|
Crystal Palace And South London Junction Railway
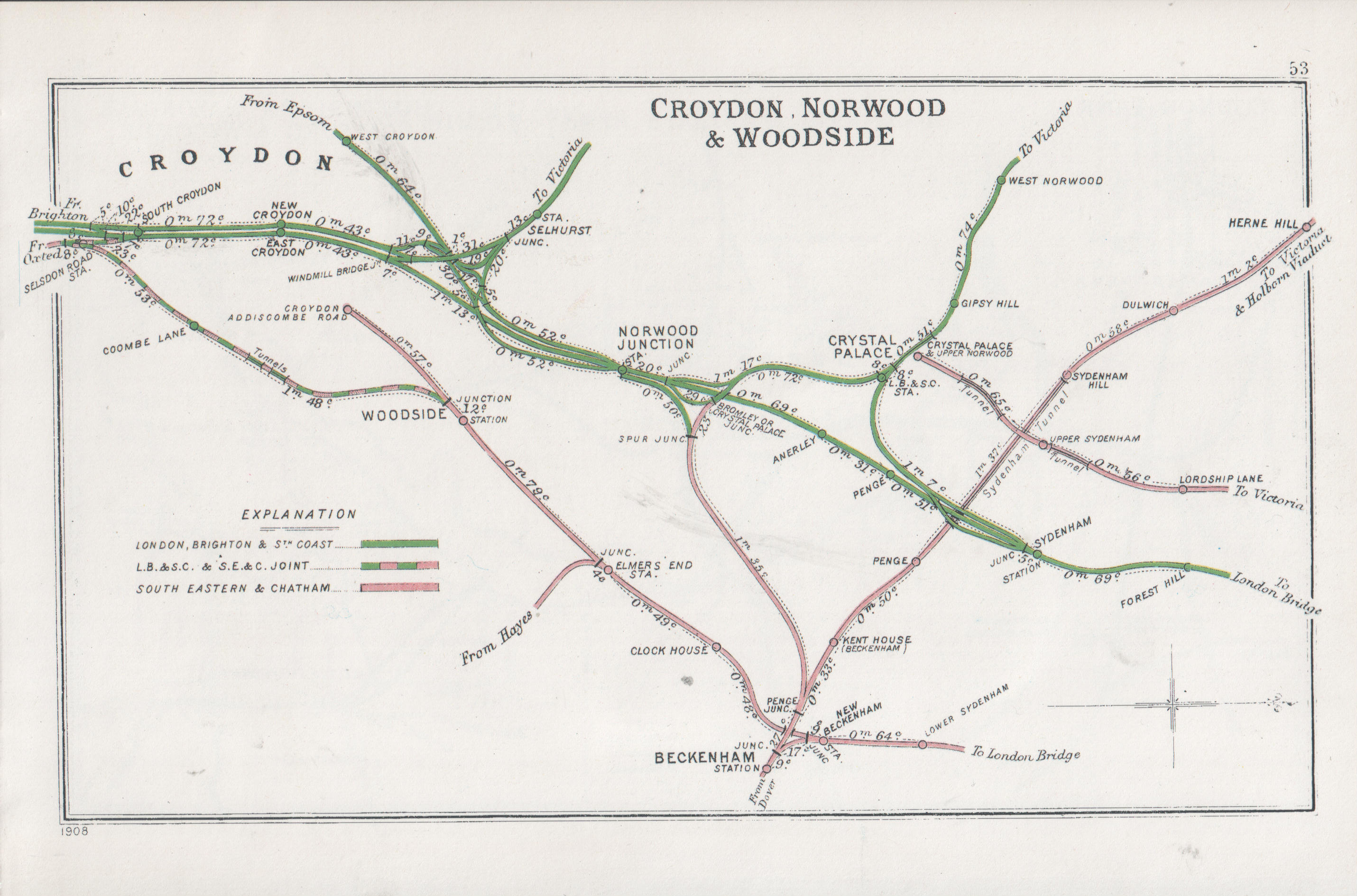
The Crystal Palace and South London Junction Railway (CPSLJR) was built by the London, Chatham and Dover Railway (LCDR) from to Crystal Palace High Level to serve the Crystal Palace after the building was moved to the area that became known as Crystal Palace (otherwise "Upper Norwood") from its original site in Hyde Park. History Origins The Great Exhibition closed in 1851, leaving the Crystal Palace building in Hyde Park redundant. Rather than simply being demolished, between 1852 and 1854 it was rebuilt in a pleasure park at Sydenham Hill as an "events" venue, creating a potential demand for lucrative leisure travel. The London Brighton and South Coast Railway (LBSCR) was the first to exploit this by running a spur up from Sydenham to a new station next to the park, opening in 1854. In 1856 the West End of London and Crystal Palace Railway (WELCPR) arrived with a line through its own platforms next to the LBSCR station, and on to . In 1858 this was extended east via to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camille Pissarro
Jacob Abraham Camille Pissarro ( , ; 10 July 1830 – 13 November 1903) was a Danish-French Impressionist and Neo-Impressionist painter born on the island of Saint Thomas, U.S. Virgin Islands, St Thomas (now in the US Virgin Islands, but then in the Danish West Indies). His importance resides in his contributions to both Impressionism and Post-Impressionism. Pissarro studied from great forerunners, including Gustave Courbet and Jean-Baptiste-Camille Corot. He later studied and worked alongside Georges Seurat and Paul Signac when he took on the Neo-Impressionist style at the age of 54. In 1873 he helped establish a collective society of fifteen aspiring artists, becoming the "pivotal" figure in holding the group together and encouraging the other members. Art historian John Rewald called Pissarro the "dean of the Impressionist painters", not only because he was the oldest of the group, but also "by virtue of his wisdom and his balanced, kind, and warmhearted personality". Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
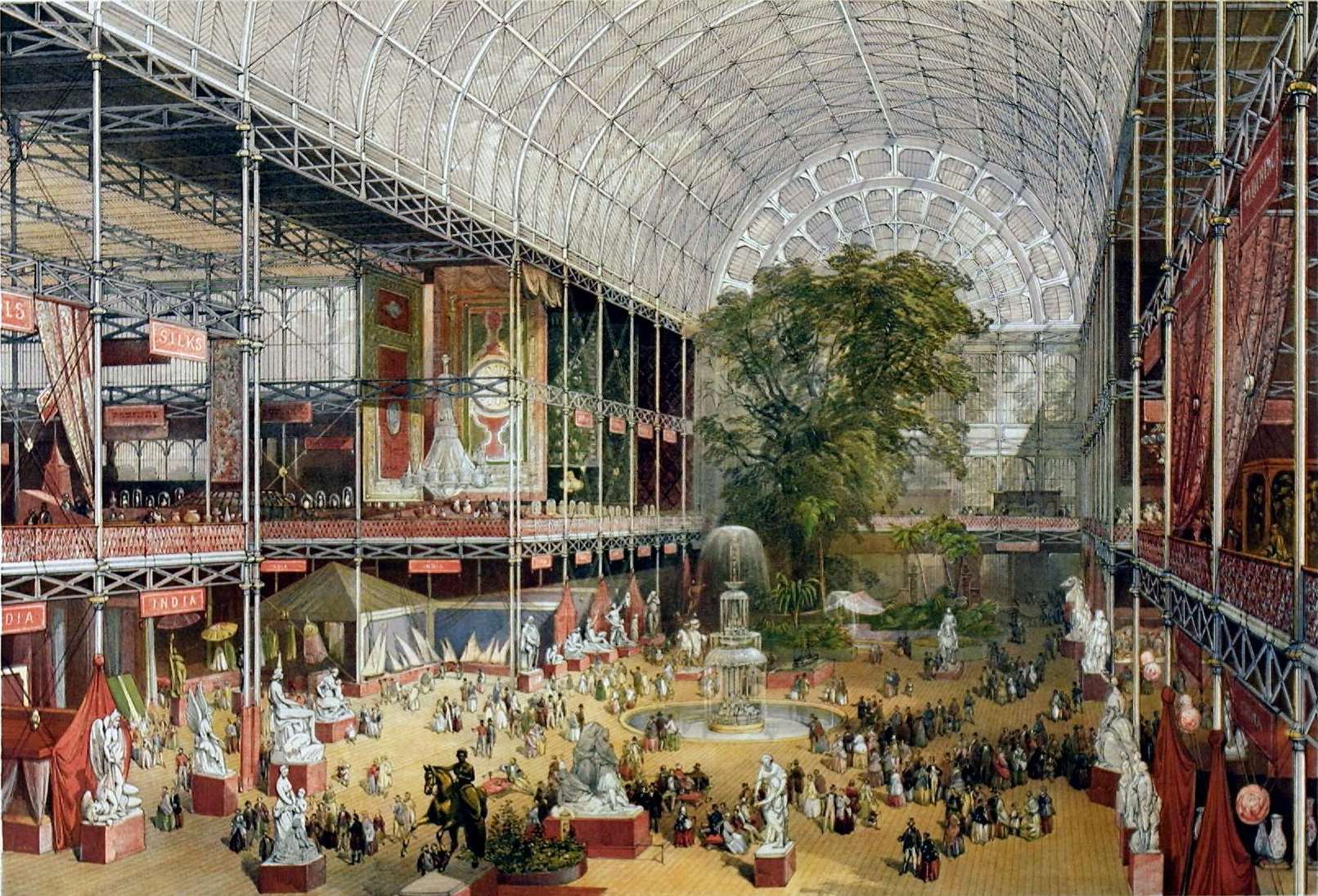
The Crystal Palace
The Crystal Palace was a cast iron and plate glass structure, originally built in Hyde Park, London, Hyde Park, London, to house the Great Exhibition of 1851. The exhibition took place from 1 May to 15 October 1851, and more than 14,000 exhibitors from around the world gathered in its exhibition space to display examples of technology developed in the Industrial Revolution. Designed by Joseph Paxton, the Great Exhibition building was long, with an interior height of , and was three times the size of St Paul's Cathedral. The introduction of the sheet glass method into Britain by Chance Brothers in 1832 made possible the production of large sheets of cheap but strong glass, and its use in the Crystal Palace created a structure with the greatest area of glass ever seen in a building. It astonished visitors with its clear walls and ceilings that did not require interior lights. It has been suggested that the name of the building resulted from a piece penned by the playwright Doug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Electrification In Great Britain
Railway electrification in Great Britain began in the late 19th century. A range of voltages has been used, employing both overhead lines and conductor rails. The two most common systems are using overhead lines, and the third rail system used in Southeast England and on Merseyrail. As of March 2020, (38%) of the British Rail transport in Great Britain, rail network was Railway electrification system, electrified. According to Network Rail, as at 2003, 64% of the electrified network used the 25kVAC overhead system, and 36% used the 660/750VDC third-rail system.Network Rail, 2003 Technical Plan, Chapter 11 "Network Capability", page 7 "Electrification". "Approximately 40% of the rail network is currently equipped with electrification." From page 1, total network is 30764 km, 7587 km of 25 kV AC, 4285 km of 650/750 V DC and 28 km of 1500 V DC. Excludes CTRL, LUL, Old Danby test track, bulk of Tyne and Wear Metro, etc. NB it does not state what method of counting length of netw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holborn Viaduct Railway Station
Holborn Viaduct was a railway station in the City of London, providing local and commuter services. It was located to the southeast of Holborn Viaduct, and east of Farringdon Street. The station was opened in 1874 by the London, Chatham and Dover Railway to alleviate increased usage of the nearby Ludgate Hill station. It was originally a through station, with services continuing through the Snow Hill Tunnel to Farringdon and King's Cross. Passenger services through the tunnel ceased in 1916, and consequently Holborn Viaduct became a terminal station. The short distance between itself and Ludgate Hill saw the latter being closed in 1929. Holborn Viaduct station became less used through the 20th century, serving a few local commuting services around southeast London and Kent. The station became redundant with the creation of the Thameslink service in the late 1980s, and was closed in 1990 under British Rail, being replaced at the same location by City Thameslink railway statio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South London Line
The South London line is a railway line in inner south London, England. The initial passenger service on the route was established by the London, Brighton & South Coast Railway on 1 May 1867 when the central London terminal stations of Victoria and London Bridge were connecting to the inner south London suburbs of Clapham, Brixton, Camberwell and Peckham. Since 2012 passenger services have been part of London Overground and run between and continuing toward via the East London line. The line is long and consists of seven stations, one of which marks the crossover into the East London line network. Most of the line was built on a high level viaduct above other transport infrastructure. Interchanges with the London Underground are at and the closest on its London Overground extension is . The line is in Travelcard Zone 2. History The London, Chatham and Dover Railway (LCDR) was authorised to build the former route of the line by the ''South London Railway Act'' 1862. De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Victoria Railway Station
Victoria station, also known as London Victoria, is a central London railway terminus and connected London Underground station in Victoria, in the City of Westminster, managed by Network Rail. Named after the nearby Victoria Street (not the Queen), the main line station is a terminus of the Brighton Main Line to and and the Chatham Main Line to and Dover via . From the main lines, trains can connect to the Catford Loop Line, the Dartford Loop Line, and the Oxted line to and . Southern operates most commuter and regional services to south London, Sussex and parts of east Surrey, while Southeastern operates trains to south-east London and Kent, alongside limited services operated by Thameslink. Gatwick Express trains run direct to Gatwick. The Underground station is on the Circle and District lines between and , and the Victoria line between and . The area around the station is an important interchange for other forms of transport: a local bus station is in the forecourt an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brighton Main Line
The Brighton Main Line (also known as the South Central Main Line) is a major railway line in the United Kingdom that links Brighton, on the south coast of England, with central London. In London the line has two branches, out of and stations respectively, which join up in Croydon and continue towards Brighton as one line. The line is electrified throughout using the third rail system. Aside from London and Brighton themselves, the line serves multiple large urban areas along its route, including Redhill, eastern Crawley, Haywards Heath and Burgess Hill. It also serves the major London suburbs of south-west Battersea, Balham, Streatham, Croydon and Purley, as well as London Gatwick Airport the second-busiest passenger airport in the country. In addition, the line operates as a "trunk" route for both mainline and suburban services all across Sussex, east Surrey and the southern boroughs of London. Towns such as Sutton, Epsom, Caterham, Reigate, East Grinstead, Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West End Of London And Crystal Palace Railway
The West End of London and Crystal Palace Railway (WELCPR) was an early railway company in south London between Crystal Palace station and Wandsworth, which was opened in 1856. The line was extended in 1858 to a station at Battersea Wharf near the bridge to Pimlico. Throughout its brief existence the railway was operated by the London Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR) to which it was leased in 1858 and sold in 1859. This relatively short line was of considerable importance to the history of railways of south London as it was the first line to create a corridor from the south and east towards Westminster and led to the development of London Victoria railway station. History Opening To coincide with the reopening of the Crystal Palace at Sydenham Hill on 10 June 1854, the LB&SCR opened a short spur line linking a new Crystal Palace station to Sydenham station on the Brighton Main Line from London Bridge. The WELCPR was an independent company that aimed to create an add ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sydenham Railway Station (London)
Sydenham (London) is a railway station in Sydenham in the London Borough of Lewisham, South London. Originally opened in 1839, the station is located on the former Croydon Canal, which is now a branch of the Brighton Main Line, often known as the Sydenham Corridor. Sydenham falls within Travelcard Zone 3 and is served by London Overground and Southern. The station is down the line from . History The Croydon Canal opened in 1809 linking the Grand Surrey Canal to Croydon, however the waterway was never successful, and in 1836, it was the first canal to be abandoned by an Act of Parliament. The alignment was purchased by the London and Croydon Railway, who drained the canal and re-opened as a railway on the 5 June 1839. In 1844, L&CR was given authority to test the first atmospheric railway equipment between Dartmouth Arms (now Forest Hill) and West Croydon. In 1846, the railway became part of the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway and in the following year, the system w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Brighton And South Coast Railway
The London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR; known also as the Brighton line, the Brighton Railway or the Brighton) was a railway company in the United Kingdom from 1846 to 1922. Its territory formed a rough triangle, with London at its apex, practically the whole coastline of Sussex as its base, and a large part of Surrey. It was bounded on its western side by the London and South Western Railway (L&SWR), which provided an alternative route to Portsmouth. On its eastern side the LB&SCR was bounded by the South Eastern Railway (SER)—later one component of the South Eastern and Chatham Railway (SE&CR)—which provided an alternative route to Bexhill, St Leonards-on-Sea, and Hastings. The LB&SCR had the most direct routes from London to the south coast seaside resorts of Brighton, Eastbourne, Worthing, Littlehampton and Bognor Regis, and to the ports of Newhaven and Shoreham-by-Sea. It served the inland towns and cities of Chichester, Horsham, East Grinstead and Lewes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Exhibition
The Great Exhibition of the Works of Industry of All Nations, also known as the Great Exhibition or the Crystal Palace Exhibition (in reference to the temporary The Crystal Palace, structure in which it was held), was an International Exhibition, international exhibition which took place in Hyde Park, London, Hyde Park, London, from 1 May to 15 October, 1851. It was the first in a series of World's fair, World's Fairs, exhibitions of culture and Manufacturing, industry that became popular in the 19th century. The event was organised by Henry Cole and Albert, Prince Consort, Prince Albert, husband of Victoria, Queen of the United Kingdom. Famous people of the time attended the Great Exhibition, including Charles Darwin, Karl Marx, Michael Faraday (who assisted with the planning and judging of exhibits), Samuel Colt, members of the Orléanist, Orléanist Royal Family and the writers Charlotte Brontë, Charles Dickens, Lewis Carroll, George Eliot, Alfred, Lord Tennyson, Alfre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_p142_-_Victoria_Station_(plan).jpg)

_railway_bridge_over_Battersea_Park_Road%2C_SW8.jpg)
