "not been observed invading intact habitats or displacing native flora", so "should be regarded at present as a widely cultivated species with low invasive potential." Description ''M. oleifera'' is a fast-growing, deciduous tree that can reach a height of and trunk diameter of . The bark has a whitish-gray color and is surrounded by thick cork. Young shoots have purplish or greenish-white, hairy bark. The tree h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitha
Pithas are a variety of food similar to pancakes, dumplings or fritters, originating from the Indian subcontinent, common in Bangladesh and India. Pitha can be sweet or savoury, and usually made from a dough or batter, which is then steamed, fried or griddled. Very few varieties are oven-baked or boiled, and most are unleavened and cooked on a stovetop (or equivalent). Some versions may have a filling, garnish, or sauce. Few may be set or shaped after cooking. They are typically eaten as a snack with tea, chai, or as treats during special occasions (similar to mithai (confectionery), mithai). Pitha is especially popular in Bangladesh and the eastern Indian states of Bihar, Uttar Pradesh (eastern parts), West Bengal, Odisha, Jharkhand, the South Indian state of Kerala, and the Northeast Indian states, especially Assam. Pithas are typically made of rice flour, although there are some types of pitha made of wheat flour. Less common types of pitha are made of Arecaceae, palm or Amorp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhooska
''Dhooska'' or ''Dhuska'' is a popular deep-fried snack eaten all over Jharkhand, India. The dish is one of the delicacy of Jharkhandi cuisine. The main ingredients in this savoury fried bread dish are powdered rice, powdered chana dal and sometimes boiled potatoes. The bread is then deep fried. It is often served with any sauce or chutney. ''Dhooska'' is mostly made in market-area stalls where people enjoy it as a snack and is rarely found in larger restaurants. See also * Bhatoora * Fried dough * Frybread * Puri Puri () is a coastal city and a Nagar Palika, municipality in the state of Odisha in eastern India. It is the district headquarters of Puri district and is situated on the Bay of Bengal, south of the state capital of Bhubaneswar. It is als ... References {{reflist Indian snack foods Fried foods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malpua
Malpua, or sometimes shortened to pua, is an Indian sweet served as a dessert or a snack originating from the Indian subcontinent, popular in India, Nepal and Bangladesh. History Barley was the most prolific grain eaten by the ''arya'' of the Vedic period. One preparation was a sweet cake called malpua, where barley flour was either fried in ghee or boiled in water, and then dipped in honey. Malpua preserves both the name and the essentials of this preparation. Malpua and its varieties Malpua is popular in Bangladesh, Odisha, West Bengal, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh and Maharashtra and Nepal where it is served during festivals along with other sweets. The batter for malpua in some areas is prepared by crushing ripe bananas or (in Bangladesh) coconut, adding flour, and water or milk. The mixture is sometimes delicately seasoned with cardamoms. It is deep fried in oil, and served hot. In Odisha the Malpua fritters are dipped in syrup after they are fried. The Bihari version of thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chilka Roti
Chhilka Roti is a traditional bread of Jharkhand, India. It is prepared using rice flour and chana dal. It is served with chutney, vegetables and meat. It is also known as Chilka Roti. Preparation The rice and chana dal soaked in water for a night. It is grinded in morning after filtering the water to make batter and salt added for taste. Then a little oil is greased in the heated tawa and half bowl of batter is dispersed in it. After the mixture turn light brown, it turned and other side roasted. If bother side turned light brown with proper roasting, the bread is ready. It is generally served with chutney, vegetables and meat. Related * Neer Dosa See also *Indian bread *Jharkhandi cuisine Jharkhandi cuisine encompasses the cuisine of the Indian state of Jharkhand. Staple foods of Jharkhand are rice, dal and vegetables. Common meals often consist of vegetables that are cooked in various ways, such as curried, fried, roasted and ... References {{reflist Indian snack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |