|
Cristian's Algorithm
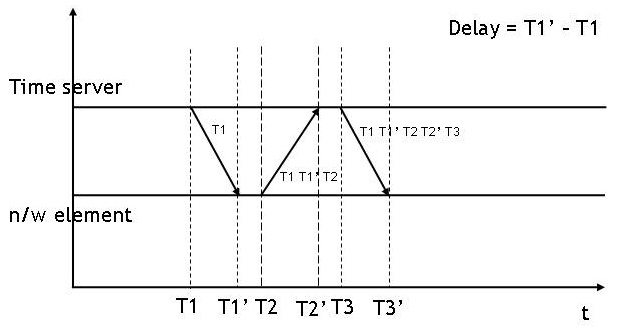
Cristian's algorithm (introduced by Flaviu Cristian in 1989) is a method for clock synchronization which can be used in many fields of distributive computer science but is primarily used in low-latency intranets. Cristian observed that this simple algorithm is probabilistic, in that it only achieves synchronization if the round-trip time (RTT) of the request is short compared to required accuracy. It also suffers in implementations using a single server, making it unsuitable for many distributive applications where redundancy may be crucial. Description Cristian's algorithm works between a process ''P'', and a time server ''S'' connected to a time reference source. Put simply: # ''P'' requests the time from ''S'' at time . # After receiving the request from ''P'', ''S'' prepares a response and appends the time from its own clock. # ''P'' receives the response at time then sets its time to be , where . If the RTT is actually split equally between request and response, the sync ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flaviu Cristian
Flaviu Cristian (25 June 1951 – 27 April 1999) was a Romanian-American computer scientist noted for his work in distributed systems and, in particular, the development of a method for clock synchronisation which bears his name, Cristian's algorithm. Biography He was born in 1951 in Cluj, in the Transylvania region of Romania, the son of Ilie and Rafila Cristian. After graduating from the Nicolae Bălcescu High School in his native city, he went in 1971 to France to study at the Grenoble Institute of Technology, in the Department of Applied Mathematics and Computer Science. After graduating in 1977 from both the Institute and the Grenoble School of Management, he pursued his graduate studies in computer science at the University of Grenoble, where he carried out research in operating systems and programming methodology, and received his Ph.D. in 1979. Cristian went on to the University of Newcastle upon Tyne in the United Kingdom, where he worked in the area of specification, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Atomic Time
International Atomic Time (abbreviated TAI, from its French name ) is a high-precision atomic coordinate time standard based on the notional passage of proper time on Earth's geoid. TAI is a weighted average of the time kept by over 450 atomic clocks in over 80 national laboratories worldwide. It is a continuous scale of time, without leap seconds, and it is the principal realisation of Terrestrial Time (with a fixed offset of epoch). It is the basis for Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), which is used for civil timekeeping all over the Earth's surface and which has leap seconds. UTC deviates from TAI by a number of whole seconds. , when another leap second was put into effect, UTC is currently exactly 37 seconds behind TAI. The 37 seconds result from the initial difference of 10 seconds at the start of 1972, plus 27 leap seconds in UTC since 1972. TAI may be reported using traditional means of specifying days, carried over from non-uniform time standards based on the rot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Server
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, to compare the duration of events or the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change of quantities in material reality or in the conscious experience. Time is often referred to as a fourth dimension, along with three spatial dimensions. Time has long been an important subject of study in religion, philosophy, and science, but defining it in a manner applicable to all fields without circularity has consistently eluded scholars. Nevertheless, diverse fields such as business, industry, sports, the sciences, and the performing arts all incorporate some notion of time into their respective measuring systems. 108 pages. Time in physics is operationally defined as "what a clock reads". The physical nature of time is addresse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Protocol
The Time Protocol is a network protocol in the Internet Protocol Suite defined in 1983 in RFC 868 by Jon Postel and K. Harrenstein. Its purpose is to provide a site-independent, machine readable date and time. The Time Protocol may be implemented over the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) or the User Datagram Protocol (UDP). A host connects to a server that supports the Time Protocol on port 37. The server then sends the time as a 32-bit unsigned integer in binary format and in network byte order, representing the number of seconds since 00:00 (midnight) 1 January, 1900 GMT, and closes the connection. Operation over UDP requires the sending of any datagram to the server port, as there is no connection setup for UDP. The fixed 32-bit data format means that the timestamp rolls over approximately every 136 years, with the first such occurrence on 7 February 2036. Programs that use the Time Protocol must be carefully designed to use context-dependent information to distinguish the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchronization
Synchronization is the coordination of events to operate a system in unison. For example, the conductor of an orchestra keeps the orchestra synchronized or ''in time''. Systems that operate with all parts in synchrony are said to be synchronous or ''in sync''—and those that are not are '' asynchronous''. Today, time synchronization can occur between systems around the world through satellite navigation signals and other time and frequency transfer techniques. Navigation and railways Time-keeping and synchronization of clocks is a critical problem in long-distance ocean navigation. Before radio navigation and satellite-based navigation, navigators required accurate time in conjunction with astronomical observations to determine how far east or west their vessel traveled. The invention of an accurate marine chronometer revolutionized marine navigation. By the end of the 19th century, important ports provided time signals in the form of a signal gun, flag, or dropping ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precision Time Protocol
The Precision Time Protocol (PTP) is a protocol used to synchronize clocks throughout a computer network. On a local area network, it achieves clock accuracy in the sub-microsecond range, making it suitable for measurement and control systems. PTP is employed to synchronize financial transactions, mobile phone tower transmissions, sub-sea acoustic arrays, and networks that require precise timing but lack access to satellite navigation signals. The first version of PTP, IEEE 1588-2002, was published in 2002. IEEE 1588-2008, also known as PTP Version 2 is not backward compatible with the 2002 version. IEEE 1588-2019 was published in November 2019 and includes backward-compatible improvements to the 2008 publication. IEEE 1588-2008 includes a ''profile'' concept defining PTP operating parameters and options. Several profiles have been defined for applications including telecommunications, electric power distribution and audiovisual. is an adaptation of PTP for use with Audio V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ntpdate
ntpdate is a computer program used to quickly synchronize and set computers' date and time by querying a Network Time Protocol (NTP) server. It is available for a wide variety of unix-like operating systems. The accuracy and reliability of ntpdate entirely depends on the accuracy and network link stability of the first server it connects with. As this inaccuracy can lead to a multitude of problems, the maintainers have decided to deprecate it in favor of only using the ntpd The Network Time Protocol daemon (ntpd) is an operating system program that maintains the system time in synchronization with time servers using the Network Time Protocol (NTP). Description The ntpd program is an operating-system daemon that ... (network time protocol daemon) or a sntp (simple network time protocol) query. References External links NTP.org — Home page of the Network Time Protocol Network time-related software {{compu-prog-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenNTPD
OpenNTPD (also known as OpenBSD NTP Daemon) is a Unix daemon implementing the Network Time Protocol to synchronize the local clock of a computer system with remote NTP servers. It is also able to act as an NTP server to NTP-compatible clients. OpenBSD NTP Daemon was initially developed by Alexander Guy and Henning Brauer as part of the OpenBSD project, with further help by many authors. Its design goals include being secure ( non-exploitable), easy to configure, and accurate enough for most purposes. Its portable version, like that of OpenSSH, is developed as a child project which adds the portability code to the OpenBSD version and releases it separately. The portable version is developed by Brent Cook. The project developers receive some funding from the OpenBSD Foundation. History The development of OpenNTPD was motivated by a combination of issues with current NTP daemons: difficult configuration, complicated and difficult to audit code, and unsuitable licensing. OpenN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ntpd
The Network Time Protocol daemon (ntpd) is an operating system program that maintains the system time in synchronization with time servers using the Network Time Protocol (NTP). Description The ntpd program is an operating-system daemon that sets and maintains a computer system's system time in synchronization with Internet-standard time servers. It is a complete implementation of the Network Time Protocol (NTP) version 4, but retains compatibility with versions 1, 2, and 3 as defined by RFC 1059, RFC 1119, and RFC 1305, respectively. ntpd performs most computations in 64-bit floating point arithmetic and uses 64-bit fixed point operations only when necessary to preserve the ultimate precision, about 232 picoseconds. While ordinary workstations and networks cannot achieve the ultimate precision , future processors and networks may require it. xntpd is the Network Time Protocol version three (1992) daemon software. The "x" was added to the name because the branch of code tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NTP Server Misuse And Abuse
NTP server misuse and abuse covers a number of practices which cause damage or degradation to a Network Time Protocol (NTP) server, ranging from flooding it with traffic (effectively a DDoS attack) or violating the server's access policy or the NTrules of engagement One incident was branded NTP vandalism in an open letter from Poul-Henning Kamp to the router manufacturer D-Link in 2006. This term has later been extended by others to retroactively include other incidents. There is, however, no evidence that any of these problems are deliberate vandalism. They are more usually caused by shortsighted or poorly chosen default configurations. deliberate form of NTP server abusecame to note at the end of 2013, when NTP servers were used as part of amplification denial-of-service attacks. Some NTP servers would respond to a single "monlist" UDP request packet, with packets describing up to 600 associations. By using a request with a spoofed IP address attackers could direct an amplifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NTP Pool
The NTP pool is a dynamic collection of networked computers that volunteer to provide highly accurate time via the Network Time Protocol to clients worldwide. The machines that are "in the pool" are part of the ''pool.ntp.org'' domain as well as of several subdomains divided by geographical zone and are distributed to NTP clients via round-robin DNS. Work is being done to make the geographic zone selection unnecessary via customized authoritative DNS servers that utilize geolocation software. , the pool consists of 3,126 active servers on IPv4 and 1,534 active servers on IPv6. Because of the decentralization of this project, accurate statistics on the number of clients cannot be obtained, but according to the project's website, the pool provides time to 5–15 million systems. Because of client growth, the project is in perpetual need of more servers. The more time servers there are in the pool, the lower the resource demand on each member. Joining the pool requires at least a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ICMP Timestamp Reply
The Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is a supporting protocol in the Internet protocol suite. It is used by network devices, including routers, to send error messages and operational information indicating success or failure when communicating with another IP address, for example, an error is indicated when a requested service is not available or that a host or router could not be reached. ICMP differs from transport protocols such as TCP and UDP in that it is not typically used to exchange data between systems, nor is it regularly employed by end-user network applications (with the exception of some diagnostic tools like ping and traceroute). ICMP for IPv4 is defined in RFC 792. A separate ICMPv6, defined by RFC 4443, is used with IPv6. Technical details ICMP is part of the Internet protocol suite as defined in RFC 792. ICMP messages are typically used for diagnostic or control purposes or generated in response to errors in IP operations (as specified in RFC 1122) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |