|
Crime Boss
A crime boss, also known as a crime lord, Don, gang lord, gang boss, mob boss, kingpin, godfather, crime mentor or criminal mastermind, is a person in charge of a criminal organization. Description A crime boss typically has absolute or nearly absolute control over the other members of the organization and is often greatly feared or respected for their cunning, strategy, and/or ruthlessness and willingness to take lives to exert their influence and profits from the criminal endeavors in which the organization engages.Manning, George A. ''Financial Investigation and Forensic Accounting.'' Boca Raton, Fla.: CRC Press, 2005. Some groups may only have as little as two ranks (a crime boss and their soldiers). Other groups have a more complex, structured organization with many ranks, and structure may vary with cultural background. Organized crime enterprises originating in Sicily differ in structure from those in mainland Italy. American groups may be structured differently from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al Capone In 1930
AL, Al, Ål or al may stand for: Arts and entertainment Fictional characters * Al (''Aladdin'') or Aladdin, the main character in Disney's ''Aladdin'' media * Al (''EastEnders''), a minor character in the British soap opera * Al (''Fullmetal Alchemist'') or Alphonse Elric, a character in the manga/anime * Al Borland, a character in the ''Home Improvement'' universe * Al Bundy, a character in the television series ''Married... with Children'' * Al Calavicci, a character in the television series ''Quantum Leap'' * Al McWhiggin, a supporting villain of ''Toy Story 2'' * Al, or Aldebaran, a character in ''Re:Zero − Starting Life in Another World'' media Music * ''A L'', an EP by French singer Amanda Lear * '' American Life'', an album by Madonna Calendar * Anno Lucis, a dating system used in Freemasonry Mythology and religion * Al (folklore), a spirit in Persian and Armenian mythology * Al Basty, a tormenting female night demon in Turkish folklore * '' Liber AL'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underboss
Underboss ( it, sottocapo) is a position within the leadership structure of certain organized crime groups, particularly in Sicilian, Greek, and Italian-American Mafia crime families. The underboss is second in command to the boss. The underboss is sometimes a family member, such as a son, who will take over the family if the boss is sick, killed, or imprisoned. However the position of street boss has somewhat challenged the rank of underboss in the modern era. The position was installed within the Genovese crime family since at least the mid-1960s. It has also been used in the Detroit crime family and the Chicago Outfit. The power of an underboss greatly varies; some are marginal figures, while others are the most powerful individual in the family. Traditionally they run day-to-day affairs of the family. In some crime families, the appointment is for life. If a new boss takes over a family with an existing underboss, that boss may marginalize or even murder the underboss ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
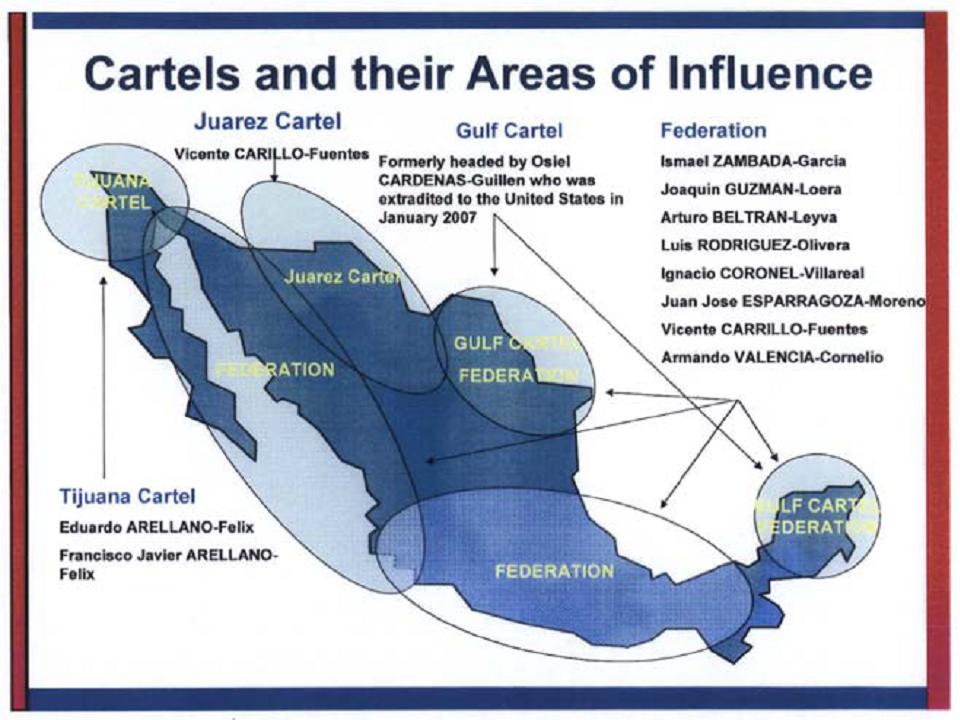
Drug Cartel
A drug cartel is any criminal organization with the intention of supplying drug trafficking operations. They range from loosely managed agreements among various drug traffickers to formalized commercial enterprises. The term was applied when the largest trafficking organizations reached an agreement to coordinate the production and distribution. The term is used to refer to any criminal narcotics related organization. The basic structure of a drug cartel is as follows: * Falcons (Spanish: ''Halcones''): Considered as the "eyes and ears" of the streets, the "falcons" are the lowest rank in any drug cartel. They are responsible for supervising and reporting the activities of the police, the military and rival groups. * Hitmen (Spanish: ''Sicarios''): The armed group within the drug cartel, responsible for carrying out assassinations, kidnappings, thefts and extortions, operating protection rackets, as well as defending their ''plaza'' (turf) from rival groups and the military. * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug Lord
A drug lord, drug baron, kingpin or narcotrafficker is a high-ranking crime boss who controls a sizable network of people involved in the illegal drug trade. Such figures are often difficult to bring to justice, as they are normally not directly in possession of something illegal but are insulated from the actual trade in drugs by several layers of staff. The prosecution of drug lords is therefore usually the result of carefully planned infiltration into their networks, often using informants from within the organizations. Organisational role Since the 1970s, research on organized crime leadership (and, by extension, drug lords) has evolved. Where once studies emphasised the importance of the leader's human capital (e.g. individual traits), it has now developed to focus upon the leader's social capital (e.g. information and resource brokers, social status, access to information). List of well-known drug lords Miguel Ángel Félix Gallardo Known as "El Padrino" (The Godfat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boss (video Games)
In video games, a boss is a significant computer-controlled opponent. A fight with a boss character is commonly referred to as a boss battle or boss fight. Bosses are generally far stronger than other opponents the player has faced up to that point. Boss battles are generally seen at climax points of particular sections of games, such as at the end of a level or stage or guarding a specific objective. A miniboss is a boss weaker or less significant than the main boss in the same area or level, though usually more powerful than the standard opponents and often fought alongside them. A superboss (sometimes 'secret' or 'hidden' boss) is generally much more powerful than the bosses encountered as part of the main game's plot and is often an optional encounter. A final boss is often the main antagonist of a game's story and the defeat of that character usually provides a positive conclusion to the game. A boss rush is a stage where the player faces multiple previous bosses agai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Man (anthropology)
A big man is a highly influential individual in a tribe, especially in Melanesia and Polynesia. Such a person may not have formal tribal or other authority (through for instance material possessions, or inheritance of rights), but can maintain recognition through skilled persuasion and wisdom. The big man has a large group of followers, both from his clan and from other clans. He provides his followers with protection and economic assistance, in return receiving support which he uses to increase his status. Big man "system" The American anthropologist Marshall Sahlins has studied the big man phenomenon. In his much-quoted 1963 article "Poor Man, Rich Man, Big Man, Chief: Political Types in Melanesia", Sahlins uses analytically constructed ideal-types of hierarchy and equality to compare a larger-scale Polynesian-type hierarchical society of chiefs and sub-chiefs with a Melanesian-type big-man system. The latter consists of segmented lineage groups, locally held together by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armed Robbery
Robbery is the crime of taking or attempting to take anything of value by force, threat of force, or by use of fear. According to common law, robbery is defined as taking the property of another, with the intent to permanently deprive the person of that property, by means of force or fear; that is, it is a larceny or theft accomplished by an assault. Precise definitions of the offence may vary between jurisdictions. Robbery is differentiated from other forms of theft (such as burglary, shoplifting, pickpocketing, or car theft) by its inherently violent nature (a violent crime); whereas many lesser forms of theft are punished as misdemeanors, robbery is always a felony in jurisdictions that distinguish between the two. Under English law, most forms of theft are triable either way, whereas robbery is triable only on indictment. The word "rob" came via French from Late Latin words (e.g., ''deraubare'') of Germanic origin, from Common Germanic ''raub'' "theft". Among the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organised Crime
Organized crime (or organised crime) is a category of transnational, national, or local groupings of highly centralized enterprises run by criminals to engage in illegal activity, most commonly for profit. While organized crime is generally thought of as a form of illegal business, some criminal organizations, such as terrorist groups, rebel forces, and separatists, are politically motivated. Many criminal organizations rely on fear or terror to achieve their goals or aims as well as to maintain control within the organization and may adopt tactics commonly used by authoritarian regimes to maintain power. Some forms of organized crime simply exist to cater towards demand of illegal goods in a state or to facilitate trade of goods and services that may have been banned by a state (such as illegal drugs or firearms). Sometimes, criminal organizations force people to do business with them, such as when a gang extorts money from shopkeepers for " protection". Street gangs may ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Made Man
In the American and Sicilian Mafia, a made man is a fully initiated member of the Mafia. To become "made", an associate first must be Italian or of Italian descent and sponsored by another made man. An inductee will be required to take the oath of '' omertà'', the Mafia code of silence and code of honor. After the induction ceremony, the associate becomes a "made man" and holds the rank of soldier (Italian: ''soldato'') in the Mafia hierarchy. Made men are the only ones who can rise through the ranks of the Mafia, from soldier to caporegime, consigliere, underboss, and boss. Other common names for members include ''man of honor'' ( it, uomo d'onore), ''man of respect'' (Italian: ''uomo di rispetto''), ''one of us'', ''friend of ours'' (Italian: ''amico nostro''), ''good fella'', and ''wiseguy''; although the last two terms can also apply to non-initiated Mafia associates who work closely with the Mafia, rather than just official "made men". Earning or making one's "b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omertà
Omertà (, ) is a Southern Italian code of silence and code of honor and conduct that places importance on silence in the face of questioning by authorities or outsiders; non-cooperation with authorities, the government, or outsiders, especially during criminal investigations; and willfully ignoring and generally avoiding interference with the illegal activities of others (i.e., not contacting law enforcement or the authorities when one is aware of, witness to, or even the victim of certain crimes). It originated and remains common in Southern Italy, where banditry or brigandage and Mafia-type criminal organizations (like the Camorra, Cosa Nostra, 'Ndrangheta, Sacra Corona Unita and Società foggiana) have long been strong. Similar codes are also deeply rooted in other areas of the Mediterranean, including Malta, Crete in Greece, and Corsica, all of which share a common or similar historic culture with Southern Italy. Retaliation against informers is common in criminal c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soldato
A soldato or soldier is the first official level of both the American Mafia and the Sicilian Mafia in the formal Mafia hierarchy or cadre. It is also commonly used as a rank in other Italian criminal organizations, such as the 'Ndrangheta and Camorra. The promotion to the rank of soldier is an elevation in the chain of command from the associate level. The associate, who is not an initiated member of the Mafia, must prove himself to the family and take the oath of Omertà in order to become an initiated made man and therefore rise to the rank of soldato. Picciotto (plural: ''picciotti'') is often used to refer to a lower-level mafioso or soldato, but it usually indicates a younger, inexperienced soldato and may even be used loosely to refer to a closely connected, up-and-coming associate who is not necessarily a made man yet (and therefore not yet officially a "soldato"). "Picciotti" usually perform simple tasks such as beatings, money collection, and robbery. Duties and ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |