|
Crew And Science Airlock Module
The Crew and Science Airlock Module is designed as an airlock module of the Lunar Gateway station, to be built by the Mohammed bin Rashid Space Centre. Background The airlock module is meant to facilitate transfers to and from the habitation modules of the Gateway and into the vacuum of space. The airlock module will therefore support deep space science research as well as external Gateway maintenance. Contract In January 2024, NASA announced the partnership with MBRSC with whom NASA shares a long-standing partnership. The United Arab Emirates, UAE, in which the MBRSC is located, was among the initial signatories of the Artemis Accords. Soon after the contract was announced, design work began. As part of the contract, the UAE will be able to send one of their own astronauts aboard a future Artemis mission. Design and manufacture The project will occur in a five phased approach: planning, design, qualification, flight preparation and operations. The MBRSC will be responsibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Gateway
The Lunar Gateway, or simply Gateway, is a planned space station which is to be assembled in orbit around the Moon. The Gateway is intended to serve as a communication hub, science laboratory, and habitation module for astronauts as part of the Artemis program. It is a multinational collaborative project: participants include NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), and the Mohammed Bin Rashid Space Centre (MBRSC). The Gateway is planned to be the first space station beyond low Earth orbit. However, the Second presidency of Donald Trump, Trump administration has called for ending the Gateway program in its 2026 budget proposal. The science disciplines to be studied on the Gateway are expected to include planetary science, astrophysics, Earth observation, heliophysics, Astrobiology, fundamental space biology, and Health, human health and performance. As of April 2024, construction is underway o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artemis Accords
The Artemis Accords are a series of non-binding multilateral arrangements between the United States government and other world governments that elaborates on the norms expected to be followed in outer space. The Accords are related to the Artemis program, an American-led effort to return humans to the Moon by 2027, with the ultimate goal of expanding space exploration to Mars and beyond. As of 15 May 2025, with the accession of Norway, 55 countries have signed the Accords, including twenty-eight in Europe, ten in Asia, seven in South America, five in North America, three in Africa, and two in Oceania. Drafted by NASA and the U.S. Department of State, the Accords establish a framework for cooperation in the civil exploration and peaceful use of the Moon, Mars, and other astronomical objects. They are explicitly grounded in the United Nations Outer Space Treaty of 1967, which signatories are obliged to uphold, and cite most major U.N.-brokered conventions constituting space law ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Using Halo Orbits
A spacecraft is a vehicle that is designed to fly and operate in outer space. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from start or on orbit (space stations) only, whereas those used for robotic space missions operate either autonomously or telerobotically. Robotic spacecraft used to support scientific research are space pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA Space Stations
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States's civil list of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research and outer space, space research. National Aeronautics and Space Act, Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA Programs
This is a list of NASA missions, both Human spaceflight, crewed and Robotic spacecraft, robotic, Creation of NASA, since the establishment of NASA in 1957. There are over 80 currently active science missions. X-Plane program Since 1945, NACA (NASA's predecessor) and, since January 26, 1958, NASA has conducted the X-Plane Program. The program was originally intended to create a family of experimental aircraft not intended for production beyond the limited number of each design built solely for flight research. The first X-Plane, the Bell X-1, was the first rocket-powered airplane to break the sound barrier on October 14, 1947. X-Planes have set numerous milestones since then, both crewed and unpiloted. Human spaceflight NASA has successfully launched over 200 crewed flights. Three have ended in failure, causing the death of the entire crew: Apollo 1 (which never launched) in 1967 lost three crew members, STS-51-L (Space Shuttle Challenger disaster, the ''Challenger'' disa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missions To The Moon
Missions to the Moon have been numerous and include some of the earliest space missions, conducting exploration of the Moon since 1959. The first partially successful lunar mission was Luna 1 (January 1959), the first probe to leave Earth and fly past another astronomical body. Soon after that the first Moon landing and the first landing on any extraterrestrial body was performed by Luna 2, which intentionally impacted the Moon on 14 September 1959. The far side of the Moon, which is always facing away from Earth due to tidal locking, was seen for the first time by Luna 3 in (7 October 1959). In 1966, Luna 9 became the first spacecraft to achieve a controlled soft landing, while Luna 10 became the first mission to enter orbit, and in 1968 Zond 5 became the first mission to carry terrestrial lifeforms (tortoises) to close proximity of the Moon through a circumlunar approach. The first crewed missions to the Moon were pursued by the Soviet Union and the United States, becomin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint Ventures
A joint venture (JV) is a business entity created by two or more parties, generally characterized by shared ownership, shared returns and risks, and shared governance. Companies typically pursue joint ventures for one of four reasons: to access a new market, particularly emerging market; to gain scale efficiencies by combining assets and operations; to share risk for major investments or projects; or to access skills and capabilities.' Most joint ventures are incorporated, although some, as in the oil and gas industry, are "unincorporated" joint ventures that mimic a corporate entity. With individuals, when two or more persons come together to form a temporary partnership for the purpose of carrying out a particular project, such partnership can also be called a joint venture where the parties are "''co-venturers''". A joint venture can take the form of a business. It can also take the form of a project or asset JV, created for the purpose of pursuing one specific project, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crewed Spacecraft
This is a list of all crewed spacecraft types that have flown into space, including sub-orbital flights above 80 km, space stations that have been visited by at least one crew member, and spacecraft currently planned to operate with crews in the future. It does not contain spacecraft that have only flown uncrewed and have retired from service, even if they were designed for crewed flight, such as Buran, or crewed flights by spacecraft below 80 km. There is some debate concerning the height at which space is reached (the Karman Line): the Fédération Aéronautique Internationale (FAI) recognizes 100 km, while NASA and the USAF recognize this as 50 miles (approx 80 km). Since the first crewed spaceflight of Vostok 1 in 1961 there have been 13 types of spacecraft that have made crewed flights into space – nine American, three Russian, and one Chinese. There are currently five operational crewed spacecraft, which form the first part of the list below; the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
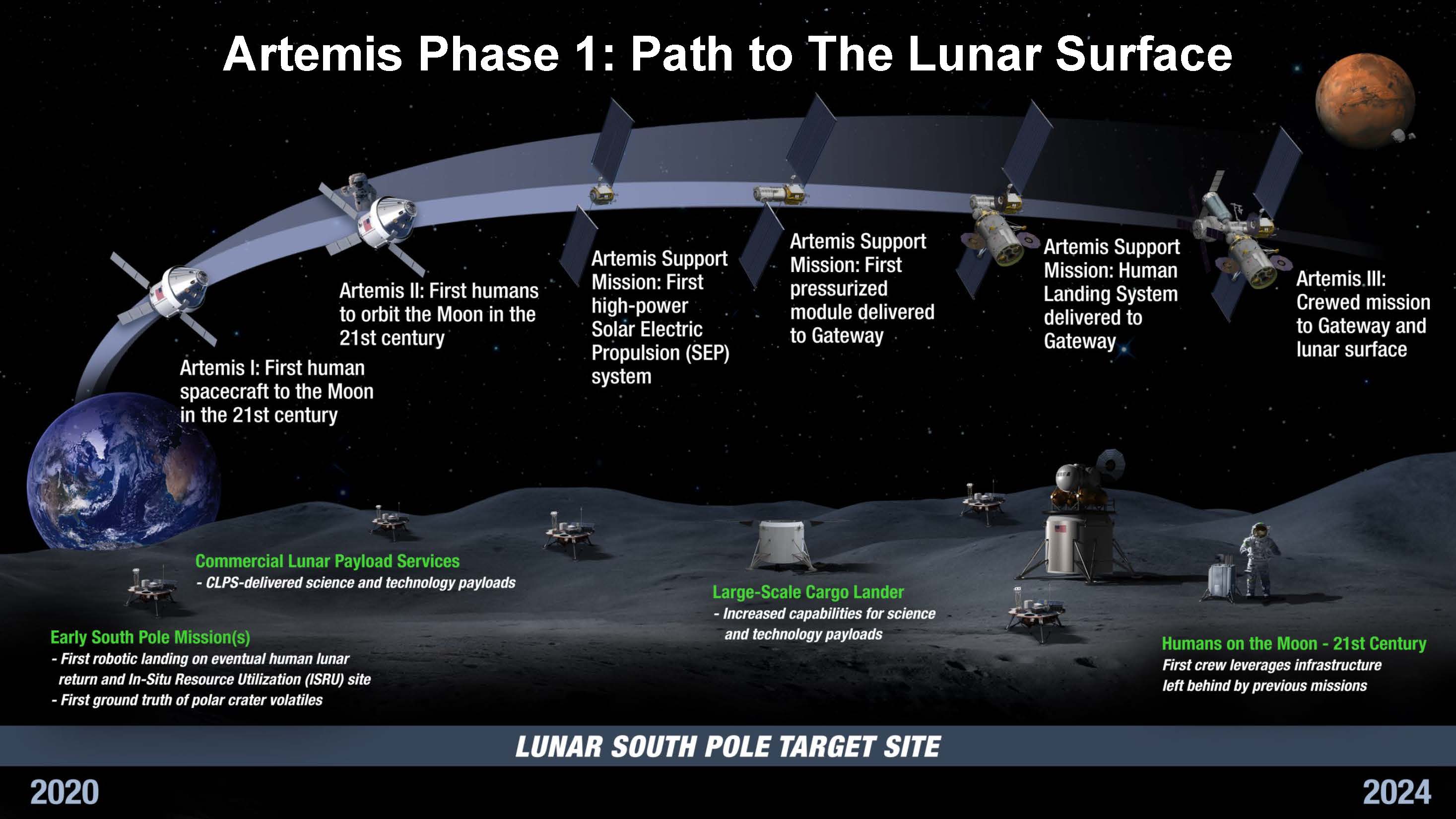
Artemis Program
The Artemis program is a Exploration of the Moon, Moon exploration program led by the United States' National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), formally established in 2017 via Space Policy Directive 1. The program's stated long-term goal is to establish a Moonbase, permanent base on the Moon to facilitate Human mission to Mars, human missions to Mars. It is intended to reestablish a human presence on the Moon for the first time since the Apollo 17 mission in 1972 and continue the direct exploration of Mars begun with data from the Mariner 9 probe in the same year. Two principal elements of the Artemis program are derived from the now-cancelled Constellation program: the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft (with the European Service Module, ESM instead of a US-built service module) and the Space Launch System's Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Booster#Five-segment booster, solid rocket boosters (originally developed for the Ares V). Other elements of the program, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE), or simply the Emirates, is a country in West Asia, in the Middle East, at the eastern end of the Arabian Peninsula. It is a Federal monarchy, federal elective monarchy made up of Emirates of the United Arab Emirates, seven emirates, with Abu Dhabi serving as its capital. It shares land borders with Oman to the east and northeast, and with Saudi Arabia to the southwest; as well as maritime borders in the Persian Gulf with Qatar and Iran, and with Oman in the Gulf of Oman. , the UAE has an estimated population of over 10 million, of which 11% are Emiratis; Dubai is List of cities in the United Arab Emirates, its most populous city and is an international hub. Islam is the State religion, official religion and Arabic is the official language, while English is the most spoken language and the language of business. The United Arab Emirates Oil reserves in the United Arab Emirates, oil and natural gas reserves are the world's List of countries by pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohammed Bin Rashid Space Centre
The Mohammed Bin Rashid Space Centre (MBRSC, ) is a Government of Dubai, Dubai Government organization working on the UAE space program, which includes various Satellite, space satellites projects, such as the Emirates Mars Mission, the Emirates Lunar Mission, and the UAE astronaut program. The center actively works to promote Outline of space science, space science and research in the region and encompasses the Emirates Institution for Advanced Science and Technology (EIAST). Overview Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum, vice president and prime minister of the United Arab Emirates and ruler of Dubai, established the Emirates Institution for Advanced Science and Technology (EIAST) on 6 February 2006. On 17th April 2015, Mohammed bin Rashid Space Center was created, incorporating EIAST into it. MBRSC contributes towards the development of various sectors within the United Arab Emirates and across the globe, using data from UAE satellites, and various applications related to space s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |