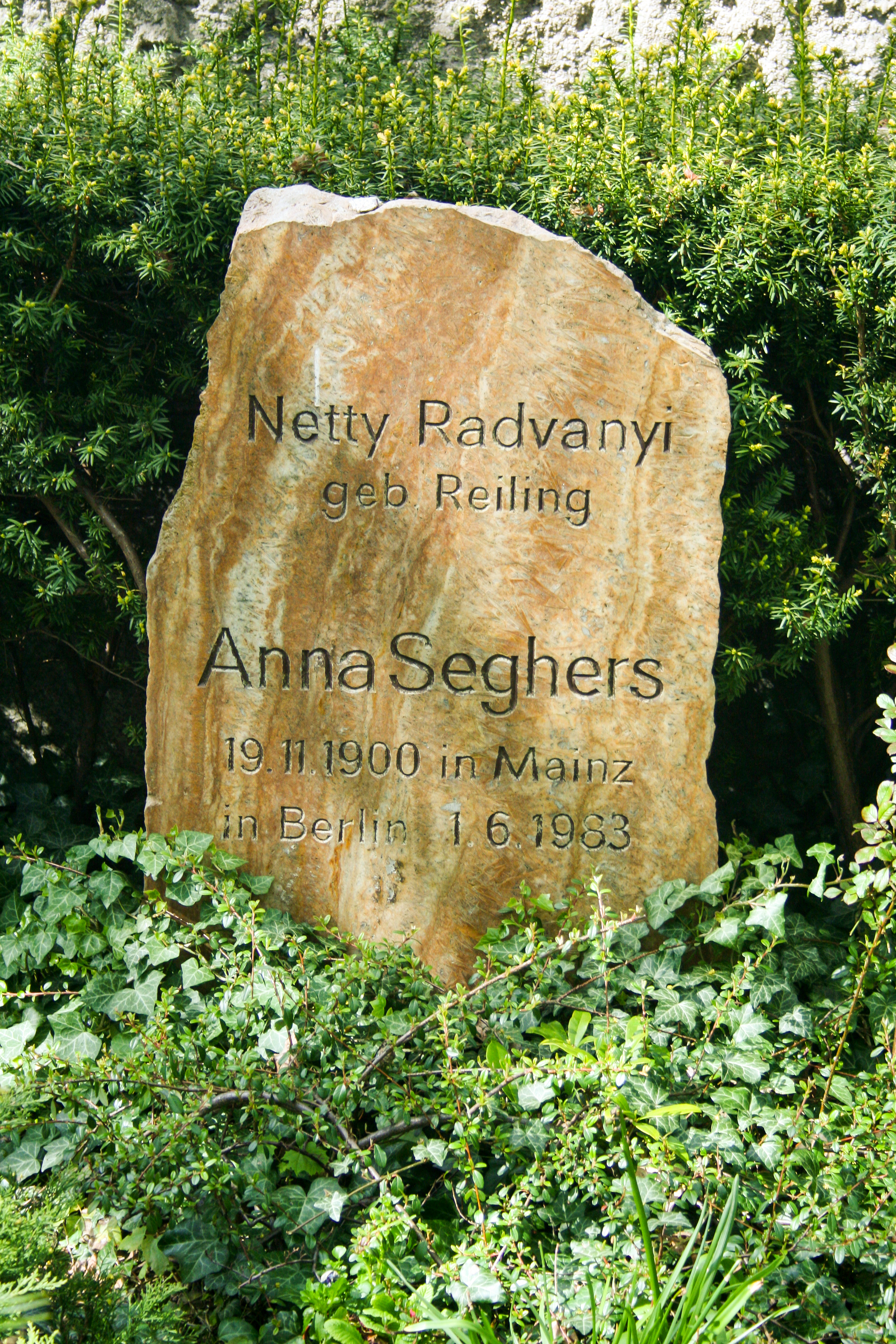|
Cultural Association Of The GDR
The Cultural Association of the GDR (german: Kulturbund der DDR, KB) was a federation of local clubs in the German Democratic Republic (GDR). It formed part of the Socialist Unity Party-led National Front, and sent representatives to the Volkskammer. The association had numerous writers as its member, including Willi Bredel, Fritz Erpenbeck, Bernhard Kellermann, Victor Klemperer, Anna Seghers, Bodo Uhse, Arnold Zweig. Its first chairman was Johannes Robert Becher. Wilfried Maaß Wilfried Maaß (22 September 1931–23 December 2005) was a German politician. He was the secretary of Science, Education, and Culture in the Frankfurt/Oder district leadership of the Socialist Unity Party of Germany 1962–1966. In 1966, he beca ... was the Secretary of ''Kulturbund'' 1984–1990. As of 1987, membership stood at 273,000.Dirk Jurich, ''Staatssozialismus und gesellschaftliche Differenzierung: eine empirische Studie'', p.32. LIT Verlag Münster, 2006, Chairmen of the Cultural Associat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Berlin
East Berlin was the ''de facto'' capital city of East Germany from 1949 to 1990. Formally, it was the Allied occupation zones in Germany, Soviet sector of Berlin, established in 1945. The American, British, and French sectors were known as West Berlin. From 13 August 1961 until 9 November 1989, East Berlin was separated from West Berlin by the Berlin Wall. The Western Allied powers did not recognize East Berlin as the GDR's capital, nor the GDR's authority to govern East Berlin. On 3 October 1990, the day Germany was officially German reunification, reunified, East and West Berlin formally reunited as the city of Berlin. Overview With the London Protocol (1944), London Protocol of 1944 signed on 12 September 1944, the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union decided to divide Germany into three occupation zones and to establish a special area of Berlin, which was occupied by the three Allied Forces together. In May 1945, the Soviet Union installed a city gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anna Seghers
Anna Seghers (; born ''Anna Reiling,'' 19 November 1900 – 1 June 1983), is the pseudonym of a German writer notable for exploring and depicting the moral experience of the Second World War. Born into a Jewish family and married to a Hungarian Communist, Seghers escaped Nazi-controlled territory through wartime France. She was granted a visa and gained ship's passage to Mexico, where she lived in Mexico City (1941–47). She returned to Europe after the war, living in West Berlin (1947–50), which was occupied by Allied forces. She eventually settled in the German Democratic Republic, where she worked on cultural and peace issues. She received numerous awards and in 1967 was nominated for the Nobel Prize by the GDR. She died and was buried in Berlin in 1983. She is believed to have based her pseudonym, Anna Seghers, on the surname of the Dutch painter and printmaker Hercules Pieterszoon Seghers or Segers (c. 1589 – c. 1638). Life Seghers was born Anna Reiling in Mainz in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East German Culture
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth. Etymology As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact that east is the direction where the Sun rises: ''east'' comes from Middle English ''est'', from Old English ''ēast'', which itself comes from the Proto-Germanic *''aus-to-'' or *''austra-'' "east, toward the sunrise", from Proto-Indo-European *aus- "to shine," or "dawn", cognate with Old High German ''*ōstar'' "to the east", Latin ''aurora'' 'dawn', and Greek ''ēōs'' 'dawn, east'. Examples of the same formation in other languages include Latin oriens 'east, sunrise' from orior 'to rise, to originate', Greek ανατολή anatolé 'east' from ἀνατέλλω 'to rise' and Hebrew מִזְרָח mizraḥ 'east' from זָרַח zaraḥ 'to rise, to shine'. ''Ēostre'', a Germanic goddess of dawn, might have been a personificatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Pischner
Hans Pischner (20 February 1914 – 15 October 2016) was a German harpsichordist, musicologist, opera director, and politician active in the German Democratic Republic. He encouraged the creation of musical and artistic cultural institutions in East Germany, and used his position in the SED to prevent any further brain drain of artists and musicians after the Berlin Wall was constructed by encouraging and supporting the arts. He served as Chairman of the Kulturbund from 1977 until German reunification in 1990. Awards and honours * Patriotic Order of Merit in Gold (1973) * National Prize of the German Democratic Republic (1976) * Star of People's Friendship in Gold (1979) * Order of Karl Marx (1989) * Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany The Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany (german: Verdienstorden der Bundesrepublik Deutschland, or , BVO) is the only federal decoration of Germany. It is awarded for special achievements in political, economic, cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Burghardt
Max or MAX may refer to: Animals * Max (dog) (1983–2013), at one time purported to be the world's oldest living dog * Max (English Springer Spaniel), the first pet dog to win the PDSA Order of Merit (animal equivalent of OBE) * Max (gorilla) (1971–2004), a western lowland gorilla at the Johannesburg Zoo who was shot by a criminal in 1997 Brands and enterprises * Australian Max Beer * Max Hamburgers, a fast-food corporation * MAX Index, a Hungarian domestic government bond index * Max Fashion, an Indian clothing brand Computing * MAX (operating system), a Spanish-language Linux version * Max (software), a music programming language * Commodore MAX Machine * Multimedia Acceleration eXtensions, extensions for HP PA-RISC Films * ''Max'' (1994 film), a Canadian film by Charles Wilkinson * ''Max'' (2002 film), a film about Adolf Hitler * ''Max'' (2015 film), an American war drama film Games * '' Dancing Stage Max'', a 2005 game in the ''Dance Dance Revolution'' series * ''DDR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilfried Maaß
Wilfried Maaß (22 September 1931–23 December 2005) was a German politician. He was the secretary of Science, Education, and Culture in the Frankfurt/Oder district leadership of the Socialist Unity Party of Germany 1962–1966. In 1966, he became deputy minister of culture of the German Democratic Republic German(s) may refer to: * Germany (of or related to) ** Germania (historical use) * Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language ** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law **G .... Between 1968 and 1972, he was a member of the presidium council of Kulturbund. In 1984 he left his ministerial position to become its secretary. References 1931 births 2005 deaths Socialist Unity Party of Germany politicians German male writers {{Germany-SED-politician-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Becher
Johannes Robert Becher (, 22 May 1891 – 11 October 1958) was a German politician, novelist, and poet. He was affiliated with the Communist Party of Germany (KPD) before World War II. At one time, he was part of the literary avant-garde, writing in an expressionist style. With the rise of the Nazi Party in Germany, modernist artistic movements were suppressed. Becher escaped from a military raid in 1933 and settled in Paris for a couple of years. He migrated to the Soviet Union in 1935 with the central committee of the KPD. After the German invasion of the Soviet Union in June 1941, Becher and other German communists were evacuated to internal exile in Tashkent. He returned to favor in 1942 and was recalled to Moscow. After the end of World War II, Becher left the Soviet Union and returned to Germany, settling in the Soviet-occupied zone that later became East Berlin. As a member of the KPD, he was appointed to various cultural and political positions and became part of the lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnold Zweig
Arnold Zweig (10 November 1887 – 26 November 1968) was a German writer, pacifist and socialist. He is best known for his six-part cycle on World War I. Life and work Zweig was born in Glogau, Prussian Silesia (now Głogów, Poland), the son of a Jewish saddler. (He is not related to Stefan Zweig.) After attending a gymnasium in Kattowitz (Katowice), he made extensive studies in history, philosophy and literature at several universities – Breslau (Wrocław), Munich, Berlin, Göttingen, Rostock and Tübingen. He was especially influenced by Friedrich Nietzsche's philosophy. His first literary works, ''Novellen um Claudia'' (1913) and ''Ritualmord in Ungarn'', gained him wider recognition. Zweig volunteered for the German army in World War I and saw action as a private in France, Hungary and Serbia. He was stationed in the Western Front at the time when Judenzählung (the Jewish census) was administered in the German army. Shaken by the experience, he wrote in his letter date ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bodo Uhse
Bodo Uhse (12 March 1904 in Rastatt, Grand Duchy of Baden – 2 July 1963 in Berlin) was a German writer, journalist and political activist. He was recognised as one of the most prominent authors in East Germany. Early years Uhse came from a Prussian Junker family with a long tradition of military service.McLellan, ''Antifascism and Memory in East Germany'', p. 32 In his early years Uhse was associated with the agrarian movement and was considered to be on the far-right of this group. This was evidenced by his involvement with the extremist ''Landvolkbewegung'' of Schleswig-Holstein. He took part in the right-wing Kapp Putsch in 1920. In 1927 he became a member of the Nazi Party as a protege of Gregor Strasser. He remained a member until 1930, when he joined the Communist Party of Germany under the influence of Bruno von Salomon (the elder brother of writer Ernst von Salomon). During his Nazi membership he became editor to the Nazi party newspaper in Ingolstadt. Communism After th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victor Klemperer
Victor Klemperer (9 October 188111 February 1960) was a German scholar who also became known as a diarist. His journals, published in Germany in 1995, detailed his life under the German Empire, the Weimar Republic, the Third Reich, and the German Democratic Republic. Those covering the period of the Third Reich have since become standard sources and have been extensively quoted by Saul Friedländer, Michael Burleigh, Richard J. Evans, and Max Hastings. Early life Klemperer was born in Landsberg an der Warthe (now Gorzów Wielkopolski, Poland) to a Jewish family. His parents were Dr. Wilhelm Klemperer, a rabbi, and Henriette née Frankel. Victor had three brothers and four sisters: * Georg, 1865–1946, physician, director of the hospital Berlin-Moabit (who treated Vladimir Lenin) * Felix, 1866–1932, physician, director of the hospital Berlin-Reinickendorf * Margarete (Grete), 1867–1942, married Riesenfeld * Hedwig, 1870–1893, married Machol * Berthold, 1871–1931, lawyer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state was a part of the Eastern Bloc in the Cold War. Commonly described as a communist state, it described itself as a socialist "workers' and peasants' state".Patrick Major, Jonathan Osmond, ''The Workers' and Peasants' State: Communism and Society in East Germany Under Ulbricht 1945–71'', Manchester University Press, 2002, Its territory was administered and occupied by Soviet forces following the end of World War II—the Soviet occupation zone of the Potsdam Agreement, bounded on the east by the Oder–Neisse line. The Soviet zone surrounded West Berlin but did not include it and West Berlin remained outside the jurisdiction of the GDR. Most scholars and academics describe the GDR as a totalitarian dictatorship. The GDR was establish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernhard Kellermann
Bernhard Kellermann (4 March 1879, Fürth, Kingdom of Bavaria – 17 October 1951) was a German author and poet. Life Bernhard Kellermann enrolled in 1899 at Technical University Munich initially in general studies, but later focused on German literature and painting. Beginning in 1904 he built a reputation as a novelist with early works such as ''Yester and Li'', and reached extraordinary success through 1939 with 183 printings. The novel ''Ingeborg'' (1906) achieved an impressive 131 printings (until 1939). In the years before World War I his novels were published following journeys in the United States and Japan. His novel ''Das Meer'' (''The Sea'') was made into film by Peter Paul Felner and Sofar-Film-Produktion GmbH, featuring prominent film stars. His main work was '' Der Tunnel'' in 1913. It was highly successful for both him and his publisher, S. Fischer Verlag: circulation exceeded one million, and the work was translated into 25 languages. Kellermann's works ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_Pechstein%2C_(Johannes^)_Stroux%2C_Kraus%2C_Benedik%2C_Lederer%2C.jpg)